今天我们分享的是发表在《
Oncotarget
》上的文章:
Lung cancer exosomes as drivers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
介绍:
Exosomes
是胞外囊泡(
EVs
)的一个亚群,已被证明是有效的作为细胞间遗传信息交换的渠道。外泌体是从各种类型的细胞释放,但癌细胞可释放大量外泌体。外泌体包含蛋白质和遗传物质(
mRNA
,
DNA
和
miRNA
)。在这项研究中,我们检测了来自高转移性和非转移性的肺癌病人血清中的外泌体对人支气管上皮细胞(
HBEC
)的影响。我们发现来自于高度转移的肺癌细胞和晚期肺癌病人的血清中的外泌体诱导的后者波形蛋白表达,以及
HBECs
的上皮间质转化(
EMT
),并且也可诱导非癌细胞移动,侵袭和增殖。我们的研究结果表明外泌体可能是介质
EMT
的因素之一。
方法:
从肺癌细胞系及病人血清中提取出外泌体,作用于
HBECs
,检测波形蛋白(
vimentin
)及其他指标的变化。
结果:
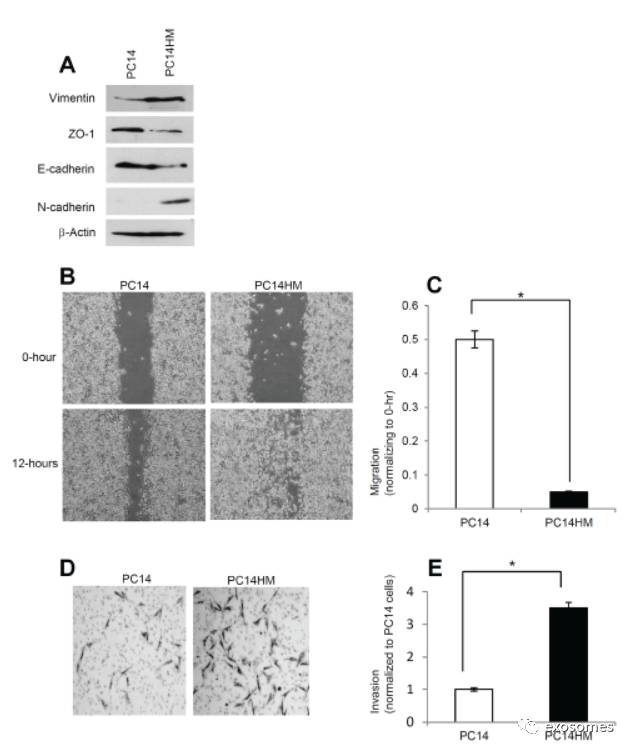
Figure 1: PC14HM cells show more mesenchymal properties and show more migratory as well as invasive capacity compared to PC14 cells. A.
Western Blot analysis for epithelial and mesenchymal markers in PC14 and PC14HM cell lysate samples.Twenty micrograms of total protein were analyzed by Western Blot usingVimentin, E-cadherin, ZO-1, and N-cadherin markers. β-Actin was used as an internal loading control.
B.
The
in vitro
wound healing motility assay in PC14 and PC14HM cells was performed as described in Materials andMethods. Cells were analyzed with a live cell microscope equipped with SC10010.6 MP CMOS Color digital camera and Analysis software (Universal Imaging)(×100).
C.
Quantification of wound width between PC14 and PC14HM cells.The bars represent normalized wound width values with mean ± SD. *pD. Matrigel invasion assays were performed with the indicated PC14 and PC14HM cells. Invaded cells were stained with 0.2% crystal violet. Representative images of the bottom membrane surface are shown (40×magnification).
E.
The number of invading cells for both PC14, andPC14HM, were counted under a light microscope and statistically analyzed.*p
(通过
western blot
、
would healing assay
、
Matrigelinvasion assays
比较
PC14HM
与
PC14
两种细胞系的差异,根据结果可观察到
PC14HM
更具
EMT
的特点,之后我们将使用来源于这两种细胞系的外泌体作用于非恶性细胞)
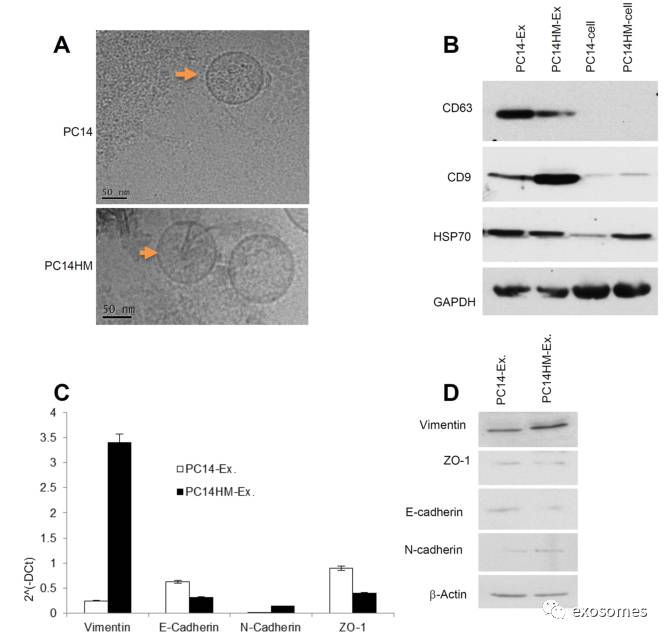
Figure2: Characterization of exosomes derived from PC14 and PC14HM cells
. A. Cryo-Transmission Electron Microscopy (cryo-TEM). TEM images of exosomes derived from PC14 and PC14HM cells. B. Western Blot analysis for exosomes marker in exosomes and cell lysates from PC14 and PC14HM cells. Twenty micrograms of total protein from exosomes or cell lysate were analyzed byWestern Blot using different exosome markers. GAPDH was used as an internal loading control. C. The relative mRNA expression of epithelial (E-cadherin, microgramsofZO-1), and mesenchymal (N-cadherin, Vimentin) markers by qRT-PCR in exosomalRNA isolated from PC14 and PC14HM cells. Normalization with housekeeping gene(GAPDH). The bars represent as mean ± SD of experiment performed in triplicate.D. Western Blot analysis of EMT marker in exosomal protemicrograms of total protein associated with exosomes were analyzed by Western Blot.β-Actin was used as an internal loading control. Ex indicates exosomes.
(
通过冰冻电镜检测收集到的
exosomes,
通过
western blot
检测
exosomes
标志物,通过
qRT-PCR
检测上皮或间质标志物,并进一步通过
western blot
检测标志物的表达量,从而分析两种细胞系的差异特点
)
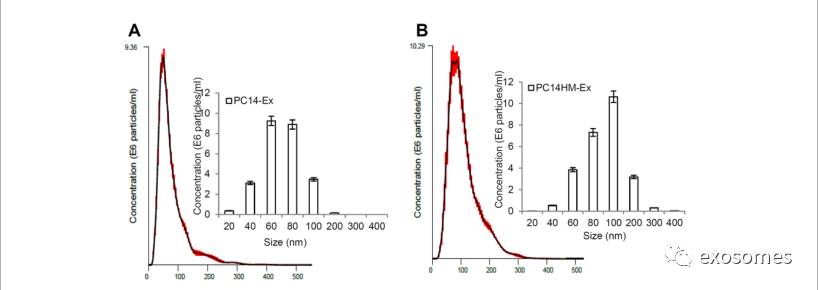
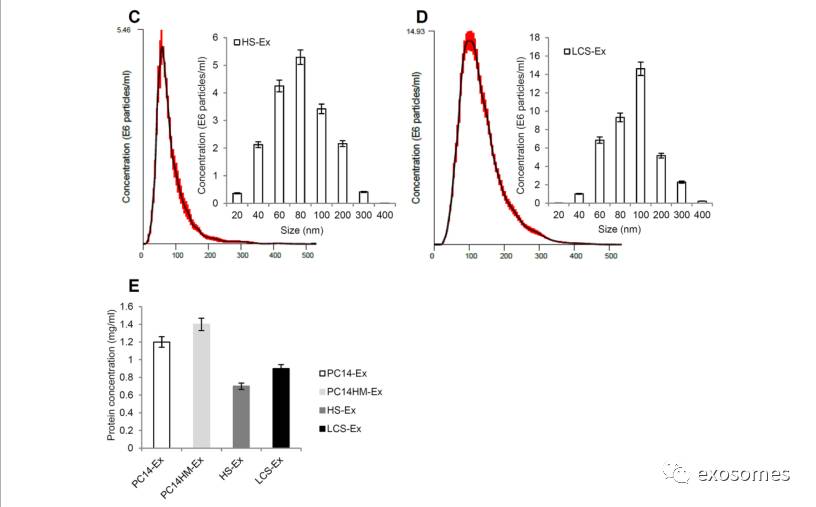
Figure 3: Exosome characterization by nanoparticletracking analysis.
Barchart showing the average percentage of nanoparticles within 20–300 nm size inin vitro exosome preparation. Concentration and size distribution of exosomesderived from A. PC14, B. PC14HM, C. healthy human serum, (HS), and D. lungcancer serum (LCS) were measured by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA).Exosomal concentration showed a peak at 60 +/− 0.5 nm (PC14 cell derivedexosomes, PC14-Ex), 100 +/−0.2 nm (PC14HM cell derived exosomes, PC14HM-Ex), 80+/−0.3 nm (healthy serum derived exosomes, HS-Ex) and 100 +/−0.7 nm (lungcancer serum derived exosomes, LCS-Ex). Bar Chart showing the particlenumber/ml of PC14, PC14HM, HS and LCS derived exosomes. E. ProteinConcentration of exosomes derived from PC14, PC14HM, healthy serum (HS) andlung cancer serum (LCS). Values are mean ± SD, all values are representative ofat least three independent experiments with four replicates.
(通过
NanoSight tracking analysis (NTA)
进一步对从
4
组细胞中提取出来的
exosomes
的大小及含量进行检测,并通过
BCA
检测
exosomes
内的蛋白含量)
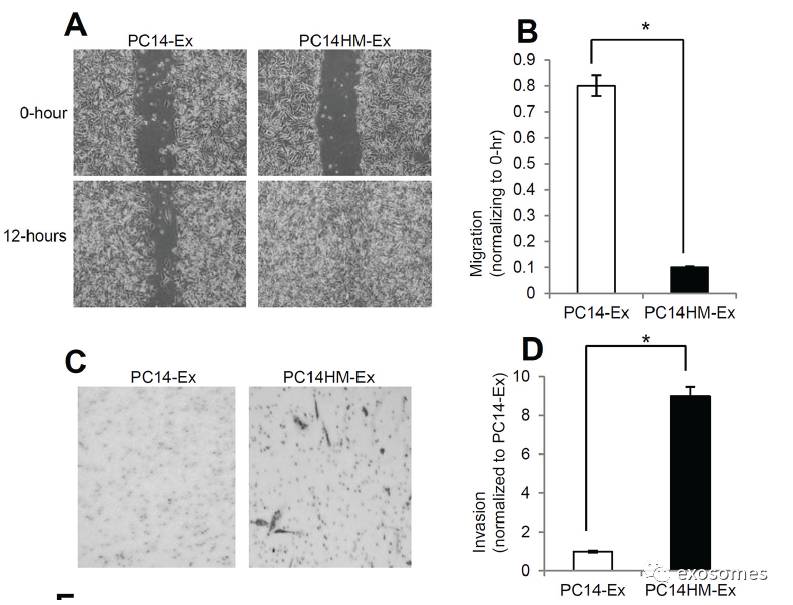
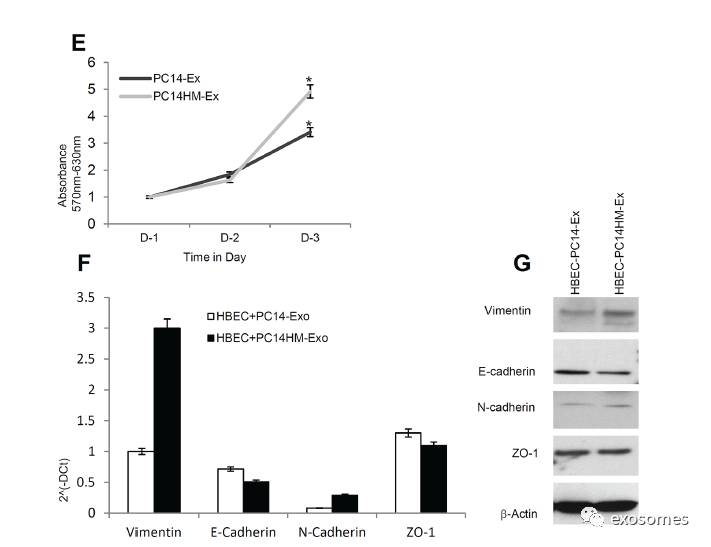
Figure4: Exosomes from highly metastatic cells induce migration, invasion and vimentin expression in recipient HBEC cells.
A.
Representative images from the wound healing motility assay. Confluent HBEC cells were treated with PC14 cell line derived exosomes (PC14-Ex) and PC14HM cell line derived exosomes (PC14HM-Ex) at20 μg/μl concentration for 16 hrs. The cells were then scratched and imaged over indicated time point (0-hour and 12-hours). Each point on the assay represents three independent experiments.
B.
Quantification of wound healing motility assay. Cells were analyzed with a live cell microscope equipped with SC100 10.6 MP CMOS Color digital camera and Analysis software(Universal Imaging) (×100). The bars represent normalized wound width values with mean ± SD. *pC. Matrigel invasion assays were performed with the HBECs cells treated with PC14-Ex andPC14HM-Ex. Invaded cells were stained with 0.2% crystal violet. Representative images of the lower membrane surface from Matrigel are shown (X400).
D.
The number of invading HBECs cells treated with either PC14-Ex or PC14HM-Ex were counted under a light microscope and statistically analyzed. *p E. PC14HM-Ex treatment increases proliferation of HBEC cells. After 16 hrs of treatment with PC14HM-Exor PC14-Ex, the proliferation of the HBEC cells was assessed by EZ-Cytox cell viability assay kit. *pF.The relative mRNA expression of epithelial (E-cadherin, ZO-1), and mesenchymal (N-cadherin, Vimentin) markers in HBECs cells treated with PC14-Exand PC14HM-Ex. After 16 hrs of treatment with exosomes, total RNA was isolated from HBECs cells, 100 ng RNA was used to prepare cDNA synthesis, both epithelial and mesenchymal marker gene expression was assessed by qRT-PCR. The bars represent as mean ± SD of experiment performed in triplicate.Normalization with housekeeping gene (GAPDH).
G.
PC14HM-Ex induced vimentin protein expression in HBECs cells. HBEC cells were treated withPC14-Ex and PC14HM-Ex for 48 hrs and total proteins were isolated using RIPAbuffer. Twenty micrograms of total protein associated with exosomes treatedHBECs cells were analyzed by Western Blot using EMT markers. β-Actin was used as an internal loading control.
(
HBECs
经外泌体处理
16h
后,再次通过划痕实验检测迁移能力的变化
,
再通过基质胶侵袭实验检测其侵袭能力变化,通过
EZ-Cytox cell viability assay kit
检测其细胞增殖变化,再通过
qRT-PCR
检测上皮或间质标志物表达量,可发现
vimentin
在
mRNA
及表达水平都有变化)
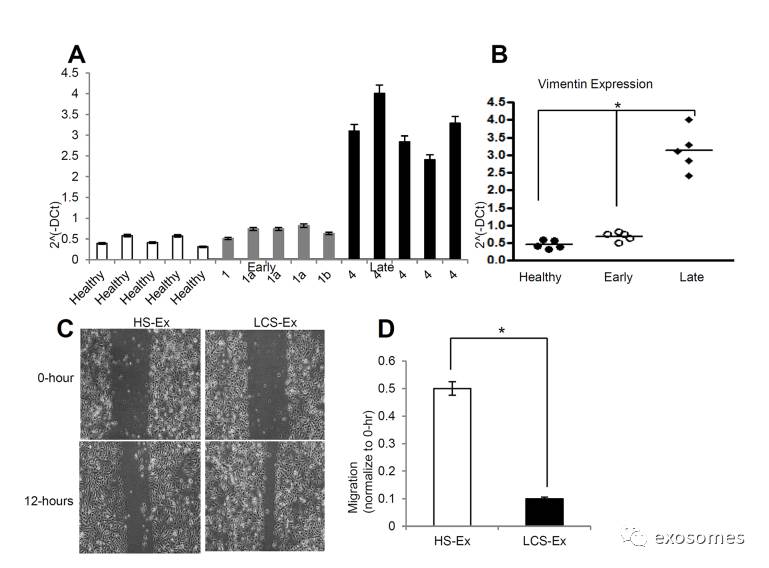
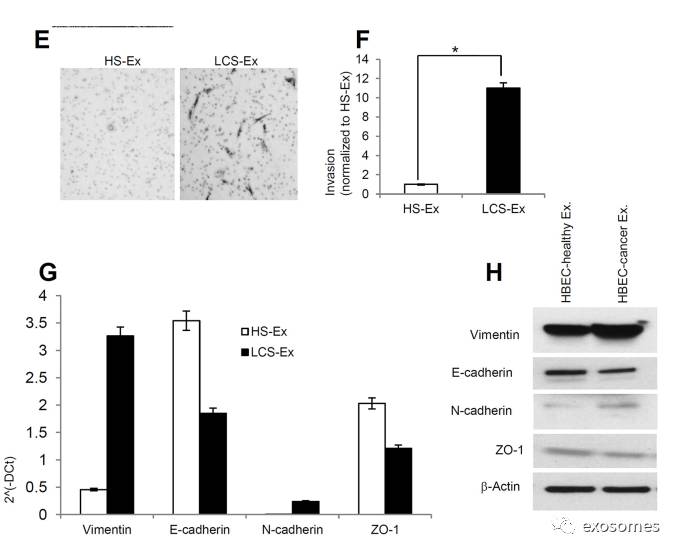
Figure5: Late stage human lung cancer serum exosomes express higher vimentin andinduce migration and invasion in recipient HBEC cells.
A.
Vimentin expression was higher in late stage lung cancer serum exosomes compared to healthy and early stage lung cancer serum exosomes. Total 100 ng RNA was used to prepare cDNAsynthesis, expression of vimentin was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Normalization with housekeeping gene (GAPDH).
B.
Quantification of vimentin expression in human lung cancer serum derived exosomes using graphpad prism software. *denotes significance higher expression of vimentin in late stage lung cancer serum derived exosomes compare to healthy and early stage lung cancer serum derived exosomes (pC. Exosomes isolated from late stage lung cancer serum (LCS-Ex) induce faster migration of recipient HBEC cells as compared to exosomes isolated from healthy serum (HS-Ex). Confluent HBEC cells were treated with exosomes (at 20 μg/μl concentration) isolated from healthy serum and late stage lung cancer serum for 16 hrs. The cells then were scratched and imaged over indicated time point (0-hour and 12-hours). Each point on the assay represents three independent experiments.
D.
Quantification of wound healing motility assay. Cells were analyzed with a live cell microscopy equipped with SC100 10.6 MP CMOS Color digital camera and Analysis software (Universal Imaging) (×100). The bars represent normalized wound width values with mean ± SD. *p E. Matrigel invasion assays were performed in HBECs cells treated with HS-Ex and late stageLCS-Ex for 24 hrs. Invaded cells were stained with 0.2% crystal violet. Representative images of the lower membrane surface from Matrigel are shown (X400).
F.
The number of invading HBECs cells treated with either HS-Ex or LCS-Ex, were counted under a light microscope and statistically analyzed. *pG. The relative mRNAexpression of epithelial (E-cadherin, ZO-1), and mesenchymal (N-cadherin, Vimentin) markers in HBECs cells treated with HS-Ex and late stage LCS-Ex.After 16 hrs of treatment with exosomes, total RNA was isolated from HBECscells, 100 ng RNA was used to prepare cDNA synthesis, both epithelial and mesenchymal marker gene expression was assessed by qRT-PCR. The bars represent mean ± SD of experiment performed in triplicate. Normalization with housekeeping gene (GAPDH).
H.
HBEC cells were treated with HS-Ex and late stage LCS-Ex for 48 hrs and total protein was isolated using RIPA buffer.Twenty micrograms of total protein associated.