编者按:
伴随人民币贬值,越来越多人进入了美股投资的大军之中。美股虽好,但是很多投资者水土不服。不仅美股、港股与A股的投资逻辑截然不同,而且很多美股上市公司的结构更是国人闻所未闻,比如REITs和MLP结构等。这些复杂的结构让一些看似便宜的股票成为了陷阱。今天格隆汇就给大家分享一篇文章,介绍能源行业中非常普遍的公司结构:MLP。
MLPS: BE CAUTIOUS WHEN THE BORING IS MADE EXCITING
MLPS(有限合伙制企业):无聊伪装成有趣,千万得小心了!
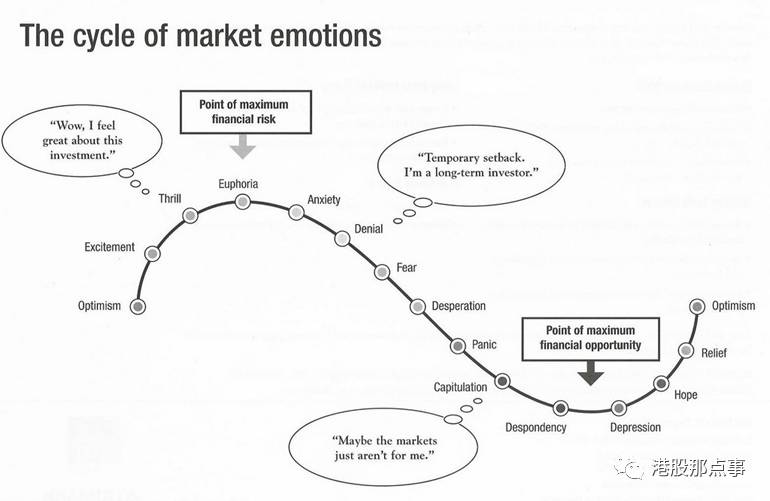
Companies and industries that are out of favor tend to attract our interest. While we focus on franchise businesses with large moats and good management at a reasonable price, investing in cyclical companies has a certain appeal. After all, it seems straightforward enough that abrupt swings in market psychology will create bargains, even huge, screaming bargains. If you can enter the market at the “point of maximum financial opportunity,” big money can be made.
一些冷门的公司和行业有的时候反而能吸引我们的注意力。虽然我们主要以合理的价格投资拥有较深护城河以及优质管理层的连锁经营企业,但是因为某些原因,我们也会投资周期性行业。很显然,市场情绪的突然动荡很容易带来便宜“货”,有的甚至便宜得惊人。如果你能在“财务机会最高点” 进入市场,就能赚大钱。
Source: Big Fat Purse
This general principle led us to take a look at a particularly cyclical industry, oil. The recent drop in the price of oil and the concomitant drop in the value of oil and oil-related companies caught our attention. We thought it was highly likely that the market was incorrectly extrapolating current oil prices far into the future and under-rating the likelihood of a return to high prices. This over-pessimism should lead to bargains in oil stocks.
在此方针下,我们研究了一个特殊的周期性行业,石油行业。油价近来下跌,随之而来造成的石油、石油产业相关公司价值的下跌引起了我们的注意。我们认为市场很有可能错误地认为现在的油价水平就代表了未来的油价水平,于是低估了油价回涨到高位的可能性。这种过度悲观情绪会造成很多油气股被低估。
In fact, as Howard Marks pointed out in a 2014 memo, the oil market tends to be self-correcting:
事实上,正如2014年霍华德马克思写道:石油市场有自我修正的倾向
•
A decline in the price of gasoline induces people to drive more, increasing the demand for oil.
•
油价下跌会吸引人们更多地开车,增加了对石油的需求
•
A decline in the price of oil negatively impacts the economics of drilling, reducing additions to supply.
•
油价下跌对原油勘测开采产生了负面影响,从而减少了对供给的补充
•
A decline in the price of oil causes producers to cut production and leave oil in the ground to be sold later at higher prices.
•
油价下跌让供应商削减供给,让石油留在地下知道价格回涨后再卖出。
Marks concluded: “In all these ways, lower prices either increase the demand for oil or reduce the supply, causing the price of oil to rise (all else being equal). In other words, lower oil prices – in and of themselves – eventually make for higher oil prices.” Therefore, the current dip in oil prices and the corresponding dip in oil company valuations should be merely temporary.
马克思认为:“上述情况中,低油价要么会增加石油需求,要么减少石油供给,会让油价回升(其它的不变)。换而言之,较低的油价自身终会带来更高的油价”。因此,当前的油价低估、以及油气公司价值的低估只不过是暂时性的。
Next, we decided to specifically focus on midstream master limited partnerships (MLPs). As midstream MLPs generally hold mature assets that require modest maintenance capital and generated stable cash flow, we saw MLPs as bond-like substitutes with high yields and very modest growth expectations. Such companies seemed attractive at the right price.
于是我们决定主要研究中游的有限合伙制企业(MLPs)。因为中游MLPs企业总体而言拥有成熟的资产、只需要适量的维护资本,并且能够产生稳定的现金牛。我们把MLPs企业当作债券的替代者,认为它能产生高收益,并且赋予它平稳增长的期望。这类公司看上去十分有吸引力,价格也很合适。
Boy, were we naïve! Walking into the cesspool that is the MLP sector was an eye-opening experience.
天呐,可是我们实在是幼稚!睁着眼睛走进了MLP的粪坑。
The Oil & Gas Value Chain
石油&天然气价值链条
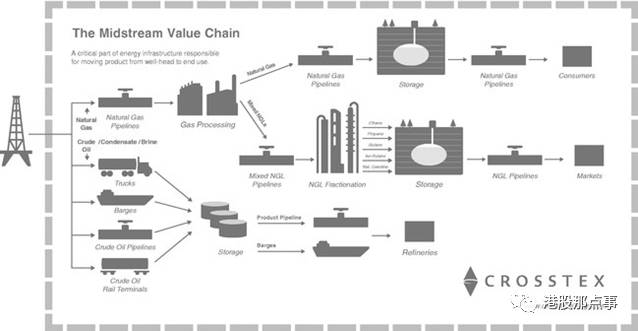
“Midstream” MLPs represent the largest single segment of the MLP universe. As the name suggests, midstream companies sit between upstream companies which actually extract the oil or natural gas and downstream companies which distribute the commodity. Midstream companies operate pipelines, storage facilities, and/or processing plants. These are predominately fixed-infrastructure assets designed to handle specific commodities and to provide transportation services in a specific direction. They charge toll-like fees to the producers for throughput on their infrastructure.
中游的MLPs企业是MLP中规模最大的那一个部分。正如名字所示,中游的公司处在上游开采原油和天然气的公司和下游分销产品的公司之间。中游企业主要负责管道、储存设施、以及/或者包括炼油厂。这些都是事先修建好的固定资产,主要为了生产特定的产品,以及提供某些固定方向的输送。它们像收过路费那样跟使用其设备的生产商收费。
With the advent of large scale horizontal drilling roughly 8 years ago and the surge in hydrocarbons flowing out of Alberta, the Bakken, DJ Basin, Marcellus, Permian, Eagle Ford, et al, the US experienced a huge build out of energy infrastructure. Much of this build out took place via MLPs.
八年前,随着大规模的水平钻井的出现,以及大量碳氢化合物从阿尔伯塔省、贝肯、丹佛朱尔斯堡盆地、马尔瑟吕、伊格尔、福特等地冒出来,美国由此进行了大量的能源基础设施建设。大量建设都是MLPs企业完成的。
Attractive Features of Midstream MLPs
中游MLPs企业吸引人的特征
Our look at Midstream MLPs focused specifically on companies providing oil storage services. The MLPs that derive 90% to 100% of their revenue from oil storage fees are;
在中游MLPs企业里,我们着重研究提供石油仓储的企业。石油储藏费用占了90%到100%总营收的MLPs企业有:
1.Arc Logistics (ARCX)
2.PBF Logistics (PBFX)
3.VTTI
4.West Point Terminals (WPT)
These companies have many of the characteristics we look for:
这些公司身上有很多我们看重的特征:
•
Stable and Predictable Cash Flows – A number of mechanisms provide a substantial degree of security around future cash flows:
•
稳定、可预测的现金流 —— 特定的运行机制为未来可持续的现金流提供了保障。
Limited Commodity Price Exposure – Although the MLPs operate in a highly cyclical industry, they are relatively insulated from the cycles because they do not take ownership of the oil at the terminals.
有限的商品价格风险— 虽然这些MLPs公司处在高度周期性企业,但是它们几乎是跟周期绝缘的,因为并不在终端拥有石油产品。
Volume Security – Many oil storage contracts contain minimum volume commitments (MVCs)
保量交易—很多石油储蓄合同会签订储存最少量。
Long Term contracts – Typically contracts have two 5-year renewal terms and inflation-based cost escalators.
长期合同—通常会签订两个5年的续约条款,并且设置基于通货膨胀的指数调解条目。
Customer Stickiness – Customers tend to stick around for a long time. The top ten customers for one storage MLP, World Point Terminals (WPT) have been with them for average of 9+ years
客户粘性—客户倾向于有较长时间的粘性。世界终端(WPT)运输MLP公司前10名客户平均跟其合作了9年之久。。
•
High barriers to entry, including:
•
高市场壁垒,包括:
Limited locations that possess the requisite characteristics necessary to support an oil storage business, such as proximity to pipelines, refineries, processing plants, waterway, demand markets and export hubs;
只有少数地点具备支撑石油仓储的必须条件,如像石油管道、炼油厂、石油加工厂、航道,这些需要市场以及出口港。
the extended length of time and risk involved in permitting and developing new projects and placing them into service, which can extend over a multi-year period depending on the type of facility, location, permitting and environmental issues and other factors;
新项目从获得准许到开展、并投入使用,需要很长的时间,并伴随着大量风险。取决于具体设施、地点、准许情况、环境问题和其它一些问题,有的甚至长达数年。
the magnitude and uncertainty of capital costs, length of the permitting and development cycle and scheduling uncertainties associated with terminal development projects present significant project financing challenges, which could be exacerbated by any tightening of the global credit markets; andthe specialized expertise required to acquire, develop and operate storage facilities, which makes it difficult to hire and retain qualified management and operational teams.
资金成本的需求量和不确定性、获得准许和建设周期的长短、以及终端项目开发计划的不确定性,代表着巨大的项目财务挑战。这一挑战会由于全球信贷市场的紧缩而加剧。并购、开发、运营储存设施所需的专业技能使得雇佣合格的管理运作团队十分艰难。
•
Easy to Understand – Even we can understand owning a big tank and being paid to store someone’s oil in it.
•
容易理解—一个大的储存仓,向储存石油的人收费,这个我们都懂。
Conventional wisdom suggests midstream MLPs are generally the most stable assets within the MLP landscape.
人们普遍的看法是中游MLPs企业总体而言是所有MLP企业中资产最稳定的。
General Organization Structure of MLPs
MLPs企业一般的组织结构
Unfortunately, the conventional wisdom is wrong. Wall Street took these straightforward boring businesses and put them in highly engineered structures. See below:
很不幸的是这个普遍看法是错误的。华尔街把这些没意思的企业放到高度模型化的结构里。如下:
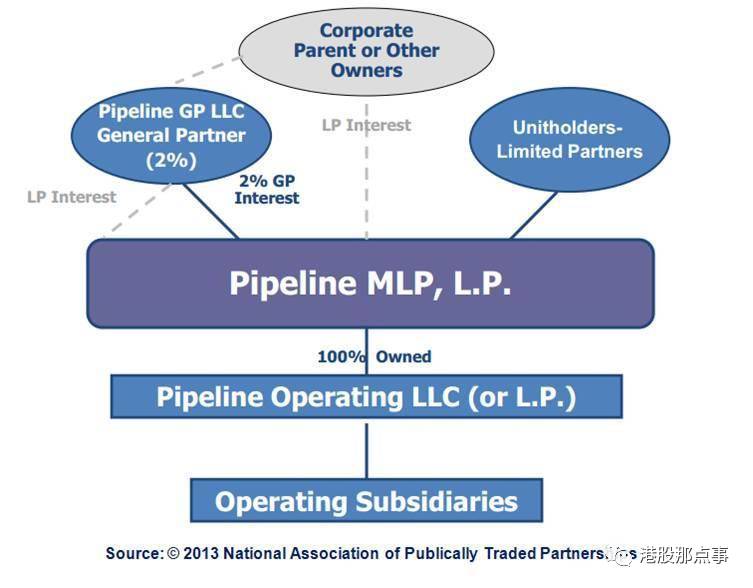
The key MLP stakeholders are:
MLP的核心股东是:
•
The “Sponsor.” The entity that forms or creates the MLP.
•
“赞助者”。形成或者创造MLP企业的主体。
•
The general partner (GP). Operates and manages the MLP.
•
普通合伙人。经营、管理MLP企业。
•
The Limited partners (LP). Simply provide capital
•
有限合伙人。仅仅提供资本。
To further confuse things, the Sponsor frequently also acts as the GP and owns LP interests.
更让人疑惑的是赞助者经常以普通合伙人的身份存在,同时享有有限合伙人的利益。
Sponsors are typically in the oil and gas field. They transfer certain assets (for example, pipelines or storage tanks) from the pre-existing business to the MLP. They then sell LP units to investors through an IPO.
赞助者往往是油气行业领域的。他们将一定资产(例如管道啊或者储油罐)从既有的企业中转移到MLP企业中。
The GP usually owns a 2% minority stake, essentially all the voting rights, and Incentive Distribution Rights (IDRs). IDRs warrant the GP to receive an incrementally larger share of the distributions paid to unitholders as the distribution grows. It is common for IDRs to split distributions 50/50 between the LP and GP at the highest level of the distribution schedule (or “tier”), a condition known as “high splits.”
普通合伙人至少拥有2%的股权,以及近乎所有的投票权和激励分配权利(IDRs)。IDRs授权普通合伙人根据单位信托证券持有者所得的分红的增加获得递增份额。通常,IDRs会以最高分红标准让有限合伙人和普通合伙人五五分成,这种情况被称作“高位分成”。
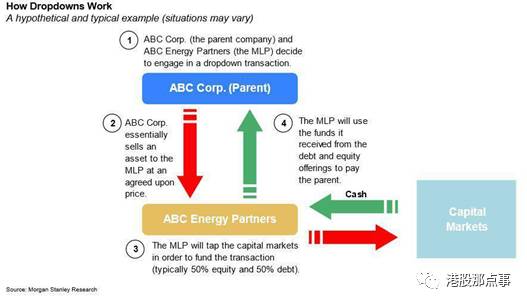
Once in place, Sponsors will transfer further assets to the MLP via transactions known as “dropdowns.” The Sponsor drops assets down to the MLP and takes back more equity in the MLP and/or debt.
一旦情形合适,赞助者会将更多的资产通过“下放”方式转移给MLP。赞助者将资产下放给MLP公司,然后拿回更多的MLP股权或者债权。
The Power of Bad Incentives
不正当激励的危害
MLPs are designed to attract retail investors with large and growing dividends while making sure the Sponsor maintains control over the vehicle and keeps their downside protected.
MLPs成立的目的就是为了用高额和不断增长的分红吸引散户投资者,同时保证赞助者掌舵,并且提供下行的安全垫。
This design as well as MLP marketing creates four important forces:
这种目的和整个MLP市场一起产生了四种重要的力量:
1.MLPs must distribute all available cash
MLP企业必须将可支配的现金分散出去。
2.MLPs are presumed to maintain stable growth
MLP企业应当保持稳定增长。
3.MLPS rely on funding from external sources
MLP企业依靠外部资源融资
4.GPs have high upside potential but little downside exposure
普通合作人面临很高的上行潜力,但是下行空间有限
When these forces combine, the end result is a highly combustible substance.
1.MLPs Must Distribute All Available Cash
MLP企业必须将可支配的现金分散出去
MLPs are contractually required to distribute “all available cash.” In practice, available cash is essentially operating cash flow less cash interest expense and less maintenance capital expenditures. This sounds great on the surface. After all, many shareholders would be better off if CEOs effectively had all discretion over capital allocation taken away from them.
受合约规定,MLP企业必须将所有可支配的现金分散出去。实际上,可支配的现金其实就是经营性现金流减去现金的利息支出、以及现金维护开支。从表面上看这听起来很好。毕竟如果公司CEO对现金分配的自由裁量权都被夺走时,很多股东就会赚跟多钱。
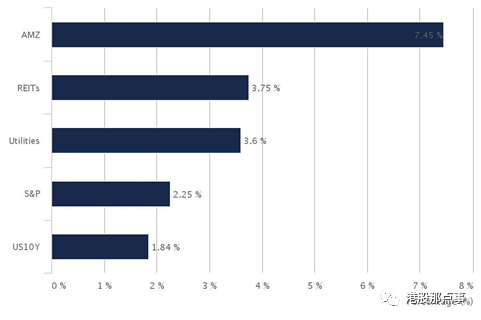
The high percentage of cash flow distributed leads to high yields. As of May 25, 2016, the Alerian MLP Index (AMZ) reported a yield of 7.45%. This yield is far higher than other asset classes as you can see below:
大比重分配现金流带来了高收益。比如,在2016年5月25日,Alerian MLP Index (AMZ)披露了7.45%的收益率。这个收益率远远高于以下的资产:
However, this high yield does not come without a price. The coverage ratio, i.e., the ratio of available cash to distributions paid, of midstream MLPs is just over 1.09x. This means for every dollar paid in distributions, there is a little more than one dollar of available cash to make the distribution. Contrast this with the more familiar dividend payout ratio – the ratio of dividends paid to reported earnings, typically associated with corporations. The aggregate payout ratio of S&P 500 companies is a bit over 32%. For MLPs, the comparable metric to the dividend payout ratio is the inverse of the coverage ratio. On that basis, one can see MLPs on average pay out nearly 92% of their cash flow in distributions. That leaves no ability to fund growth out of cash flow from operations. This high payout ratio raises a host of other issues discussed below.
然而这种高收益率并非没有代价的。比如中游MLP公司的流动比率,即可支配现金与分配现金的比重,才刚刚超过了1.09倍。这意味着每分配一美元,就有稍高于一美元的用于分配的可支配现金。我们将这个跟更熟悉的股息率进行对比—股息率即分红跟实际利润的比率,通常是跟企业相关。标普500公司的总体派息率略微高于32%。对于MLP企业而言,跟派息率相当的比率就是偿还能力比率的倒数。在此基础上,我们可以看到MLP企业平均将近花92%的现金流用于分红,所以MLP企业无法再满足经营性现金流的增长。
2.MLPs Are Presumed to Maintain Stable Growth
MLP企业应当保持稳定增长
Below is a typical slide from an MLP investor presentation showing hockey stick distribution growth.
下面是一张典型的MLP企业路演PPT,展示了直线上升的分红增长。
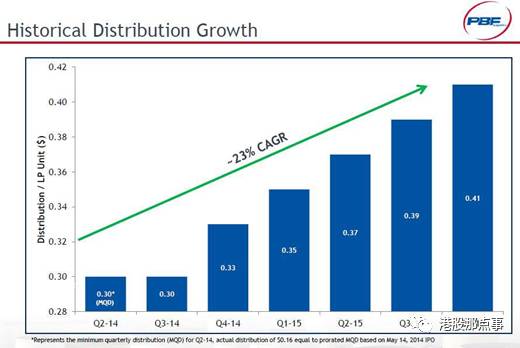
Source: PBFX Investor Presenation
来源:PBFX投资者关系会
The pressure for an MLP to maintain a stable and growing DCF is much more intense than that of a normal company to maintain steady earnings.
MLP企业保持分红现金流平稳增长的压力比普通企业维持稳定利润的压力要大得多。
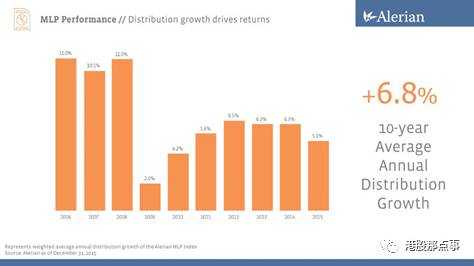
The question then becomes, how do you fund this type of growth when almost no cash is retained?
这时候问题变成,当现金所剩无几时我们要如何资助这种增长呢?
3.MLPS Rely on Funding from External Sources
MLP企业依靠外部资源融资
Any capital to the MLP business must come from external sources. This is not a good position to be in. “The ability to make accretive capital investments is largely dependent on others – a risky position that most competitive, strategic-thinking entities would rather not be in.” For one thing, should the capital markets largely dry up or become more expensive to access, the sources and rates of MLP distribution growth could be greatly reduced. For another, if the MLP comes to rely on debt, they can find themselves in a very awkward position should business turn down. If the MLP relies on equity infusions, minority owners suffer dramatic dilution.
MLP企业的资本都必须是来自外部资源,而这绝对不是个有利情况。“(这时候)累积资本投资的能力很大程度上取决于他人——这种风险境地是任何一个有竞争性、有策略的企业都不想置身其中的。” 一个原因是一旦资本市场大面积干涸,或者变得昂贵难以进入, MLP企业分红增长的来源和速度都会被大大削减。另一个原因是如果MLP企业过度依赖于负债,它们可能就会置身于面临破产的尴尬境地。如果MLP依赖于注资,那么少数股东的权益将被大幅度稀释。
4.GPs have high upside potential but little downside exposure
普通合作人面临很高的上行潜力,但是下行空间有限
IDRs entitle the GP to receive increasing percentages of the incremental as the MLP raises distributions to limited partners. Initially, the general partner receives only 0-2% of the partnership’s cash flow. However, as certain pre-determined distribution levels are met, the GP receives an incremental 15%, then 25%, and up to 50% of incremental cash flow. The purpose of the IDRs is to give the GP some “skin in the game” and incentivize the general partner to raise the quarterly cash distribution to reach higher tiers, which benefits the LP unitholders, as well.
激励分配权利让普通合伙人在MLP企业增加对有限合伙人的分红时也获得相应增加的增量收益。起初,普通合伙人只享有0-2%的合伙人的现金流。但是,一旦事先确定的固定分红水平达到了,普通合伙人就能获得15%的增量收益,然后是25%,真是是增量现金流的50%。吉利分配权力的目的就是为了让普通合伙人有参与游戏的感受,然后激励他们提高季度性现金分红以达到更高的水平,这对有限合伙人来说也是有益的。
Below is a typical IDR profit split arrangement:
如下所示是典型的激励分配权利下的分配安排:
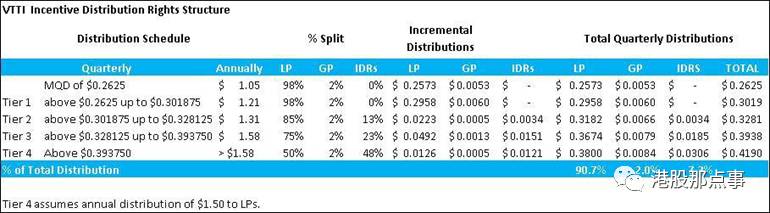
Source: VTTI 10-K & Punchcard Calculations
There are significant flaws in this theory. The key issue is that the GP gets the lion’s share of upside potential without commensurate downside exposure. A general partner commonly owns a 2% stake in an MLP it manages. In a static scenario (i.e., one in which the distribution is not growing), the GP receives 2% of distributions, equal to its ownership stake. At worst, the GP’s 2% stake could become worthless. On the other hand, IDRs allow the GP to take home an increasing share of incremental distributions, while LPs receive a declining share.
这个理论中有十分显著的漏洞。主要问题是普通合伙人有巨大的上涨潜力,但是却没有相对应的下行风险。一个普通合伙人通常在其管理的MLP企业里有2%的股权。从统计角度来看,(比如:当分红没有增长时),普通合伙人享有2%的分红,跟其所拥有的股权一致。普通合伙人最不济也就是那2%的股票变得分文不值。另一方面,激励分配权利让普通合伙人得到的增量分红中的比重不断增加,而有限合伙人享有的份额不断减少。
格隆汇声明:
格隆汇作为免费、开放、共享的海外投资研究交流平台,并未持有任何关联公司股票。转载本文,请务必注明来源“港股那点事”及作者。
●
投稿给格隆汇。投稿邮箱:
[email protected]
;
●
添加微服妹妹微信号:
guruclub_011
,
参加格隆汇三大线下活动:
汇说、汇路演、汇调研
;
●
直接添加格隆个人微信公众号:
guru-lama
●
广告投放:
0755-86332133-823
●
商务合作
:
0755-86332133-823