
数据挖掘入门与实战 公众号: datadw
不错的学习聊天机器人的资源,不知道小伙伴们有没有去学习呢。
自己动手做聊天机器人教程
http://www.shareditor.com/blogshow/?blogId=121
我最近每天都会学一点,拿出解读来和大家分享一下。
本文结构:
聊天机器人的架构简图
用 TensorFlow 实现 Chatbot 的模型
如何准备 chatbot 的训练数据
Chatbot 源码解读
1. 聊天机器人的架构简图
学习资源:
[自己动手做聊天机器人 九-聊天机器人应该怎么做]
(http://www.shareditor.com/blogshow/?blogId=73)
聊天机器人的工作流程大体为:提问-检索-答案抽取。
提问:就是要分析主人的问句中关键词,提问类型,还有真正想知道的东西。
检索:根据前一步的分析,去找答案。
答案抽取:找到的答案,并不能直接应用,还要整理成真正有用的,可以作为答案的回答。
涉及到的关键技术如图中所示。
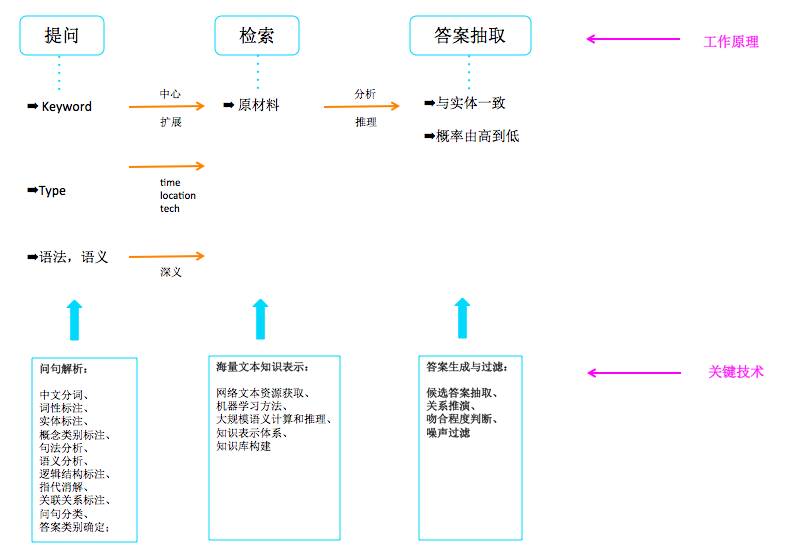
看不清图的话,就是酱紫:
问句解析:
中文分词、词性标注、实体标注、概念类别标注、句法分析、语义分析、逻辑结构标注、指代消解、关联关系标注、问句分类、答案类别确定;
海量文本知识表示:
网络文本资源获取、机器学习方法、大规模语义计算和推理、知识表示体系、知识库构建
答案生成与过滤:
候选答案抽取、关系推演、吻合程度判断、噪声过滤
2. 用 TensorFlow 实现 Chatbot 的模型
之前有根据 Siraj 的视频写过一篇《自己动手写个聊天机器人吧》,
http://www.jianshu.com/p/d0f4a751012b
文章里只写了主函数的简单过程:Data-Model-Training,是用 Lua 实现的,详细的代码回复公众号关键字“聊天”即可获取。
下面这篇文章是用 TensorFlow + tflearn 库 实现,在 建模, 训练 和 预测 等环节可以学到更多细节:
学习资源:自己动手做聊天机器人 三十八-原来聊天机器人是这么做出来的
http://www.shareditor.com/blogshow/?blogId=121
两篇的共同点是都用了 Seq2Seq 来实现。
LSTM的模型结构为:
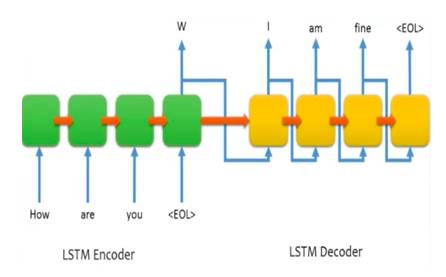
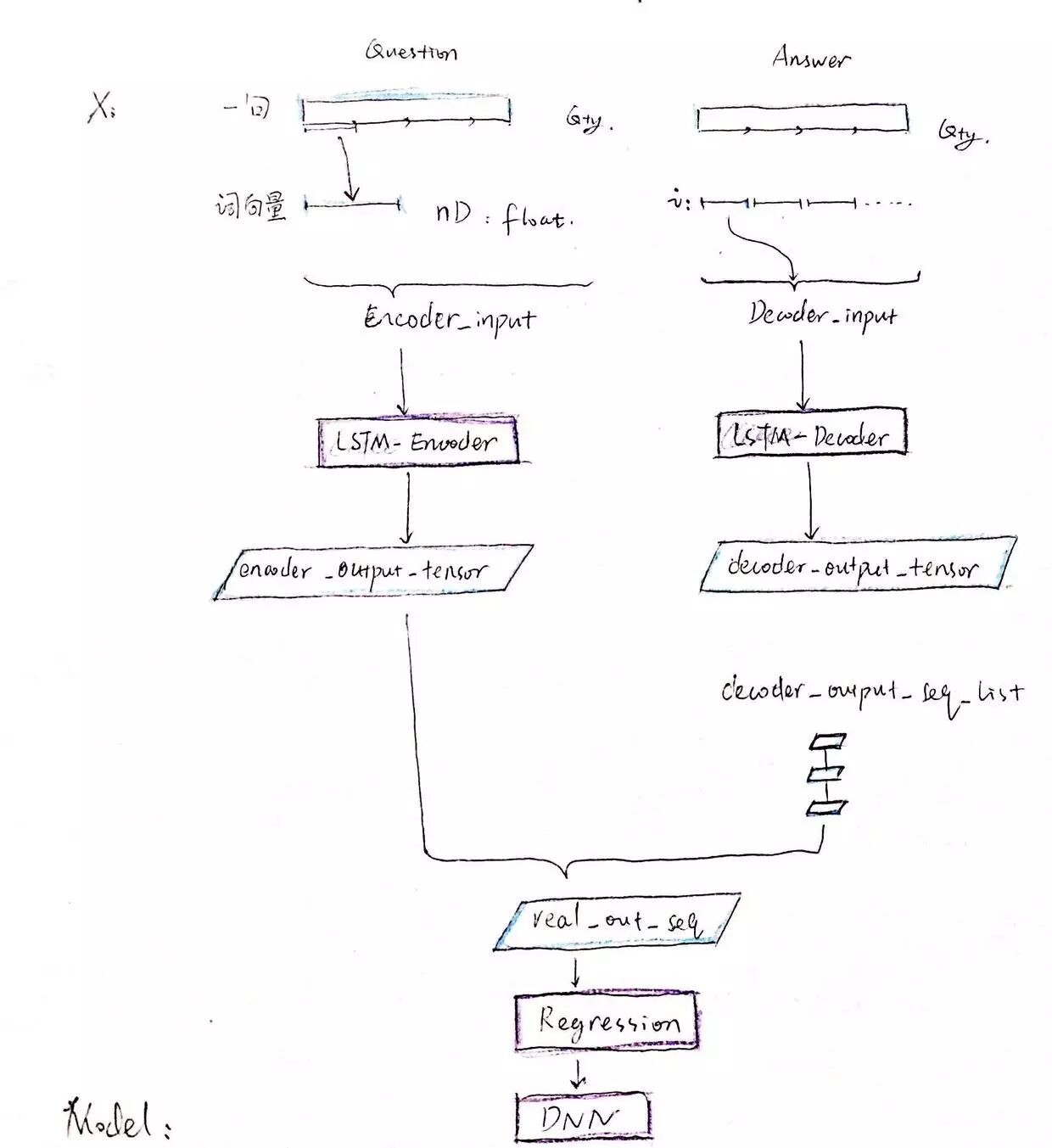
细节的话可以直接去看上面那篇原文,这里 po 出建立模型阶段简要的流程图和过程描述:
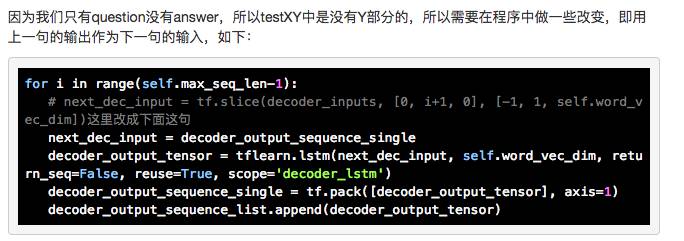
作为 Input data X 传入下面流程:
question 进入 LSTM 的 encoder 环节,answer 进入 decoder 环节,
分别生成 output tensor。
其中 decoder 是一个词一个词的生成结果,将所有结果加入到一个 list 中。
最后和 encoder 的输出,一起做为下一环节 Regression 的输入,并传入 DNN 网络。
3. 如何准备 chatbot 的训练数据
学习资源:
自己动手做聊天机器人 三十八-原来聊天机器人是这么做出来的
http://www.shareditor.com/blogshow/?blogId=121
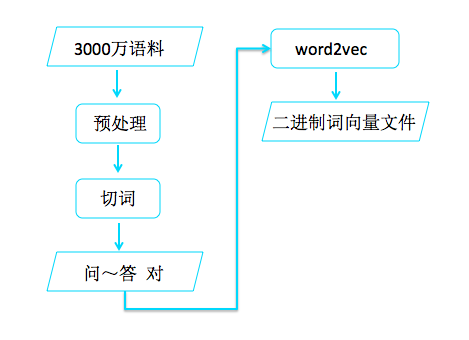
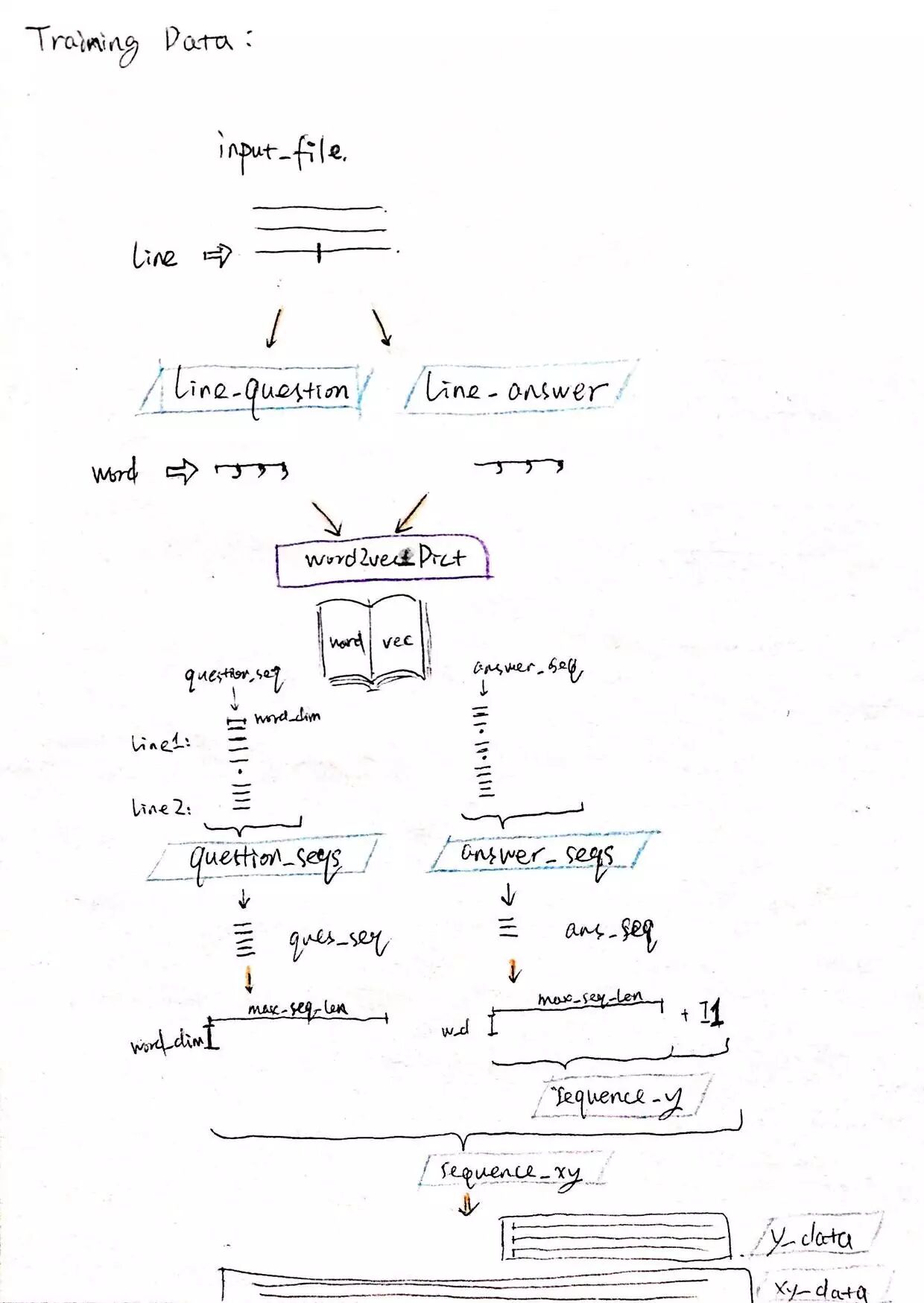
训练数据的生成过程如下:
首先在 input file 里读取每一行,并根据 ‘|’ 拆分成 question 和 answer 句子。
每个句子,都将 word 通过 word2vec 转化成词向量。
每一句的向量序列都转化成相同维度的形式:self.word_vec_dim * self.max_seq_len
最后 answer 构成了 y 数据,question+answer 构成了 xy 数据,再被投入到 model 中去训练:
model.fit(trainXY, trainY, n_epoch=1000,snapshot_epoch=False, batch_size=1)
代码如下:
def init_seq(input_file):
"""读取切好词的文本文件,加载全部词序列
"""
file_object = open(input_file, 'r')
vocab_dict = {}
while True:
question_seq = []
answer_seq = []
line = file_object.readline()
if line:
line_pair = line.split('|')
line_question = line_pair[0]
line_answer = line_pair[1]
for word in line_question.decode('utf-8').split(' '):
if word_vector_dict.has_key(word):
question_seq.append(word_vector_dict[word])
for word in line_answer.decode('utf-8').split(' '):
if word_vector_dict.has_key(word):
answer_seq.append(word_vector_dict[word])
else:
break
question_seqs.append(question_seq)
answer_seqs.append(answer_seq)
file_object.close()
def generate_trainig_data(self):
xy_data = []
y_data = []
for i in range(len(question_seqs)):
question_seq = question_seqs[i]
answer_seq = answer_seqs[i]
if len(question_seq) < self.max_seq_len and len(answer_seq) < self.max_seq_len:
sequence_xy = [np.zeros(self.word_vec_dim)] * (self.max_seq_len-len(question_seq)) + list(reversed(question_seq))
sequence_y = answer_seq + [np.zeros(self.word_vec_dim)] * (self.max_seq_len-len(answer_seq))
sequence_xy = sequence_xy + sequence_y
sequence_y = [np.ones(self.word_vec_dim)] + sequence_y
xy_data.append(sequence_xy)
y_data.append(sequence_y)
return np.array(xy_data), np.array(y_data)
4. Chatbot 源码解读
这篇文章在 源码:
回复公众号关键字“聊天”即可获取。
提炼出步骤如下:
其中 2. 准备数据, 3. 建立模型 就是上文着重说的部分。
引入包
准备数据
建立模型
训练
预测
1. 引入包
import sys
import math
import tflearn
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.ops import rnn_cell
from tensorflow.python.ops import rnn
import chardet
import numpy as np
import struct
2. 准备数据
def load_word_set()
将 3000 万语料,分成 Question 和 Answer 部分,提取出 word。
def load_word_set():
file_object = open('./segment_result_lined.3000000.pair.less', 'r')
while True:
line = file_object.readline()
if line:
line_pair = line.split('|')
line_question = line_pair[0]
line_answer = line_pair[1]
for word in line_question.decode('utf-8').split(' '):
word_set[word] = 1
for word in line_answer.decode('utf-8').split(' '):
word_set[word] = 1
else:
break
file_object.close()
def load_vectors(input)
从 vectors.bin 加载词向量,返回一个 word_vector_dict 的词典,key 是词,value 是200维的向量。
def init_seq(input_file)
将 Question 和 Answer 中单词对应的词向量放在词向量序列中 question_seqs, answer_seqs。
def init_seq(input_file):
"""读取切好词的文本文件,加载全部词序列
"""
file_object = open(input_file, 'r')
vocab_dict = {}
while True:
question_seq = []
answer_seq = []
line = file_object.readline()
if line:
line_pair = line.split('|')
line_question = line_pair[0]
line_answer = line_pair[1]
for word in line_question.decode('utf-8').split(' '):
if word_vector_dict.has_key(word):
question_seq.append(word_vector_dict[word])
for word in line_answer.decode('utf-8').split(' '):
if word_vector_dict.has_key(word):
answer_seq.append(word_vector_dict[word])
else:
break
question_seqs.append(question_seq)
answer_seqs.append(answer_seq)
file_object.close()
def vector_sqrtlen(vector)
用来求向量的长度。
def vector_sqrtlen(vector):
len = 0
for item in vector:
len += item * item
len = math.sqrt(len)
return len
def vector_cosine(v1, v2)
用来求两个向量间的距离。
def vector_cosine(v1, v2):
if len(v1) != len(v2):
sys.exit(1)
sqrtlen1 = vector_sqrtlen(v1)
sqrtlen2 = vector_sqrtlen(v2)
value = 0
for item1, item2 in zip(v1, v2):
value += item1 * item2
return value / (sqrtlen1*sqrtlen2)
def vector2word(vector)
给定一个词向量,去 word-vector 字典中查找与此向量距离最近的向量,并记忆相应的单词,返回单词和 cosine 值。
def vector2word(vector):
max_cos = -10000
match_word = ''
for word in word_vector_dict:
v = word_vector_dict[word]
cosine = vector_cosine(vector, v)
if cosine > max_cos:
max_cos = cosine
match_word = word
return (match_word, max_cos)
3. 建立模型
class MySeq2Seq(object)
在前两篇笔记中单独写了这两块。
def generate_trainig_data(self)
由 question_seqs, answer_seqs 得到 xy_data 和 y_data 的形式。
def model(self, feed_previous=False)
用 input data 生成 encoder_inputs 和带GO头的 decoder_inputs。
将 encoder_inputs 传递给编码器,返回一个输出(预测序列的第一个值)和一个状态(传给解码器)。
在解码器中,用编码器的最后一个输出作为第一个输入,预测过程用前一个时间序的输出作为下一个时间序的输入。
4. 训练
def train(self)
用 generate_trainig_data() 生成 X y 数据,传递给 上面定义的 model,并训练 model.fit,再保存。
5. 预测
用 generate_trainig_data() 生成数据,用 model.predict 进行预测,predict 结果的每一个 sample 相当于一句话的词向量序列,每个 sample 中的每个 vector 在 word-vector 字典中找到与其最近的向量,并返回对应的 word,及二者间的 cosine。
if __name__ == '__main__':
phrase = sys.argv[1]
if 3 == len(sys.argv):
my_seq2seq = MySeq2Seq(word_vec_dim=word_vec_dim, max_seq_len=max_seq_len, input_file=sys.argv[2])
else:
my_seq2seq = MySeq2Seq(word_vec_dim=word_vec_dim, max_seq_len=max_seq_len)
if phrase == 'train':
my_seq2seq.train()
else:
model = my_seq2seq.load()
trainXY, trainY = my_seq2seq.generate_trainig_data()
predict = model.predict(trainXY)
for sample in predict:
print "predict answer"
for w in sample[1:]:
(match_word, max_cos) = vector2word(w)
#if vector_sqrtlen(w) < 1:
# break
print match_word, max_cos, vector_sqrtlen(w)
数据挖掘入门与实战
搜索添加微信公众号:datadw
教你机器学习,教你数据挖掘

长按图片,识别二维码,点关注
公众号: weic2c
据分析入门与实战

长按图片,识别二维码,点关注















