(点击
上方公众号
,可快速关注)
来源:今天你不奋斗明天你就落后,
www.jianshu.com/p/9e73b9216322
如有好文章投稿,请点击 → 这里了解详情
一、 前言
常用的并发队列有阻塞队列和非阻塞队列,前者使用锁实现,后者则使用CAS非阻塞算法实现,使用非阻塞队列一般性能比较好,下面就看看常用的非阻塞ConcurrentLinkedQueue是如何使用CAS实现的。
二、 ConcurrentLinkedQueue类图结构
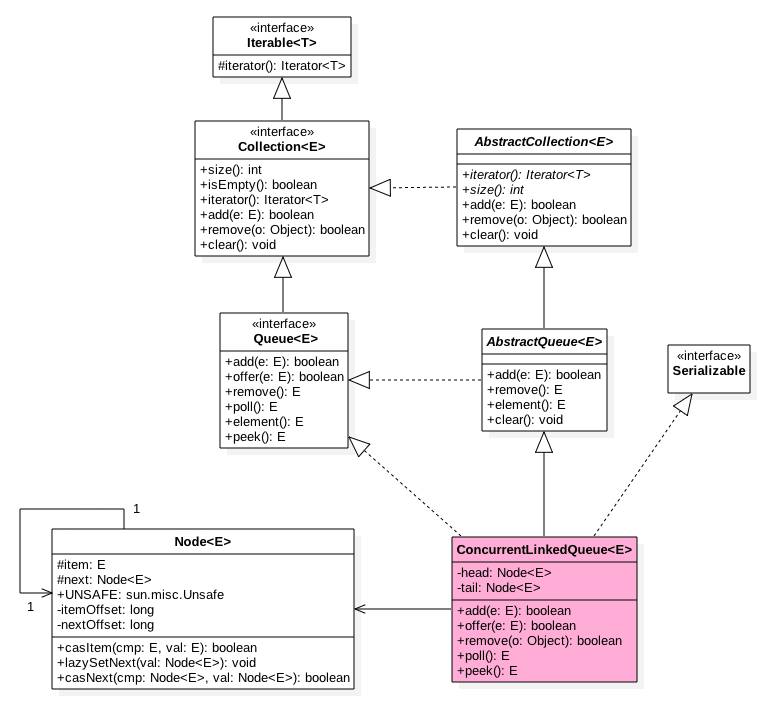
如图ConcurrentLinkedQueue中有两个volatile类型的Node节点分别用来存在列表的首尾节点,其中head节点存放链表第一个item为null的节点,tail则并不是总指向最后一个节点。Node节点内部则维护一个变量item用来存放节点的值,next用来存放下一个节点,从而链接为一个单向无界列表。
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue() {
head = tail = new Node
(null);
}
如上代码初始化时候会构建一个item为NULL的空节点作为链表的首尾节点。
三、offer操作
offer操作是在链表末尾添加一个元素,下面看看实现原理。
public boolean offer(E e) {
//e为null则抛出空指针异常
checkNotNull(e);
//构造Node节点构造函数内部调用unsafe.putObject,后面统一讲
final Node
newNode = new Node
(e);
//从尾节点插入
for (Node
t = tail, p = t;;) {
Node
q = p.next;
//如果q=null说明p是尾节点则插入
if (q == null) {
//cas插入(1)
if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) {
//cas成功说明新增节点已经被放入链表,然后设置当前尾节点(包含head,1,3,5.。。个节点为尾节点)
if (p != t) // hop two nodes at a time
casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK.
return true;
}
// Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next
}
else if (p == q)//(2)
//多线程操作时候,由于poll时候会把老的head变为自引用,然后head的next变为新head,所以这里需要
//重新找新的head,因为新的head后面的节点才是激活的节点
p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
else
// 寻找尾节点(3)
p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
}
}
从构造函数知道一开始有个item为null的哨兵节点,并且head和tail都是指向这个节点,然后当一个线程调用offer时候首先
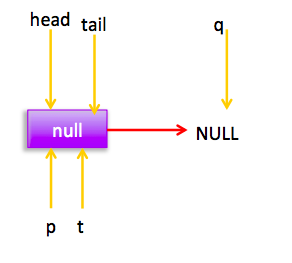
如图首先查找尾节点,q==null,p就是尾节点,所以执行p.casNext通过cas设置p的next为新增节点,这时候p==t所以不重新设置尾节点为当前新节点。由于多线程可以调用offer方法,所以可能两个线程同时执行到了(1)进行cas,那么只有一个会成功(假如线程1成功了),成功后的链表为:
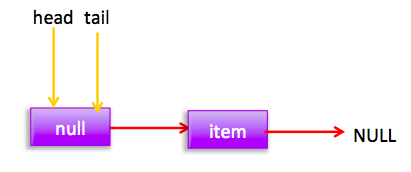
失败的线程会循环一次这时候指针为:
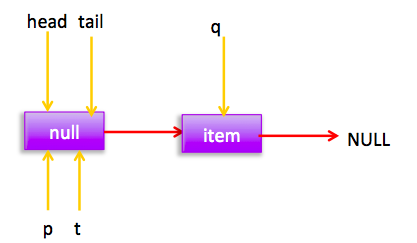
这时候会执行(3)所以p=q,然后在循环后指针位置为:
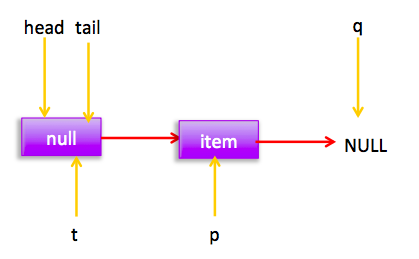
所以没有其他线程干扰的情况下会执行(1)执行cas把新增节点插入到尾部,没有干扰的情况下线程2 cas会成功,然后去更新尾节点tail,由于p!=t所以更新。这时候链表和指针为:
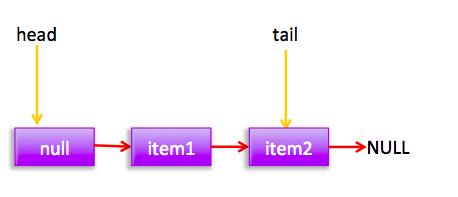
假如线程2cas时候线程3也在执行,那么线程3会失败,循环一次后,线程3的节点状态为:
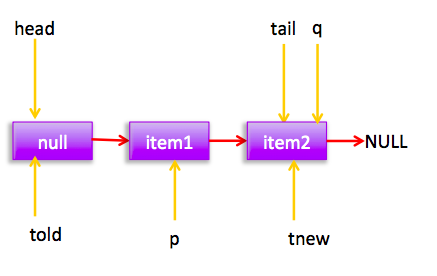
这时候p!=t ;并且t的原始值为told,t的新值为tnew ,所以told!=tnew,所以 p=tnew=tail;
然后在循环一下后节点状态:
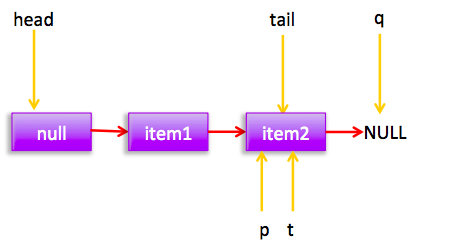
q==null所以执行(1)。
现在就差p==q这个分支还没有走,这个要在执行poll操作后才会出现这个情况。poll后会存在下面的状态

这个时候添加元素时候指针分布为:
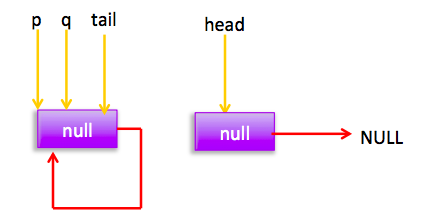
所以会执行(2)分支 结果 p=head
然后循环,循环后指针分布:
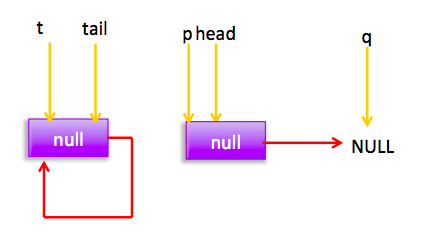
所以执行(1),然后p!=t所以设置tail节点。现在分布图:
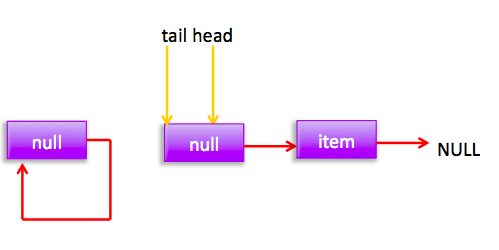
自引用的节点会被垃圾回收掉。
四、 add操作
add操作是在链表末尾添加一个元素,下面看看实现原理。
其实内部调用的还是offer
public boolean add(E e) {
return offer(e);
}
五、poll操作
poll操作是在链表头部获取并且移除一个元素,下面看看实现原理。
public E poll() {
restartFromHead:
//死循环
for (;;) {
//死循环
for (Node
h = head, p = h, q;;) {
//保存当前节点值
E item = p.item;
//当前节点有值则cas变为null(1)
if (item != null && p.casItem(item, null)) {
//cas成功标志当前节点以及从链表中移除
if (p != h) // 类似tail间隔2设置一次头节点(2)
updateHead(h, ((q = p.next) != null) ? q : p);
return item;
}
//当前队列为空则返回null(3)
else if ((q = p.next) == null) {
updateHead(h, p);
return null;
}
//自引用了,则重新找新的队列头节点(4)
else if (p == q)
continue restartFromHead;
else//(5)
p = q;
}
}
}
final void updateHead(Node
h, Node
p) {
if (h != p && casHead(h, p))
h.lazySetNext(h);
}
当队列为空时候:
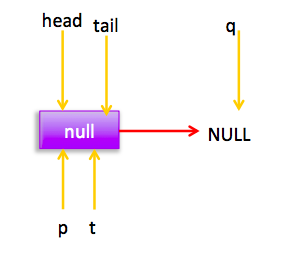
可知执行(3)这时候有两种情况,第一没有其他线程添加元素时候(3)结果为true然后因为h!=p为false所以直接返回null。第二在执行q=p.next前,其他线程已经添加了一个元素到队列,这时候(3)返回false,然后执行(5)p=q,然后循环后节点分布:
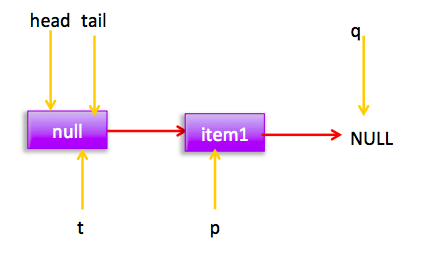
这时候执行(1)分支,进行cas把当前节点值值为null,同时只有一个线程会成功,cas成功 标示该节点从队列中移除了,然后p!=h,调用updateHead方法,参数为h,p;h!=p所以把p变为当前链表head节点,然后h节点的next指向自己。现在状态为:

cas失败 后 会再次循环,这时候分布图为:
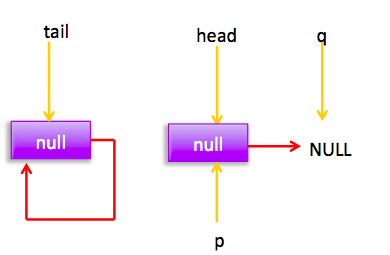
这时候执行(3)返回null.
现在还有个分支(4)没有执行过,那么什么时候会执行那?

这时候执行(1)分支,进行cas把当前节点值值为null,同时只有一个线程A会成功,cas成功 标示该节点从队列中移除了,然后p!=h,调用updateHead方法,假如执行updateHead前另外一个线程B开始poll这时候它p指向为原来的head节点,然后当前线程A执行updateHead这时候B线程链表状态为:
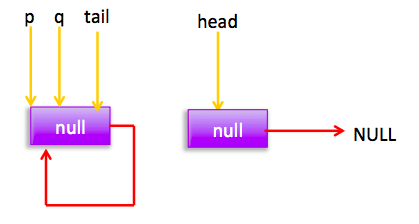
所以会执行(4)重新跳到外层循环,获取当前head,现在状态为:
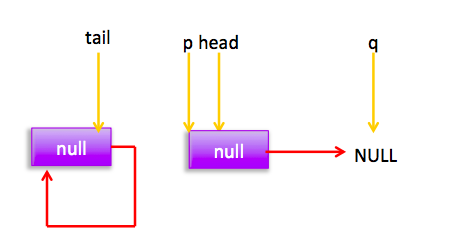
六、peek操作
peek操作是获取链表头部一个元素(只读取不移除),下面看看实现原理。
代码与poll类似,只是少了castItem.并且peek操作会改变head指向,offer后head指向哨兵节点,第一次peek后head会指向第一个真的节点元素。
public E peek() {
restartFromHead:
for (;;) {
for (Node
h = head, p = h, q;;) {
E item = p.item;
if (item != null || (q = p.next) == null) {
updateHead(h, p);
return item;
}
else if (p == q)
continue restartFromHead;
else
p = q;
}
}
}
七、size操作
获取当前队列元素个数,在并发环境下不是很有用,因为使用CAS没有加锁所以从调用size函数到返回结果期间有可能增删元素,导致统计的元素个数不精确。
public int size() {
int count = 0;
for (Node
p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p))
if (p.item != null)
// 最大返回Integer.MAX_VALUE
if (++count == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
break;
return count;
}
//获取第一个队列元素(哨兵元素不算),没有则为null
Node
first() {
restartFromHead:
for (;;) {
for (Node
h = head, p = h, q;;) {
boolean hasItem = (p.item != null);
if (hasItem || (q = p.next) == null) {
updateHead(h, p);
return hasItem ? p : null;
}
else if (p == q)
continue restartFromHead;
else
p = q;
}
}
}
//获取当前节点的next元素,如果是自引入节点则返回真正头节点
final Node
succ(Node
p) {
Node
next = p.next;
return (p == next) ? head : next;
}
八、remove操作
如果队列里面存在该元素则删除给元素,如果存在多个则删除第一个,并返回true,否者返回false
public boolean remove(Object o) {
//查找元素为空,直接返回false
if (o == null) return false;
Node
pred = null;
for (Node
p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p)) {
E item = p.item;
//相等则使用cas值null,同时一个线程成功,失败的线程循环查找队列中其他元素是否有匹配的。
if (item != null &&
o.equals(item) &&
p.casItem(item, null)) {
//获取next元素
Node
next = succ(p);
//如果有前驱节点,并且next不为空则链接前驱节点到next,
if (pred != null && next != null)
pred.casNext(p, next);
return true;
}
pred = p;
}
return false;
}
九、contains操作
判断队列里面是否含有指定对象,由于是遍历整个队列,所以类似size 不是那么精确,有可能调用该方法时候元素还在队列里面,但是遍历过程中才把该元素删除了,那么就会返回false.
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
for (Node
p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p)) {
E item = p.item;
if (item != null && o.equals(item))
return true;
}
return false;
}
十、开源框架中使用
Tomcat中NioEndPoint中的每个poller里面就维护一个ConcurrentLinkedQueue
用来作为缓冲存放任务。
10.1 Acceptor线程
accept线程作用是接受客户端发来的连接请求并放入到事件队列。
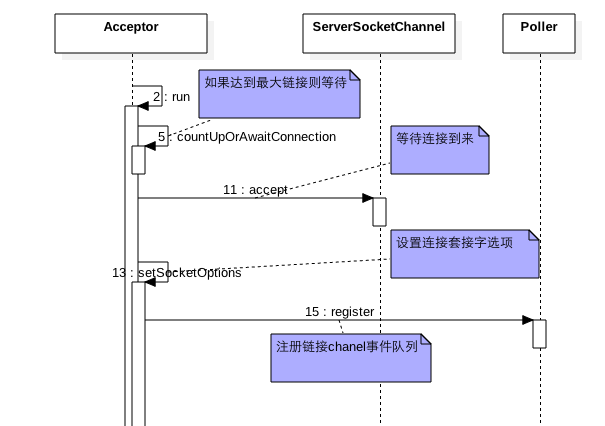
看下代码:
protected class Acceptor extends AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor {
@Override
public void run() {
int errorDelay = 0;
// 一直循环直到接收到shutdown命令
while (running) {
...
if (!running) {
break;
}
state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
try {
//如果达到max connections个请求则等待
countUpOrAwaitConnection();
SocketChannel socket = null;
try {
// 从TCP缓存获取一个完成三次握手的套接字,没有则阻塞
// socket
socket = serverSock.accept();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
...
}
// Successful accept, reset the error delay
errorDelay = 0;
if (running && !paused) {
if (!setSocketOptions(socket)) {
countDownConnection();
closeSocket(socket);
}
} else {
countDownConnection();
closeSocket(socket);
}
....
} catch (SocketTimeoutException sx) {
// Ignore: Normal condition
....
}
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
}
}
protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) {
// Process the connection
try {
//disable blocking, APR style, we are gonna be polling it
...
getPoller0().register(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
return false;
}
return true;
}
public void register(final NioChannel socket) {
...
addEvent(r);
}
public void addEvent(Runnable event) {
events.offer(event);
...
}
10.2 Poll线程
poll线程作用是从事件队列里面获取事件把链接套接字加入selector,并且监听socket事件进行处理。
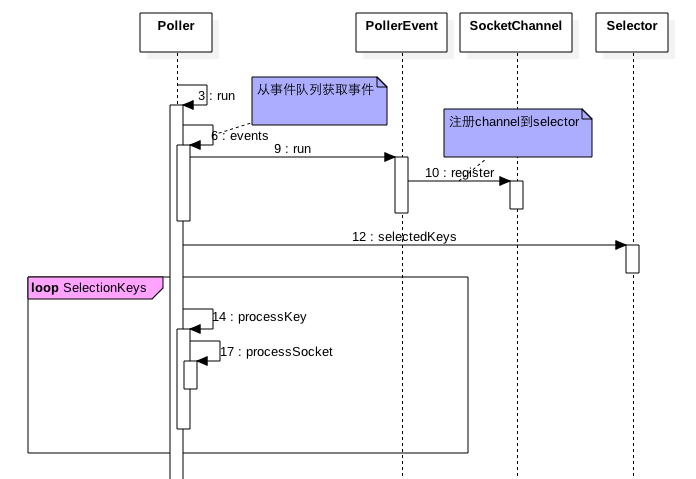
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
...
if (close) {
...
} else {
hasEvents = events();
}
try {
...
} catch ( NullPointerException x ) {...
}
Iterator
iterator =
keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null;
// 遍历所有注册的channel对感兴趣的事件处理
while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
KeyAttachment attachment = (KeyAttachment)sk.attachment();
if (attachment == null) {
iterator.remove();
} else {
attachment.access();
iterator.remove();
processKey(sk, attachment);
}
}//while
//process timeouts
timeout(keyCount,hasEvents);
if ( oomParachute > 0 && oomParachuteData == null ) checkParachute();
} catch (OutOfMemoryError oom) {
...
}
}//while
synchronized (this) {
this.notifyAll();















