本文约5500字,建议阅读10+分钟
本文探讨在量化交易领域中结合时序特征和静态特征的混合建模方法。
通过整合堆叠稀疏降噪自编码器(SSDA)和基于LSTM的自编码器(LSTM-AE),我们要构建一个能够全面捕捉市场动态特性的交易系统。
特征表示学习
在特征工程阶段,SSDA通过降噪技术提取股票数据的鲁棒表示。该方法能够有效过滤市场噪声,保留对价格走势具有实质影响的关键特征,如趋势变化点和异常波动。
import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler from tensorflow.keras.models import Model from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Dropout from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam import tensorflow as tf mse_loss = tf.keras.losses.MeanSquaredError() def build_ssda(input_dim): """ 构建堆叠降噪自编码器(SSDA)模型。 参数: - input_dim: 输入特征维度(对应股票数据的时间窗口长度)。 返回: - ssda: 编译完成的Keras模型。 """ input_layer = Input(shape=(input_dim,)) encoded = Dense(16, activation='relu')(input_layer) encoded = Dropout(0.1)(encoded) decoded = Dense(input_dim, activation='linear')(encoded) ssda = Model(inputs=input_layer, outputs=decoded) ssda.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.001), loss='mse') return ssda prices = data['Adj Close'].values.reshape(-1, 1) scaler = MinMaxScaler() normalized_prices = scaler.fit_transform(prices).flatten() window_size = 20 ssda_train_data = np.array([ normalized_prices[i:i + window_size] for i in range(len(normalized_prices) - window_size) ]) ssda = build_ssda(input_dim=window_size) ssda.fit( ssda_train_data, ssda_train_data, epochs=50, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, verbose=1 ) ssda.save("ssda_model.h5") print("SSDA model saved as 'ssda_model.h5'.")
时序模式建模
LSTM自编码器专注于捕捉市场的时序依赖关系。通过对滑动窗口内的价格序列进行建模,系统能够学习到市场的周期性特征和长期依赖关系,从而更好地理解价格变化的历史背景和未来趋势。
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, LSTM, RepeatVector from tensorflow.keras.models import Model import tensorflow as tf mse_loss = tf.keras.losses.MeanSquaredError() def build_lstm_ae(timesteps, input_dim): """ 构建LSTM自编码器模型。 参数: - timesteps: 时间序列长度。 - input_dim: 每个时间步的特征维度。 返回: - lstm_ae: LSTM自编码器模型。 """ inputs = Input(shape=(timesteps, input_dim)) encoded = LSTM(16, activation='relu', return_sequences=False)(inputs) decoded = RepeatVector(timesteps)(encoded) decoded = LSTM(input_dim, activation='linear', return_sequences=True)(decoded) lstm_ae = Model(inputs, decoded) lstm_ae.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mse') return lstm_ae timesteps = 20 input_dim = 1 lstm_ae = build_lstm_ae(timesteps, input_dim) features = data['Adj Close'].values.reshape(-1, 1) lstm_train_data = np.array([features[i:i + timesteps] for i in range(len(features) - timesteps)]) lstm_ae.fit(lstm_train_data, lstm_train_data, epochs=100, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
状态增强机制
本文提出了一种状态增强机制,通过融合SSDA和LSTM-AE的输出,构建了一个综合表征静态特征和动态时序依赖关系的增强状态空间。这个增强状态将作为强化学习代理的决策依据。
import numpy as np t = 20 window_size = 20 def get_augmented_state(adj_close_prices, t, window_size, ssda, lstm_ae): """ 基于SSDA和LSTM-AE模型生成增强状态表示。 参数: - adj_close_prices: 调整后收盘价序列。 - t: 当前时间步。 - window_size: 特征提取窗口大小。 - ssda: 预训练的SSDA特征提取器。 - lstm_ae: 预训练的LSTM-AE序列编码器。 返回: - augmented_state: 融合后的特征向量。 """ if t < window_size - 1: raise ValueError(f"Invalid slicing at t={t}. Ensure t >= window_size - 1.") features = adj_close_prices.iloc[t - window_size + 1:t + 1].values.reshape(-1, 1) ssda_features = ssda.predict(features.reshape(1, -1)).flatten() lstm_input = features.reshape(1, window_size, 1) lstm_features = lstm_ae.predict(lstm_input).flatten() augmented_state = np.concatenate((ssda_features, lstm_features)) if len(augmented_state) < window_size: augmented_state = np.pad(augmented_state, (0, window_size - len(augmented_state)), mode='constant') elif len(augmented_state) > window_size: augmented_state = augmented_state[:window_size] return augmented_state augmented_state = get_augmented_state(adj_close_prices, t, window_size, ssda, lstm_ae) print("Augmented State:", augmented_state)
强化学习框架设计
本文采用优势演员评论家(Advantage Actor-Critic, A2C)算法作为强化学习框架的核心。A2C算法通过演员网络和评论家网络的协同作用,实现了在复杂金融市场环境中的高效决策学习。
框架组成
此架构设计可以充分考虑了金融市场的特殊性,通过演员网络的探索性学习发现潜在的获利机会,同时借助评论家网络的价值评估确保策略的稳定性和可靠性。这种探索与利用的平衡机制,使得系统特别适合处理股票市场这类高度复杂和动态变化的环境。
import numpy as np class A2CAgent: def __init__(self, state_size, action_size, gamma=0.99, alpha=0.001, beta=0.005, initial_balance=1000, epsilon=0.1): self.state_size = state_size self.action_size = action_size self.gamma = gamma self.alpha = alpha self.beta = beta self.balance = initial_balance self.inventory = [] self.epsilon = epsilon self.actor_model = self.build_actor() self.critic_model = self.build_critic() def build_actor(self): model = tf.keras.Sequential([ Dense(32, input_shape=(self.state_size,), activation='relu'), Dense(16, activation='relu'), Dense(self.action_size, activation='softmax') ]) model.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=self.alpha), loss='categorical_crossentropy') return model def build_critic(self): model = tf.keras.Sequential([ Dense(32, input_shape=(self.state_size,), activation='relu'), Dense(16, activation='relu'), Dense(1, activation='linear') ]) model.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=self.beta), loss='mse') return model def get_action(self, state): if np.random.rand() < self.epsilon: return np.random.choice(self.action_size) else: policy = self.actor_model.predict(state.reshape(1, -1), verbose=0)[0] temperature = 1.0 policy = np.exp(policy / temperature) / np.sum(np.exp(policy / temperature)) return np.random.choice(self.action_size, p=policy) def train(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done): value = self.critic_model.predict(state.reshape(1, -1), verbose=0) next_value = self.critic_model.predict(next_state.reshape(1, -1), verbose=0) advantage = reward + self.gamma * (1 - int(done)) * next_value - value advantage = (advantage - np.mean(advantage)) / (np.std(advantage) + 1e-8) actions = np.zeros([1, self.action_size]) actions[0, action] = 1.0 self.actor_model.fit(state.reshape(1, -1), actions, sample_weight=advantage.flatten(), verbose=0) self.critic_model.fit(state.reshape(1, -1), value + advantage, verbose=0)
风险收益建模
我们采用多维度的奖励计算机制,综合考虑交易的盈利能力、市场波动性和最大回撤等因素。这种设计理念与现代投资组合理论相一致,旨在在可接受的风险水平下实现收益最大化。优势函数的设计确保了系统在追求高收益的同时,能够有效控制风险敞口。
def compute_reward(profit, volatility, drawdown, risk_penalty=0.1, scale=True, volatility_threshold=0.02, drawdown_threshold=0.05): """ 多维度奖励计算函数。 参数: - profit: 交易获利。 - volatility: 市场波动率。 - drawdown: 最大回撤比例。 - risk_penalty: 风险惩罚系数。 - scale: 是否对输入进行归一化。 - volatility_threshold: 波动率阈值。 - drawdown_threshold: 回撤阈值。 返回: - reward: 综合奖励值。 """ if scale: volatility = min(volatility / volatility_threshold, 1.0) drawdown = min(drawdown / drawdown_threshold, 1.0) reward = profit - risk_penalty * (volatility + drawdown) return reward
系统整体架构
数据处理与状态表示
首先对原始市场数据进行预处理,通过滑动窗口方法构建特征序列。这些数据随后通过SSDA和LSTM-AE进行特征提取和降维,最终生成包含市场静态特征和动态特征的增强状态表示。
A2C决策机制
基于增强状态表示,演员网络输出交易决策的概率分布,而评论家网络则对当前市场状态的价值进行评估。这种双网络协同机制能够在保证决策稳定性的同时,保持对新型交易机会的探索能力。
评估与反馈系统
交易执行后,系统通过综合奖励函数评估交易表现,并将评估结果用于更新演员和评论家网络的参数,从而不断优化交易策略。
系统实现与训练过程
训练过程采用多轮次迭代方式,每轮训练中代理需要在当前市场环境下做出一系列交易决策。系统通过设计合理的奖惩机制来引导代理形成稳健的交易策略:买入操作设置小额惩罚以避免过度投资,卖出操作基于价格涨幅给予相应奖励,持有操作则设置轻微惩罚以防止过度保守。
import gc from tqdm import tqdm window_size = 20 episode_count = 15 batch_size = 32 agent = A2CAgent(state_size=window_size, action_size=3, initial_balance=1000) for e in tqdm(range(episode_count), desc="Training Episodes", unit="episode"): print(f"\n--- Episode {e+1}/{episode_count} ---") start_t = window_size - 1 state = get_augmented_state(adj_close_prices, start_t, window_size, ssda, lstm_ae) total_profit = 0 agent.inventory = [] for t in range(start_t, len(data) - 1): current_price = data['Adj Close'].iloc[t] next_price = data['Adj Close'].iloc[t + 1] action = agent.get_action(state.reshape(1, -1)) next_state = get_augmented_state(adj_close_prices, t + 1, window_size, ssda, lstm_ae) reward = 0 done = t == len(data) - 2 if action == 0: if len(agent.inventory) < 100: agent.inventory.append(current_price) print(f"Buy: {current_price:.2f} at time {t}") reward = -0.01 elif action == 2 and agent.inventory: bought_price = agent.inventory.pop(0) profit = current_price - bought_price reward = max(profit, 0) total_profit += profit print(f"Sell: {current_price:.2f} at time {t} | Profit: {profit:.2f}") else: print(f"Hold: No action at time {t}") reward = -0.005 agent.train( state.reshape(1, -1), action, reward, next_state.reshape(1, -1), done=done ) state = next_state print(f"Episode {e+1} Ended | Total Profit: {total_profit:.2f}") if e % 5 == 0: agent.actor_model.save(f"actor_model1_ep{e}.h5") agent.critic_model.save(f"critic_model1_ep{e}.h5") gc.collect()
实验评估与结果分析
我们选择了波动特征各异的三只股票进行测试:特斯拉(中等波动性)、亚马逊和英伟达。测试过程中,系统需要在实际市场数据上进行交易决策,并通过累积收益率评估系统性能。同时,我们记录了买入卖出信号,通过可视化分析系统的决策模式。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd import yfinance as yf data = yf.download('AMZN', start='2024-01-01', end='2024-11-01') data.columns = data.columns.droplevel(1) data = data.reset_index() data['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(data['Date']) print("Available columns:", data.columns) adj_close_prices = data.get("Adj Close", data["Close"]) print(adj_close_prices.head()) def evaluate_agent(agent, adj_close_prices, window_size, ssda, lstm_ae): """ 交易代理评估函数 """ state = get_augmented_state(adj_close_prices, window_size, window_size, ssda, lstm_ae) total_profit = 0 buy_signals = [] sell_signals = [] profits = [] agent.inventory = [] for t in range(window_size, len(adj_close_prices) - 1): action = agent.get_action(state.reshape(1, -1)) next_state = get_augmented_state(adj_close_prices, t + 1, window_size, ssda, lstm_ae) current_price = adj_close_prices[t] next_price = adj_close_prices[t + 1] if action == 0: if len(agent.inventory) < 100: agent.inventory.append(current_price) buy_signals.append(t) print(f"Buy at {current_price:.2f} on day {t}") profit = 0 elif action == 2 and agent.inventory: bought_price = agent.inventory.pop(0) profit = current_price - bought_price sell_signals.append(t) total_profit += profit print(f"Sell at {current_price:.2f} on day {t} | Profit: {profit:.2f}") else: print(f"Hold at {current_price:.2f} on day {t}") profit = 0 profits.append(profit) total_profit += profit state = next_state print(f"Total Profit: {total_profit:.2f}") plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6)) plt.plot(data['Date'], adj_close_prices, label="AMZN Adjusted Close Price", color='blue') if buy_signals: plt.plot(data['Date'].iloc[buy_signals], adj_close_prices.iloc[buy_signals], '^', markersize=10, color='green', label="Buy Signal") if sell_signals: plt.plot(data['Date'].iloc[sell_signals], adj_close_prices.iloc[sell_signals], 'v', markersize=10, color='red', label="Sell Signal") plt.title("Buy and Sell Signals for AMZN Stock") plt.xlabel("Date") plt.ylabel("Adjusted Close Price") plt.legend(loc="best") plt.xticks(rotation=45) plt.tight_layout() plt.show() evaluate_agent(agent, adj_close_prices, window_size, ssda, lstm_ae)

亚马逊股票交易信号分析
实验结果显示,系统在亚马逊这类波动相对平稳的股票上表现出良好的适应性,能够准确捕捉价格走势并做出合理的交易决策。
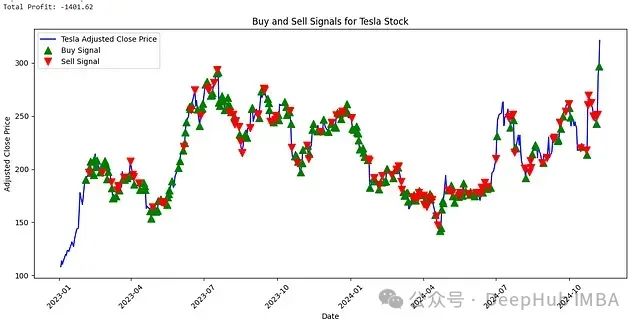
特斯拉股票交易信号分析
对于特斯拉这类波动性较高的股票,系统表现出了一定的局限性,说明高波动性股票的交易策略优化仍然是一个具有挑战性的研究方向。
值得注意的是,系统在英伟达股票的交易中展现出优异的表现。这可能得益于英伟达股票近年来由于GPU需求增长而呈现的相对稳定的上升趋势,使得系统能够更好地把握交易机会。
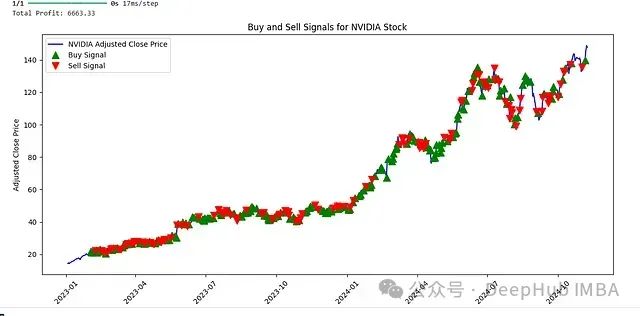
英伟达股票交易信号分析
结论
通过对三只具有不同波动特征的股票进行实证研究,我们可以看到:
系统对不同市场环境表现出差异化的适应能力。在波动相对平稳的亚马逊股票上,模型能够较好地捕捉价格趋势;而在高波动性的特斯拉股票上,系统的表现受到一定程度的限制。
SSDA与LSTM-AE的组合能够有效提取市场的静态特征和动态特征,这一点在英伟达股票的交易结果中得到了充分验证。特别是在存在明确市场趋势的情况下,系统表现出较强的决策准确性。
通过多维度的奖励计算机制,系统在追求收益的同时保持了对风险的有效控制,这体现在交易信号的时机选择和持仓管理上。
局限性分析
尽管本文取得了一定的成果,但仍存在以下需要改进的方面:
特征提取过程中可能存在信息损失的问题。
未来研究方向
基于本研究的发现和局限性,未来的研究可以从以下几个方向展开:
实践价值
本文的方法论和实证结果为量化交易系统的设计和实现提供了新的思路。特别是在当前市场环境日益复杂的背景下,混合深度学习架构的应用价值值得进一步探索。通过持续优化和改进,这类系统有望在实际交易环境中发挥更大的作用。
随着深度学习技术的不断发展和计算能力的提升,类似的混合架构系统在量化交易领域将具有广阔的应用前景。
数据派THU作为数据科学类公众号,背靠清华大学大数据研究中心,分享前沿数据科学与大数据技术创新研究动态、持续传播数据科学知识,努力建设数据人才聚集平台、打造中国大数据最强集团军。

新浪微博:@数据派THU
微信视频号:数据派THU
今日头条:数据派THU















