正文
If you’re coming from an Android background like me then you’ve probably missed those
POJO
classes in
Flutter
. I believe the developers who do app development in flutter will encounter such problems. After requesting
data from the server, the server will often return a
json
string and if we want to use data flexibly, we need to convert the
json
string into an
object
object .
Since flutter only provides json to
Map
. Handwritten deserialization is extremely unstable in large projects and can easily lead to parsing failure. So today I will introduce you to
json_annotation,
an
automatic deserialization library recommended by flutter team.
What you’ll learn
-
Generate code with
build_runner
build_runner.
-
How to parse json object in the flutter with
json_serialization
json_serialization.
Include Dependencies
We’re gonna need to add some libraries in the
pupspec.yaml
pupspec.yaml, which is the package management and build system file. Here we need to add three dependencies
json_annotation
json_annotation,
build_runner
build_runner
and
json_serializable
json_serializable in the
pupspec.yaml
pupspec.yamlfile.
dependencies: flutter: sdk: flutter # The following adds the Cupertino Icons font to your application. # Use with the CupertinoIcons class for iOS style icons. cupertino_icons: ^0.1.2 json_annotation: ^1.2.0 // dependecy
dev_dependencies: flutter_test: sdk: flutter build_runner: ^1.0.0 // | // | -> dev dependencies json_serializable: ^1.5.1 // |
Recommended for you
Once you have done these run packets get which is in the toolbar of the file from IntelliJ/Android Studio you can also execute
flutter packages pub get
flutter packages pub get from the terminal in the current project directory
if you prefer that.
Now let’s say we need to make a login request and download some
json
content. The following shows the sample
json
of a simplified login rest call.
{
"status" : true,
"message" : "User successfuly logged in!",
"user_name" : "Ahsen Saeed",
"profile_url" : "www.codinginfinite.com",
"user_id" : 280
}
Now we need to write a dart entity class based on above
json
data.
class LoginResponse{
bool status;
String message;
String userName;
String profileUrl;
int userId;
LoginResponse(this.status,this.message,this.userName,this.profileUrl,this.userId);
factory LoginResponse.fromJson(map<String,dynamic> json) {
return LoginResponse(
status : json['status'],
message : json['message'],
userName : json['user_name'],
profileUrl : json['profile_url'],
userId : json['user_id']
)
}
}
I know, I know, I just want to show you guys, the manual deserialization before showing the
auto-generated
json deserialization.
Generate an auto-generated json File
The following shows the
JsonSerializer
JsonSerializer model of above
json
.
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
@JsonSerializable()
class LoginResponse {
bool status;
String message;
@JsonKey(name: 'user_name')
String userName;
@JsonKey(name: 'profile_url')
String profileUrl;
@JsonKey(name: 'user_id')
int userId;
LoginResponse(
this.status, this.message, this.userName, this.profileUrl, this.userId);
}
If we want to use
JsonSerializer
JsonSerializer to generate code, we must add the annotation
@JsonSerializable()
@ JsonSerializable() before the signature of class that needs to generate the code and if you need to
define the name case of the member, use the
@JsonKey
@JsonKey annotation.
So, the question is how should the code be generated..? If you guys have remembered that we add the
build_runner
build_runner dependency in our
pupspec.yaml
pupspec.yaml file.
So, in order to generate the
Pojo
class for a
LoginResponse
LoginResponse run the following command in the current project directory
flutter packages pub run build_runner build
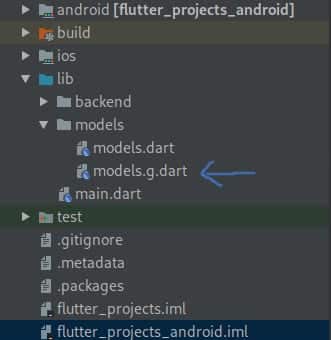
After the command runs successfully, we should be able to find a new file under the entity file.
![json_serialization_generated_file]()
The
models.g.dart
json parsing file generated by
build_runner
build_runner based on
JsonSerializer
JsonSerializer. Below is the generated dart file.
// **************************************************************************
// JsonSerializableGenerator
// **************************************************************************
LoginResponse _$LoginResponseFromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return LoginResponse(
json['status'] as bool,
json['message'] as String,
json['user_name'] as String,
json['profile_url'] as String,
json['user_id'] as int);
}
Map<String, dynamic> _$LoginResponseToJson(LoginResponse instance) =>
<String, dynamic>{
'status': instance.status,
'message': instance.message,
'user_name': instance.userName,
'profile_url': instance.profileUrl,
'user_id': instance.userId
};
Now we only need to associate our generated file in our entity class and provide a way to parse the
json
in the entity class. Let’s see how we can associate the generated file with our generated file.
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
part 'package:flutter_projects/models/models.g.dart'; // associated generated dart file
@JsonSerializable()
class LoginResponse {
bool status;
String message;
@JsonKey(name: 'user_name')
String userName;
@JsonKey(name: 'profile_url')
String profileUrl;
@JsonKey(name: 'user_id')
int userId;
LoginResponse(this.status, this.message, this.userName, this.profileUrl,
this.userId);
factory LoginResponse.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) =>
_$LoginResponseFromJson(json);
}
In order for the entity class file to find the generated file, we need
part
part
and let the entity class to mix with the generated file. Finally, a factory constructor is provided, which actually calls
_$LoginResponseFromJson
_$LoginResponseFromJson the method of the generated file. The
_$LoginResponseFromJson
_$LoginResponseFromJson method is the one who deserializes our
json
. And that’s how we can simply deserialize
our
json
into dart object.
Let’s take another example where we have a user
json
and within that
user
object, we have subjects of a user. Let’s see the
json
first.
{
"status" : true,
"message" : "User successfuly logged in!",
"user_name" : "Ahsen Saeed",
"profile_url" : "www.codinginfinite.com",
"user_id" : 280,
"subjects" : [
{
"subject_name" : "ComputerProgramming"
},
{
"subject_name" : "Calculus"
}
]
}
You see in order to parse the above
json,
we need to add a list of subjects in our
LoginResponse
LoginResponse model.