Sails.js是一个可伸缩的、数据驱动的、面向服务的现代App架构。它致力于构建基于Node.js服务的定制化企业级应用。在Sails.js之前,构建一个实用的产品级Node.js应用的时间成本通常以月为单位计算。但是使用Sails.js后,只需要数周,便可以完成这一切。下面我们一步一步的建立一个基于Sails.js的示例App
环境搭建
打开一个命令行窗口,依次执行下列的命令
-
安装Node.js:https://nodejs.org/en/
-
安装Sails.js:
npm install sails -g
-
新建一个Sails.js的App
sails new test-project
然后你会看到
info: Created a new Sails app `test-project`!
意味着你已经成功创建了一个Sails.js的应用
-
执行
cd test-project
sails lift
然后你就可以打开浏览器访问localhost:1337,看到Sails.js的欢迎界面
应用结构
Sails应用的结构与一般的node.js应用目录一致,比较特殊的目录如下:
-
api
-
assets
-
config
-
tasks
-
views
api目录实现了一整套的MVC模式的后台接口。
assets目录存放项目所有的静态资源,包括图片,js文件,样式文件,前端模板文件等
config目录存放项目的配置文件,包括项目构建时的环境变量,部署时的语言版本,以及一些session和路由相关的配置
tasks目录存放项目构建时的各种任务,比如打包js文件;监听项目文件的热部署;注入静态资源等。
views目录存放项目的所有界面
重要概念
Middleware(中间件)
中间件概念是node.js应用的一个重要特点。Sails.js使用了一个额外的可配置的中间件栈,这样当服务器收到一个http的请求时,配置好的中间件栈为为这个请求依次执行。
中间件定义在
config/http.js
:
// ...
middleware: {
// Define a custom HTTP middleware fn with the key " foobar="foobar" foobar:="foobar:" function="function" req="req" next="next" define="define" another="another" couple="couple" of="of" custom="custom" http="http" middleware="middleware" fns="fns" with="with" keys="keys" passportinit="passportinit" and="and" passportsession="passportsession" notice="notice" that="that" this="this" time="time" we="we" using="using" an="an" existing="existing" library="library" from="from" npm="npm" require="require" override="override" the="the" conventional="conventional" cookie="cookie" parser:="parser:" cookieparser:="cookieparser:" res="res" now="now" configure="configure" order="order" our="our" order:="order:" startrequesttimer="startrequesttimer" cookieparser="cookieparser" session="session" amp="===" passport="passport" should="should" run="run" after="after" quot="quot" see="see" https:="https:" bodyparser="bodyparser" compress="compress" can="can" put="put" stuff="stuff" wherever="wherever" want="want" methodoverride="methodoverride" poweredby="poweredby" router="router" www="www" favicon="favicon" custommiddleware:="custommiddleware:" intended="intended" for="for" other="other" doesn="doesn" follow="follow" app="app" convention="convention" code="#" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
middleware: {
foobar: function (req,res,next) { next(); },
passportInit : require('passport').initialize(),
passportSession : require('passport').session(),
cookieParser: function (req, res, next) { next(); },
order: [ 'startRequestTimer', 'cookieParser', 'session', 'passportInit',
'passportSession',
'bodyParser', 'compress', 'foobar',
'methodOverride', 'poweredBy', '$custom', 'router', 'www', 'favicon', '404', '500'
]
},
customMiddleware: function(app){
require('other-middleware').initialize(app);
}
Models and ORM
Sails.js默认安装Waterline,这是一个强大的SQL/noSQL的数据映射引擎(ORM/ODM)。Waterline在数据库之上抽象了一个操作层,可以屏蔽掉底层的数据库操作,显著的简化一个或者多个数据库的交互。
比如使用了表结构的Oracle和Mysql;使用了集合概念的MongoDB;使用了key/value键值对的Redis。它们都有自己的一套操作语言,如果你的项目需要在这几中数据库之间迁移,或者你需要使用多个数据库,那你需要针对不同的数据库编写不同的操作语句,极大的浪费了资源。
你需要做的仅仅是在config/connecttions.js中配置:
// ...
connections:{
local_mysql:{ //arbitrary name
module: 'sails-mysql',
user: 'root',
password: 'root',
url: 'mysql://root:root@localhost:3306/sailstest1'
}
}
// ...
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
connections:{
local_mysql:{
module
:
'sails-mysql'
,
user:
'root'
,
password:
'root'
,
url:
'mysql://root:root@localhost:3306/sailstest1'
}
}
Sessions
在Sails.js中,sessions是用来在不同请求之间存储客户端信息的。由于http协议是无状态的协议,所以无法保持客户端的状态.通过sessions,我们可以通过请求中的特定参数,确定是否是来自于统一个客户端的请求,从而达到客户端状态保持效果。
Sails.js的sessions主要由三个组件实现:
-
session存储,可以是默认的Sails session store,或者数据库。
-
session管理,Sails.js通过中间件管理session。
-
请求中的cookie,Sails.js在每次前端发送请求时,都会在cookie添加一个特别的标志位(默认是sails.sid)。
在api/controller下,我们可以新建一个js如下:
module.exports = {
login: function(req, res) {
// Authentication code here
// If successfully authenticated
req.session.userId = foundUser.id; // returned from a database
return res.json(foundUser);
}
}
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
module
.exports = {
login:
function
(req, res)
{
req.session.userId = foundUser.id;
return
res.json(foundUser);
}
}
它只包含一个login的action方法,如上所示,我们在Sails.js中,我们可以直接通过request访问当前客户端的session。
Policies
Sails.js通过policies来实现认证和访问控制相关功能。你可以在api/policies中,配置如下:
// policies/canWrite.js
module.exports = function canWrite (req, res, next) {
var targetFolderId = req.param('id');
// If the requesting user is not logged in, then they are _never_ allowed to write.
// No reason to continue-- we can go ahead and bail out now.
if (!req.session.me) {
return res.redirect('/login');
}
// Check the database to see if a permission record exists which matches both the
// target folder id, the appropriate "type", and the id of the logged-in user.
Permission.findOne({
folder: targetFolderId,
user: req.session.me,
type: 'write'
})
.exec(function (err, permission) {
// Unexpected error occurred-- use the app's default error (500) handler.
//
// > We do this because this should never happen, and if it does, it means there
// > is probably something wrong with our database, and we want to know about it!)
if (err) { return res.serverError(err); }
// No "write" permission record exists linking this user to this folder.
// Maybe they got removed from it? Or maybe they never had permission in the first place...
if (!permission) {
return res.redirect('/login');
}
// If we made it all the way down here, looks like everything's ok, so we'll let the user through.
// (from here, the next policy or the controller action will run)
return next();
});
};
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
module
.exports =
function
canWrite
(req, res, next)
{
var
targetFolderId = req.param(
'id'
);
if
(!req.session.me) {
return
res.redirect(
'/login'
);
}
Permission.findOne({
folder: targetFolderId,
user: req.session.me,
type:
'write'
})
.exec(
function
(err, permission)
{
if
(err) {
return
res.serverError(err); }
if
(!permission) {
return
res.redirect(
'/login'
);
}
return
next();
});
};
接口示例
现在,我们要实际测试一下Sails.js整个数据流程。
1. UserController
我们在api/controllers目录下新建UserController.js文件,如下:
/**
* UserController
*
* @description :: Server-side logic for managing users
* @help :: See http://sailsjs.com/documentation/concepts/Controllers
*/
module.exports = {
};
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
module
.exports = {
};
2. User
我们在api/models目录下新建User.js如下:
/**
* User.js
*
* @description :: TODO: You might write a short summary of how this model works and what it represents here.
* @docs :: http://sailsjs.org/documentation/concepts/models-and-orm/models
*/
module.exports = {
attributes: {
name: {type: "string"},
age: {type: "integer"}
}
};
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
module
.exports = {
attributes: {
name: {type:
"string"
},
age: {type:
"integer"
}
}
};
3. 测试
首先,我们访问一下
http://localhost:1337/user
[]
/user接口,表示获取当前用户列表。
然后,我们访问一下
http://localhost:1337/user/create?name=abby&age=24
{
“name”: “abby”,
“age”: 24,
“createdAt”: “2017-10-16T10:16:51.154Z”,
“updatedAt”: “2017-10-16T10:16:51.154Z”,
“id”: 2
}
可以看到已经创建了一个名叫abby的用户
这个时候我们在创建一个用户
:http://localhost:1337/user/create?name=connor&age=28
然后访问
http://localhost:1337/user
[
{
“createdAt”: “2017-10-16T10:14:55.028Z”,
“updatedAt”: “2017-10-16T10:16:31.173Z”,
“id”: 1,
“name”: “connor”,
“age”: 28
},
{
“name”: “abby”,
“age”: 24,
“createdAt”: “2017-10-16T10:16:51.154Z”,
“updatedAt”: “2017-10-16T10:16:51.154Z”,
“id”: 2
}
]
接着,我们修改connor用户
:http://localhost:1337/user/update/1?name=connor123&age=30
然后查看用户列表
http://localhost:1337/user:
[
{
“createdAt”: “2017-10-16T10:14:55.028Z”,
“updatedAt”: “2017-10-16T10:20:28.337Z”,
“id”: 1,
“name”: “connor123”,
“age”: 30
},
{
“name”: “abby”,
“age”: 24,
“createdAt”: “2017-10-16T10:16:51.154Z”,
“updatedAt”: “2017-10-16T10:16:51.154Z”,
“id”: 2
}
]
最后我们删除abby用户
http://localhost:1337/user/destroy/2
[
{
“createdAt”: “2017-10-16T10:14:55.028Z”,
“updatedAt”: “2017-10-16T10:20:28.337Z”,
“id”: 1,
“name”: “connor123”,
“age”: 30
}
]
可以看到,当我们创建一个User的controller和model的时候,Sails.js自动为我们实现关于这个user的增删改查接口,这在很多时候可以节省很多的开发时间。
服务端界面渲染
很多时候,我们需要服务端直接渲染好界面返回前端,而不是返回一些数据。下面我们一步一步实现服务端的渲染
1. 配置路由
// config/routes.js
module.exports.routes = {
'/': {
view: 'homepage'
},
'get /renderUser': 'UserController.renderUser'
}
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
module
.exports.routes = {
'/'
: {
view:
'homepage'
},
'get /renderUser'
:
'UserController.renderUser'
}
2. 修改UserController.js
// api/UserController.js
module.exports = {
renderUser: function(req, res) {
var params = _.extend(req.query || {}, req.params || {}, req.body || {});
var id = params.id;
User.findAll().exec(function(err, users){
res.view('manage/renderUser', {users: users});
});
}
}
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
module
.exports = {
renderUser:
function
(req, res)
{
var
params = _.extend(req.query || {}, req.params || {}, req.body || {});
var
id = params.id;
User.findAll().exec(
function
(err, users)
{
res.view(
'manage/renderUser'
, {users: users});
});
}
}
3. 用户列表界面
<%for (var i = 0; i < users.length; i++) {%>
<%}%>
| 姓名 |
年龄 |
|
<%=users[i].name%>
|
<%=users[i].age%>
|
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
然后我们访问:
http://localhost:1337/renderUser:
姓名 年龄
connor 28
访问控制
目前来说,访问控制通常是根据用户请求时的cookie中的某个标志位来校验。这里我们简单实现一下拦截用户请求,校验后返回对应的结果。修改代码如下:
// api/policies/sessionAuth.js
module.exports = function(req, res, next) {
// User is allowed, proceed to the next policy,
// or if this is the last policy, the controller
if (req.cookies.authenticated === '1') {
return next();
}
// User is not allowed
// (default res.forbidden() behavior can be overridden in " config="config" return="return" res="res" are="are" not="not" permitted="permitted" to="to" perform="perform" this="this" action="#" code="#" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">module.exports = function(req, res, next) {
if (req.cookies.authenticated === '1') { return next();
}
return res.forbidden('You are not permitted to perform this action.');
};
module.exports.policies = {
// config/policies.js
'*': true,
'UserController': {
'*': false,
'renderUser': 'sessionAuth'
}
}
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
module
.exports.policies = {
'*'
:
true
,
'UserController'
: {
'*'
:
false
,
'renderUser'
:
'sessionAuth'
}
}
可以看到我们取request带有cookies里面的authenticated属性,如果属性为
1
,那么可以访问网站,否则抛出错误。然后,我们访问http://localhost:1337/renderUser:网站会抛出一个403(Forbidden)错误。这个时候,我们在cookie中加入authenticated = 1,如下:
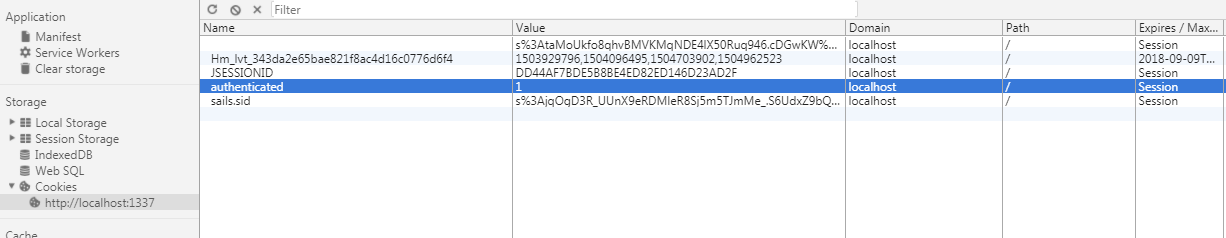
然后再访问http://localhost:1337/renderUser,可以发现已经可以正常访问了。
数据库的配置
以上,我们完成了一个网站从前端到后台的业务层面的相关代码。但是我们还有一个很重要的地方没有涉及,那就是我们的数据库。我们先看看Sails.js默认的数据存储:
// config/connections.js
module.exports.connections = {
localDiskDb: {
adapter: 'sails-disk'
}
}
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
module
.exports.connections = {
localDiskDb: {
adapter:
'sails-disk'
}
}
这里的sails-disk是sails默认的存放数据的方式,我们可以在项目根目录的
.temp/localDiskDb.db
文件中看到:
{
"data": {
"user": [
{
"name": "connor",
"age": 28,
"createdAt": "2017-10-17T05:48:47.682Z",
"updatedAt": "2017-10-17T05:48:47.682Z",
"id": 11
}
]
},
"schema": {
"user": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"id": {
"type": "integer",
"autoIncrement": true,
"primaryKey": true,
"unique": true
},
"createdAt": {
"type": "datetime"
},
"updatedAt": {
"type": "datetime"
}
}
},
"counters": {
"user": {
"id": 11
}
}
}
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">{
"
data
":
{
"
user
":
[
{
"
name
":
"connor"
,
"
age
":
28
,
"
createdAt
":
"2017-10-17T05:48:47.682Z"
,
"
updatedAt
":
"2017-10-17T05:48:47.682Z"
,
"
id
":
11
}
]
}
,
"
schema
":
{
"
user
":
{
"
name
":
{
"
type
":
"string"
}
,
"
age
":
{
"
type
":
"integer"
}
,
"
id
":
{
"
type
":
"integer"
,
"
autoIncrement
":
true
,
"
primaryKey
":
true
,
"
unique
":
true
}
,
"
createdAt
":
{
"
type
":
"datetime"
}
,
"
updatedAt
":
{
"
type
":
"datetime"
}
}
}
,
"
counters
":
{
"
user
":
{
"
id
":
11
}
}
}
可以看到,我们之前定义的user的表,以及一条connor的用户数据。但是,在真实的产品级服务中,我们不可能使用这种方式来存储数据,下面我们实现一个Sails.js把数据存储到mysql中的示例。
1. 安装Mysql
前往 mysql 下载地址,下载免费的Mysql社区版本,并且按照安装提示,安装好mysql。之后,建立一个测试用的sails-test数据库,并建一个user表:包含name和age两个属性。
2. Sails.js代码
// config/connections.js
module.exports.connections = {
someMysqlServer: {
adapter: 'sails-mysql',
host: '127.0.0.1',
user: 'root', //optional
password: '123456', //optional
database: 'sails_test' //optional
},
}
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
module
.exports.connections = {
someMysqlServer: {
adapter:
'sails-mysql'
,
host:
'127.0.0.1'
,
user:
'root'
,
password:
'123456'
,
database:
'sails_test'
},
}
// config/models.js
module.exports.models = {
connection: 'someMysqlServer',
migrate: 'alter'
};
" style="border-radius: 3px; overflow-wrap: break-word; border-width: 0px; border-style: none; border-color: currentcolor; -moz-border-top-colors: none; -moz-border-right-colors: none; -moz-border-bottom-colors: none; -moz-border-left-colors: none; padding: 0px 5px; margin: 0px; display: block; font-family: Consolas,Inconsolata,Courier,monospace; font-weight: 700; white-space: pre; font-size: 1em; letter-spacing: -1px; text-align: justify;">
module
.exports.models = {
connection:
'someMysqlServer'
,
migrate:
'alter'
};
然后,我们访问http://localhost:1337/user/create?name=abby&age=24创建一个abby用户。登录mysql,查看use表:
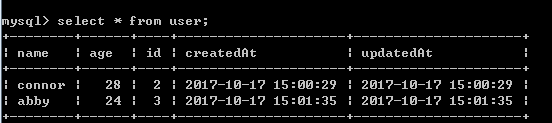
可以看到abby这条数据确实插入了mysql数据库中。
结语
至此,我们已经使用Sails.js完成了一整套的网站业务。可以发现,由于我们使用了Sails.js这个架构,给我们带来了极大的方便,各种基础业务:数据库链接、前端路由、后台渲染、访问控制等,都已经封装得比较完善。我们只需要关注业务逻辑,无需关心底层实现。当然,Sails.js在我写作这篇文章时已经是过时的架构,但是我们依然可以吸取这种全栈架构的思路,如果对全栈架构有兴趣,可以到meteor这个地方去看看最新最火的JavaScript全栈架构。






