
简介
在本教程中,我们将对来自10X和snATAC-seq技术产生的成年小鼠大脑的单细胞ATAC-seq测序数据进行整合分析。该示例的所有数据可以从以下链接进行下载:http://renlab.sdsc.edu/r3fang/share/github/Mouse_Brain_10X_snATAC/
分析流程
-
Step 0. Download data
-
Step 1. Create snap object
-
Step 2. Select barcode
-
Step 3. Add cell-by-bin matrix
-
Step 4. Combine snap objects
-
Step 5. Filter bins
-
Step 6. Dimensionality reduction
-
Step 7. Determine significant components
-
Step 8. Remove batch effect
-
Step 9. Graph-based cluster
-
Step 10. Visualization
Step 0. Download data
# 下载所需的数据集
$ wget http:
//renlab.sdsc.edu/r3fang/share/github/Mouse_Brain_10X_snATAC/CEMBA180305_2B.snap
$ wget http:
//renlab.sdsc.edu/r3fang/share/github/Mouse_Brain_10X_snATAC/CEMBA180305_2B.barcode.txt
$ wget http:
//renlab.sdsc.edu/r3fang/share/github/Mouse_Brain_10X_snATAC/atac_v1_adult_brain_fresh_5k.snap
$ wget http:
//renlab.sdsc.edu/r3fang/share/github/Mouse_Brain_10X_snATAC/atac_v1_adult_brain_fresh_5k.barcode.txt
Step 1. Create snap object
首先,我们将所用的两个数据集读取到snap对象列表中。
#
加载SnapATAC包
>
library(SnapATAC);
>
file.list = c(
"CEMBA180305_2B.snap"
,
"atac_v1_adult_brain_fresh_5k.snap"
);
>
sample.list = c(
"snATAC"
,
"10X"
);
#
读取snap文件
>
x.sp.ls = lapply(seq(file.list),
function
(i){
x.sp = createSnap(file=file.list[i], sample=sample.list[i]);
x.sp
})
>
names(x.sp.ls) = sample.list;
#
查看snap文件信息
>
x.sp.ls
#
# $snATAC
#
# number of barcodes: 15136
#
# number of bins: 0
#
# number of genes: 0
#
# number of peaks: 0
#
# number of motifs: 0
#
#
#
# $`10X`
#
# number of barcodes: 20000
#
# number of bins: 0
#
# number of genes: 0
#
# number of peaks: 0
#
# number of motifs: 0
Step 2. Select barcode
接下来,我们将读取这两个数据集的barcode信息,并选择高质量的barcodes。
>
barcode.file.list = c(
"CEMBA180305_2B.barcode.txt"
,
"atac_v1_adult_brain_fresh_5k.barcode.txt"
);
#
读取barcode信息
>
barcode.list = lapply(barcode.file.list,
function
(file){
read.table(file)[,1];
})
>
x.sp.list = lapply(seq(x.sp.ls),
function
(i){
x.sp = x.sp.ls[[i]];
x.sp = x.sp[x.sp@barcode %in% barcode.list[[i]],];
})
>
names(x.sp.list) = sample.list;
>
x.sp.list
#
# $snATAC
#
# number of barcodes: 9646
#
# number of bins: 0
#
# number of genes: 0
#
# number of peaks: 0
#
# number of motifs: 0
#
#
#
# $`10X`
#
# number of barcodes: 4100
#
# number of bins: 0
#
# number of genes: 0
#
# number of peaks: 0
#
# number of motifs: 0
Step 3. Add cell-by-bin matrix
#
使用addBmatToSnap函数计算cell-by-bin计数矩阵并添加到snap对象中
>
x.sp.list = lapply(seq(x.sp.list),
function
(i){
x.sp = addBmatToSnap(x.sp.list[[i]], bin.size=5000);
x.sp
})
>
x.sp.list
#
# $snATAC
#
# number of barcodes: 9646
#
# number of bins: 545118
#
# number of genes: 0
#
# number of peaks: 0
#
# number of motifs: 0
#
#
#
# $`10X`
#
# number of barcodes: 4100
#
# number of bins: 546206
#
# number of genes: 0
#
# number of peaks: 0
#
# number of motifs: 0
可以看到,这两个snap对象中含有不同数目的bins,这是因为这两个数据集使用的参考基因组有细微的差异。
Step 4. Combine snap objects
接下来,我们将这个数据集进行合并。
To combine these two snap objects, common bins are selected.
#
选择两个数据集共有的bins
>
bin.shared = Reduce(intersect, lapply(x.sp.list,
function
(x.sp) x.sp@feature
$name
));
>
x.sp.list function
(x.sp){
idy = match(bin.shared, x.sp@feature$name);
x.sp[,idy, mat="bmat"];
})
#
合并两个数据集
>
x.sp = Reduce(snapRbind, x.sp.list);
>
rm(x.sp.list);
# free memory
>
gc();
>
table(x.sp@sample);
#
# 10X snATAC
#
# 4100 9646
Step 5. Binarize matrix
#
使用makeBinary函数将计数矩阵转换为二进制矩阵
>
x.sp = makeBinary(x.sp, mat=
"bmat"
);
Step 6. Filter bins
首先,我们将与ENCODE中blacklist区域重叠的bins进行过滤,以防止潜在的artifacts。
>
system(
"wget http://mitra.stanford.edu/kundaje/akundaje/release/blacklists/mm10-mouse/mm10.blacklist.bed.gz"
);
>
library(GenomicRanges);
>
black_list = read.table(
"mm10.blacklist.bed.gz"
);
>
black_list.gr = GRanges(
black_list[,1],
IRanges(black_list[,2], black_list[,3])
);
>
idy = queryHits(findOverlaps(x.sp@feature, black_list.gr));
>
if
(length(idy) > 0){x.sp = x.sp[,-idy, mat=
"bmat"
]};
>
x.sp
#
# number of barcodes: 13746
#
# number of bins: 545015
#
# number of genes: 0
#
# number of peaks: 0
#
# number of motifs: 0
接下来,我们将过滤掉那些不需要的染色体信息。
>
chr.exclude = seqlevels(x.sp@feature)[grep(
"random|chrM"
, seqlevels(x.sp@feature))];
>
idy = grep(paste(chr.exclude, collapse=
"|"
), x.sp@feature);
>
if
(length(idy) > 0){x.sp = x.sp[,-idy, mat=
"bmat"
]};
>
x.sp
#
# number of barcodes: 13746
#
# number of bins: 545011
#
# number of genes: 0
#
# number of peaks: 0
#
# number of motifs: 0
第三,bins的覆盖率大致是服从对数正态分布的。我们将与不变特征(如管家基因的启动子)重叠的前5%的bins进行删除 。
>
bin.cov = log10(Matrix::colSums(x.sp@bmat)+1);
>
bin.cutoff = quantile(bin.cov[bin.cov > 0], 0.95);
>
idy =
which
(bin.cov <= bin.cutoff="" bin.cov=""> 0);
>
x.sp = x.sp[, idy, mat=
"bmat"
];
>
x.sp
#
# number of barcodes: 13746
#
# number of bins: 479127
#
# number of genes: 0
#
# number of peaks: 0
#
# number of motifs: 0
Step 7. Reduce dimensionality
我们使用diffusion maps的方法来计算landmark diffusion maps进行数据降维。首先,我们随机选择出10,000个细胞作为landmarks,然后将剩余的query细胞映射到diffusion maps embedding中。
>
row.covs = log10(Matrix::rowSums(x.sp@bmat)+1);
>
row.covs.dens = density(
x = row.covs,
bw = 'nrd', adjust = 1
);
>
sampling_prob = 1 / (approx(x = row.covs.dens
$x
, y = row.covs.dens
$y
, xout = row.covs)
$y
+ .Machine
$double
.eps);
>
set.seed(1);
>
idx.landmark.ds = sort(sample(x = seq(nrow(x.sp)), size = 10000, prob = sampling_prob));
>
x.landmark.sp = x.sp[idx.landmark.ds,];
>
x.query.sp = x.sp[-idx.landmark.ds,];
>
x.landmark.sp = runDiffusionMaps(
obj= x.landmark.sp,
input.mat="bmat",
num.eigs=50
);
>
x.query.sp = runDiffusionMapsExtension(
obj1=x.landmark.sp,
obj2=x.query.sp,
input.mat="bmat"
);
>
x.landmark.sp@metaData
$landmark
= 1;
>
x.query.sp@metaData
$landmark
= 0;
>
x.sp = snapRbind(x.landmark.sp, x.query.sp);
#
# combine landmarks and query cells;
>
x.sp = x.sp[order(x.sp@sample),];
# IMPORTANT
>
rm(x.landmark.sp, x.query.sp);
# free memory
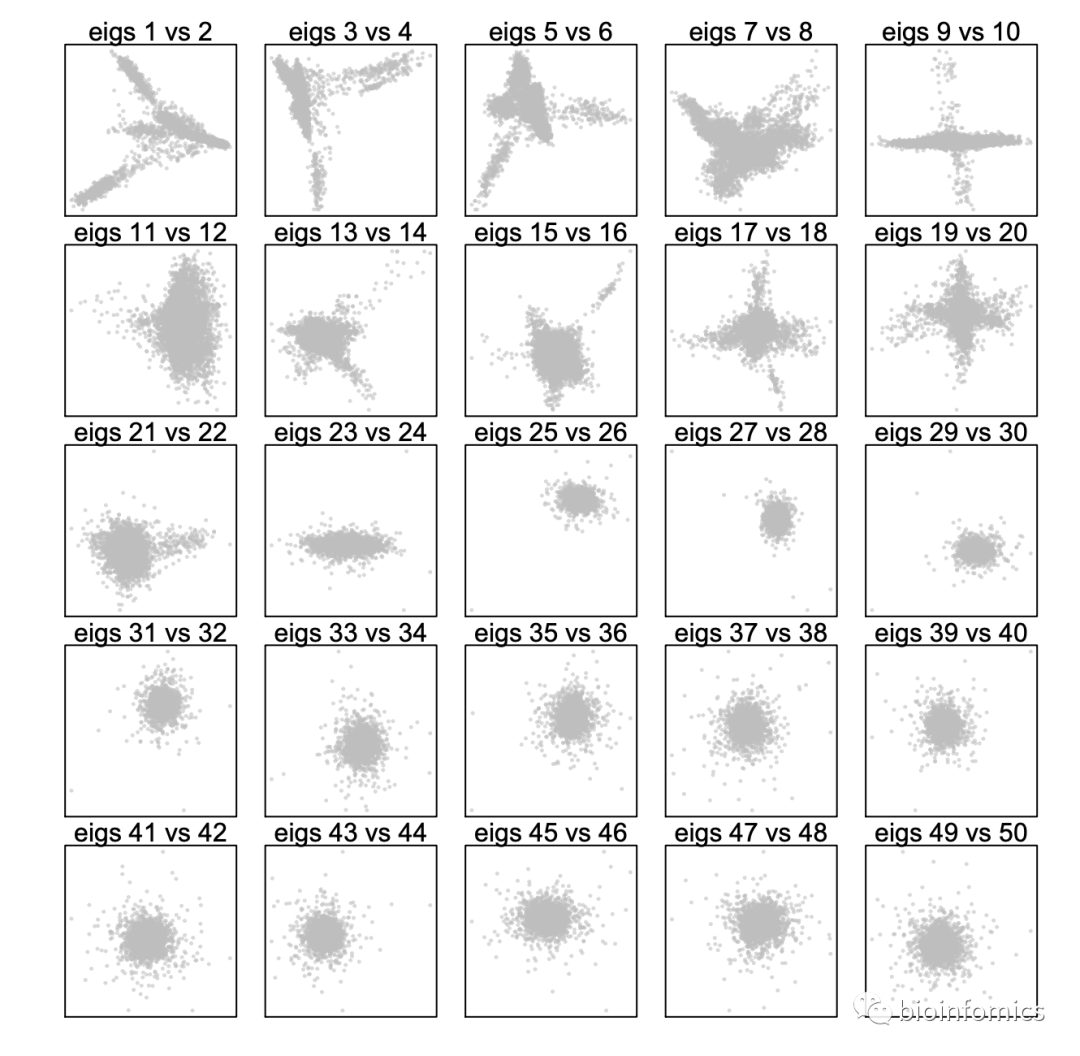
Step 8. Determine significant components
> plotDimReductPW(
obj=x.sp,
eigs.dims=
1
:
50
,
point.size=
0.3
,
point.color=
"grey"
,
point.shape=
19
,
point.alpha=
0.6
,
down.sample=
5000
,
pdf.file.name=
NULL
,
pdf.height=
7
,
pdf.width=
7
);

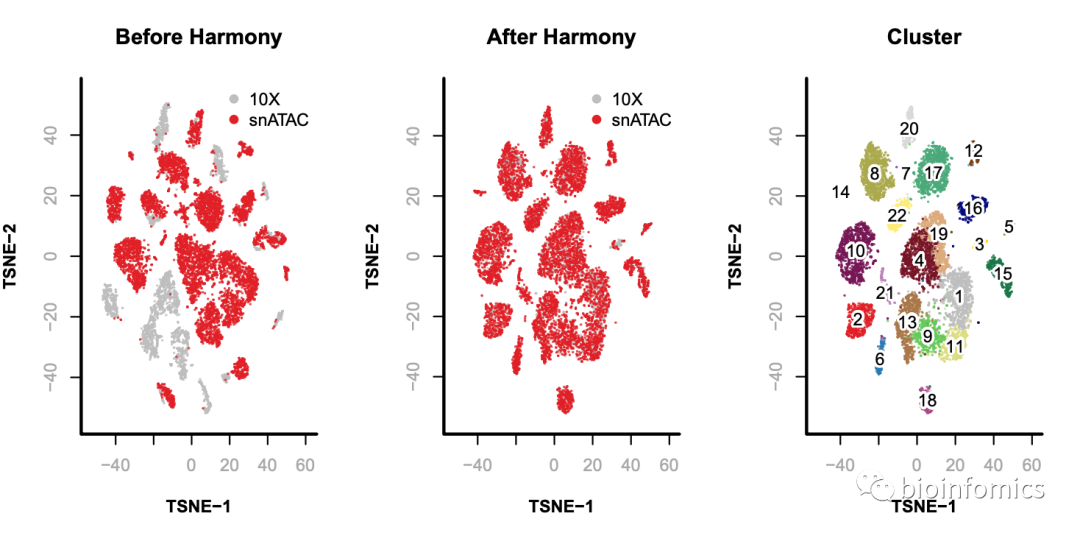
Step 9. Remove batch effect
> library(harmony);
# 使用runHarmony函数进行批次校正
> x.after.sp = runHarmony(
obj=x.sp,
eigs.dims=
1










