转自:量化投资与机器学习公众号,ID:ZXL_LHTZ_JQXX
作者 | Jason Brownlee
编译 | 公众号编辑部
你应该使用哪种机器学习算法?
这是应用机器学习中的一个让大家很捉急的问题。
在Randal Olson和其他人最近的一篇论文中,他们试图去回答它,并给出一个指导关于算法和参数。
在这篇文章中,你将展开一项研究和评估
许多机器学习算法
通过大量的机器学习数据集。并且得到对这项研究的一些意见。
论文
2017年,Randal Olson等人发表了一篇标题为
“Data-driven Advice for Applying Machine Learning to Bioinformatics Problems”
的论文。
论文下载地址:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.05070
他们的工作目标是解决每个从业人员在开始预测建模问题时所面临的问题,即:
我应该使用什么算法?
作者将此问题描述为choice overload,如下所示:
Although having several readily-available ML algorithm implementations is advantageous to bioinformatics researchers seeking to move beyond simple statistics, many researchers experience “choice overload” and find difficulty in selecting the right ML algorithm for their problem at hand.
他们通过在
大量
机器学习数据集的样本上运行其算法样本来解决这个问题,以了解通常哪些算法和参数最适合。
论文描述为:
… a thorough analysis of 13 state-of-the-art, commonly used machine learning algorithms on a set of 165 publicly available classification problems in order to provide data-driven algorithm recommendations to current researchers
机器学习算法
A total of 13 different algorithms were chosen for the study.
Algorithms were chosen to provide a mix of types or underlying assumptions.The goal was to represent the most common classes of algorithms used in the literature, as well as recent state-of-the-art algorithms The complete list of algorithms is provided below.
下面提供了完整的13种算法列表:
-
Gaussian Naive Bayes (GNB)
-
Bernoulli Naive Bayes (BNB)
-
Multinomial Naive Bayes (MNB)
-
Logistic Regression (LR)
-
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
-
Passive Aggressive Classifier (PAC)
-
Support Vector Classifier (SVC)
-
K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN)
-
Decision Tree (DT)
-
Random Forest (RF)
-
Extra Trees Classifier (ERF)
-
AdaBoost (AB)
-
Gradient Tree Boosting (GTB)
scikit-learn库被用来实现这些算法。
每个算法具有零个或多个参数,并且针对每个算法执行合理参数值的网格搜索。
对于每种算法,使用固定的网格搜索来调整超参数。
下面列出了算法和超参数评估表:

使用10倍交叉验证和平衡准确性度量来评估算法。
交叉验证没有重复,可能会在结果中引入一些统计噪音。
机器学习数据集
研究选择了165种标准机器学习问题。
许多问题来自生物信息学领域,尽管并非所有数据集都属于这一研究领域。
所有的预测问题都是两类或更多类的分类问题。
The algorithms were compared on 165 supervised classification datasets from the Penn Machine Learning Benchmark (PMLB). […] PMLB is a collection of publicly available classification problems that have been standardized to the same format and collected in a central location with easy access via Python.
数据集来自Penn机器学习基准(PMLB)集合,你可以在GitHub项目中了解关于此数据集的更多信息。地址:
https://github.com/EpistasisLab/penn-ml-benchmarks
在拟合模型之前,所有数据集均已标准化。
结果分析
The entire experimental design consisted of over 5.5 million ML algorithm and parameter evaluations in total, resulting in a rich set of data that is analyzed from several viewpoints…
对每个数据集对算法性能进行排名,然后计算每个算法的平均排名。
这提供了一个粗略和容易理解每一种算法在平均情况下好或不好活的方法。
结果表明,
梯度提升
(Gradient boosting)和
随机森林
(random forest )的排名最低(
表现最好
),
朴素贝叶斯
(
Naive Bayes
)平均得分最高(
表现最差
)。
The post-hoc test underlines the impressive performance of Gradient Tree Boosting, which significantly outperforms every algorithm except Random Forest at the p < 0.01 level.
通过这张图,展示了所有算法的结果,摘自论文。
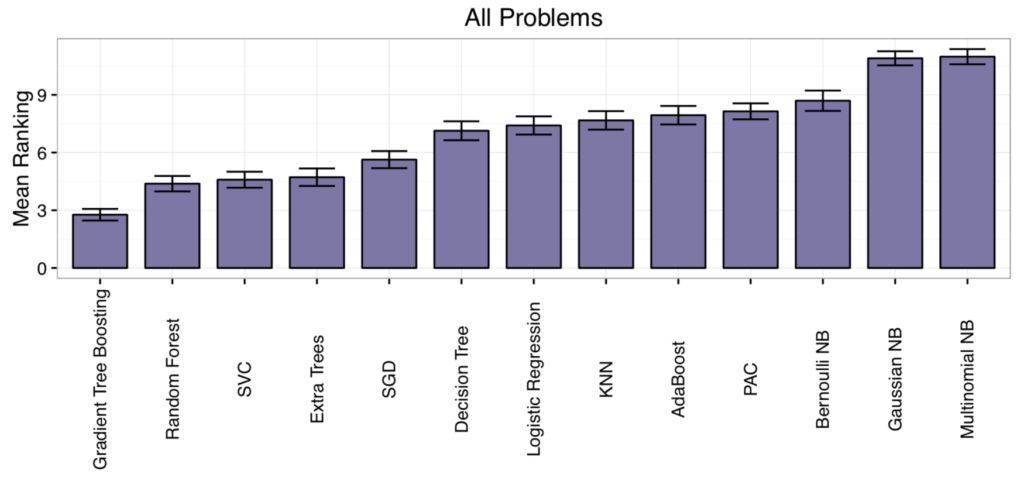
没有单一的算法表现最好或最差。
这是机器学习实践者所熟知的,但对于该领域的初学者来说很难掌握。
你必须在一个给定的数据集上测试一套算法,看看什么效果最好。
… it is worth noting that no one ML algorithm performs best across all 165 datasets. For example, there are 9 datasets for which Multinomial NB performs as well as or better than Gradient Tree Boosting, despite being the overall worst- and best-ranked algorithms, respectively. Therefore, it is still important to consider different ML algorithms when applying ML to new datasets.
此外,选择正确的算法是不够的。你还必须为数据集选择正确的算法配置。
选择正确的ML算法并调整其参数对于大多数问题是至关重要的。
结果发现,根据算法和数据集的不同,调整算法可将该方法的性能从提高至3%——50%。
The results demonstrate why it is unwise to use default ML algorithm hyperparameters: tuning often improves an algorithm’s accuracy by 3-5%, depending on the algorithm. In some cases, parameter tuning led to CV accuracy improvements of 50%.
本图表展示了参数调整对每种算法的改进情况。
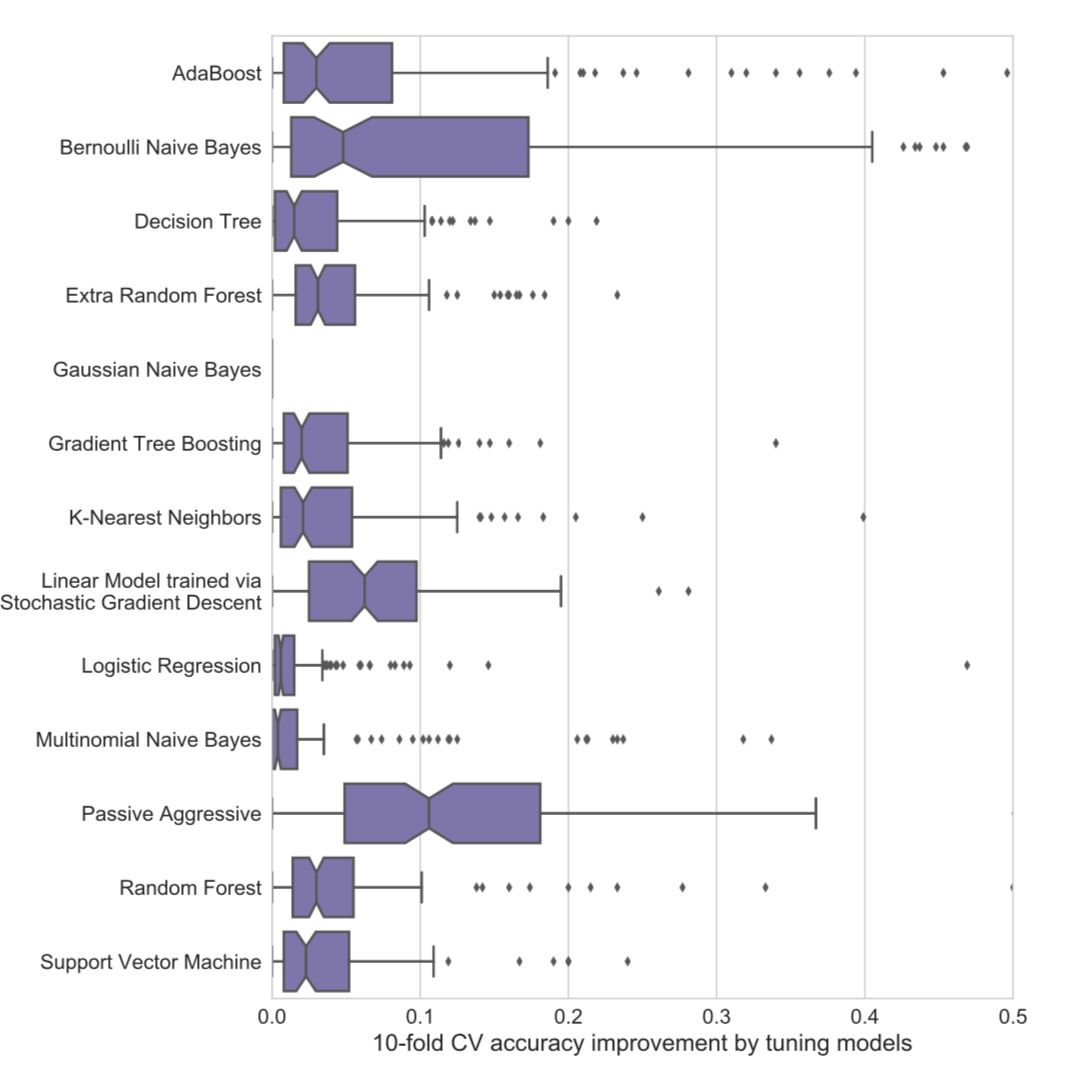
并非所有算法都是必需的。
结果发现,在165个测试数据集中的106个中,五种算法和特定参数的性能达到Top1%。
推荐这五种算法:















