同时,Meyer博士还发现,当幽门螺杆菌侵入时,胃粘膜下方的间质成纤维细胞会分泌一种名为R-脊髓蛋白(Rspo)的物质,作用于胃粘膜下方干细胞池,激活干细胞的WNT通路调节干细胞的增殖以应对幽门螺杆菌感染。
但是,Meyer博士发现,这两种细胞对WNT通路的反应是不同的。正常Rspo作用于分化程度低,增殖较快的干细胞在后,会使干细胞的增殖速度显著加快,导致其过度增殖。而Rspo作用于增殖较慢的细胞后,会显著抑制其增殖。
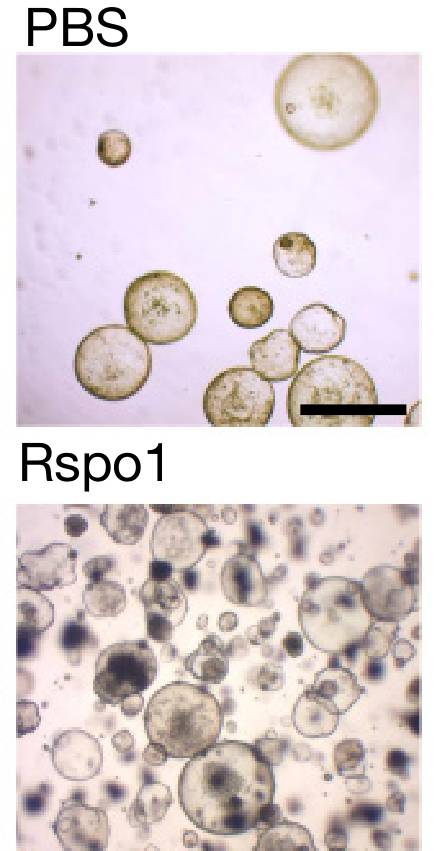
Rspo会显著增强敏感干细胞的扩增速度(单细胞培养24小时)
正如Sigal博士所说,“由于幽门螺杆菌引起感染机体无法自我治愈,因此,若不治疗,幽门螺杆菌可能长期持续刺激间质成纤维细胞分泌Rspo来刺激干细胞分裂,这也许足以解释为什么幽门螺杆菌感染会显著增加胃癌风险(10)。”
总的来说,Meyer博士的研究揭示了慢性细菌感染是如何干扰组织的功能的,并提供了关于幽门螺杆菌如何增加胃癌风险的首个宝贵线索。而我国人口基数大,幽门螺杆菌的感染率高,这也是我国胃癌发病人数以及死亡人数如此之高的可能原因。而此前的研究表明,进行幽门螺杆菌根治治疗可以减少65%的胃癌风险(11)。因此,为了减少胃癌的发生,感染者还是应该尽早接受幽门螺杆菌根除治疗。
参考资料:
1.http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nature23642.html?foxtrotcallback=true
2.https://www.nature.com/scientificamerican/journal/v292/n2/full/scientificamerican0205-38.html
3.Warren JR, Marshall BJ. Unidentifi ed curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1983;I:1273–5.
4.Parsonnet J, Friedman G D, Vandersteen D P, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma[J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 1991, 325(16): 1127-1131.
5.IARC. Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Helicobacter pylori. In: Schistosomes, liver fl ukes and Helicobacter pylori views and expert opinions of an IARC Working Group On The Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks To Humans. Lyon: IARC 1994. p. 177–240.
6.张万岱, 胡伏莲, 萧树东, 等. 中国自然人群幽门螺杆菌感染的流行病学调查[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗, 2010, 15(5): 265-270.
7.Stewart B, Wild C P. World cancer report 2014[J]. Health, 2017.
8.Sigal, M. et al. Helicobacter pylori activates and expands Lgr5+ stem cells through direct colonization of the gastric glands. Gastroenterology 148, 1392–404.e21 (2015).
9.Tomasetti C, Vogelstein B. Variation in cancer risk among tissues can be explained by the number of stem cell divisions[J]. Science, 2015, 347(6217): 78-81.
10.https://www.mpg.de/11437780/stomach-cancer-helicobacter-pylori-infection
11.Fuccio L, Zagari R M, Eusebi L H, et al. Meta-analysis: can Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment reduce the risk for gastric cancer?[J]. Annals of internal medicine, 2009, 151(2): 121-128.














