Miguel Comesaña 及其同事在最新的论文中介绍了一种利用光催化降解处理污水的可能方案。该论文刊登在 J. Phys. D 的电磁活性纳米粒子的生物学应用特刊中(论文信息见文末)。
撰文 Dean Williams
翻译 许雅澜
审校 卓思琪
从现代工业化开始至今,人类活动对水质产生了巨大影响,导致全球水生态系统的污染和恶化。在众多污染物中,源自农业和纺织业的多环芳香类分子因其存在致癌可能,尤为臭名昭著。如今,各方正努力减少水污染对环境和公众健康带来的负面影响。
为此,研究者将目光投向了纳米复合材料,欲使它能利用可持续能源——阳光来降解水中的污染物,并在复杂的环境中(比如在污水处理厂的角角落落)选择性地作用于特定的污染物。沿着这一思路,
研究者制备了由两种材料组合而成的杂化纳米结构。其中一种材料为半导体,它能在紫外照射下催化降解水体污染物;另一种是光敏剂,它能帮助半导体材料在更宽的光谱范围内保持光催化活性。
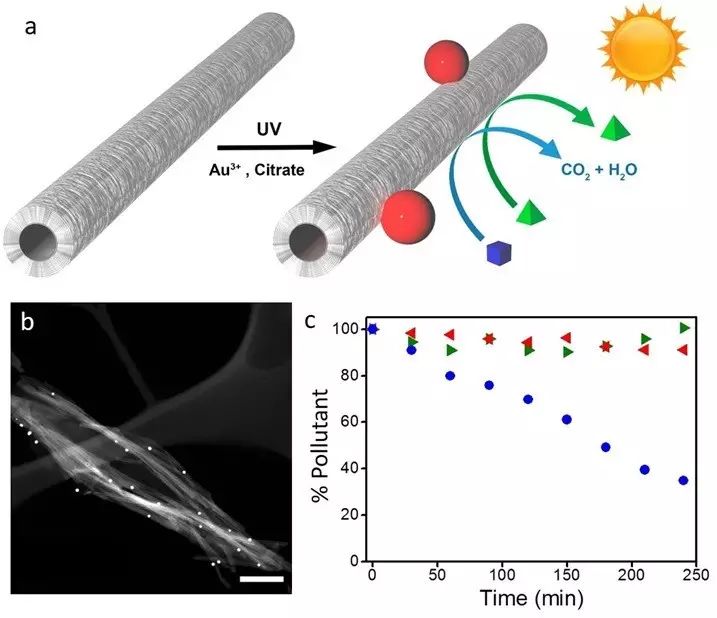
a.该材料的合成和光催化机理图示;b.杂化纳米材料的电子显微镜表征;c.多环芳香类污染物的选择性光催化降解(图片来源:论文原文)
确切地说,这种杂化复合材料为饰有纳米金粒子(等离子态)的钛酸钠纳米管,它结合了钛酸钠纳米管的选择性光催化性能与纳米金粒子吸收可见光和近红外光的能力。研究结果表明,这种组合很有潜力发展成为一项具有选择性的环境修复技术。
文章来源
https://jphysplus.iop.org/2017/03/23/cleaning-up-water-pollution-using-light/
论文信息
【题目】Au-decorated sodium titanate nanotubes as high-performance selective photocatalysts for pollutant degradation
【作者】Waleed M A El Rouby, Miguel Comesaña-Hermo, Martín Testa-Anta, Enrique Carbó-Argibay, Verónica Salgueiriño, Moisés Pérez-Lorenzo and Miguel A Correa-Duarte
【刊期】Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, Volume 50, Number 14
【日期】Published 8 March 2017
【摘要】The bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic compounds originating from textile processing industries is nowadays a major environmental problem worldwide. In order to tackle this situation, several inorganic semiconductors have been tested as photocatalysts for the degradation of these harmful pollutants in the search of sustainable and cost-effective solutions. Nevertheless, these semiconductor materials often involve important limitations, such as poor efficiency and selectivity, which, in the end, substantially restrict their implementation at the industrial scale. As an alternative, we herein report the fabrication and application of Au-decorated titanate nanotubes (TNTs) as high-performance architectures for the selective degradation of organic contaminants. This synthetic strategy is intended to establish a synergetic integration of the physicochemical and photocatalytic features of these hybrid nanostructures, by combining the remarkable adsorption capabilities of TNTs with the enhanced light-harvesting efficiency provided by the incorporation of a noble metal component. The obtained results evidence the great potential that rationally designed plasmonic composites may have for the development of selective environmental remediation technologies and in particular on the current challenges faced by the wastewater treatment sector.
【链接】
http://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1361-6463/aa604c

阅读更多
内容合作请联系
[email protected]






