(点击
上方蓝字
,快速关注我们)
作者:伯乐在线 - iPytLab
如有好文章投稿,请点击 → 这里了解详情
前言
本文对遗传算法中的几种选择策略进行了总结, 其中包括:
对于每种选择策略我都使用Python进行了相应的实现并以内置插件的形式整合进了本人所写的遗传算法框架GAFT中。对需要使用遗传算法优化问题以及学习遗传算法的童鞋可以作为参考.
项目链接:
遗传算法中的选择算子
遗传算法(genetic algorithms, GAs)是一种自适应的启发式搜索算法, 它模仿达尔文进化论中的“适者生存”的原则, 最终获取优化目标的最优解。下图描述了一个简单的遗传算法流程:
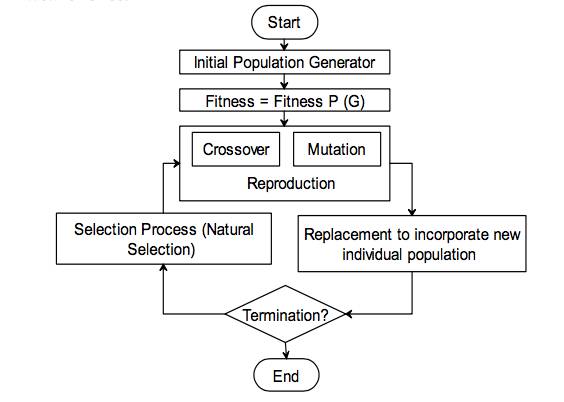
对于种群中需要进行杂交的物种选择方法有很多,而且选择一种合适的选择策略对于遗传算法整体性能的影响将是很大的。如果一个选择算法选择多样性降低,便会导致种群过早的收敛到局部最优点而不是我们想要的全局最优点,也就是所谓的”早熟”。而选择策略过于发散则会导致算法难以收敛到最优点。因此在这两点中我们需要进行平衡才能使遗传算法以一种高效的方式收敛到全局最优点。
GAFT框架中的算子插件
GAFT是我根据自己需求开发的一个遗传算法框架,相关介绍的博客可以参见《
GAFT-一个使用Python实现的遗传算法框架
》,《
使用MPI并行化遗传算法框架GAFT
》。该框架提供了插件接口,用户可以通过自定义算子以及on-the-fly分析插件来放到gaft框架中运行遗传算法流程对目标问题进行优化。
本部分我稍微介绍下gaft关于遗传算子相关接口规范,以及编写能用于gaft的算子的编写方法。
在gaft中遗传算子的编写都是需要继承框架内置的基类,然后根据基类提供的接口,实现自己的算子。其中基类的定义都在/gaft/plugin_interfaces/operators/目录下,下面我以选择算子为例,介绍下接口。
gaft中选择算子的基类为GASelection,其中在遗传算法流程中会调用该类实例的select方法,进而根据算子中的相关选择策略完成从种群中选取一对物种作为父亲和母亲产生子代。基类的定义为:
class
GASelection
(
metaclass
=
SelectionMeta
)
:
'''
Class for providing an interface to easily extend the behavior of selection
operation.
'''
def
select
(
self
,
population
,
fitness
)
:
'''
Called when we need to select parents from a population to later breeding.
:param population: The current population.
:type population: GAPopulation
:return parents: Two selected individuals for crossover.
:type parents: Tuple of tow GAIndividual objects.
'''
raise
NotImplementedError
select的方法的参数为当前种群population以及相应的适应度函数fitness,其中population需要是GAPopulation对象,fitness也必须是callable的对象。
当然,这些在Python这种动态类型语言中貌似看起来有些鸡肋,但是为了能够更加规范使用者,
我利用Python的元类在实例化类对象的时候对接口的实现以及接口的参数类型加以限制。
具体的实现都在/gaft/plugin_interfaces/metaclasses.py中,有兴趣的童鞋可以看看实现方法。
具体自定义算子的编写方法我将在下一部分同选择策略一起贴出来。
不同的选择策略
本部分我主要对四种不同的选择策略进行总结并加以gaft插件形式的Python实现。
选择算子决定了哪些个体将会从种群中被选择出来用于繁衍下一代种群中的新个体。其主要的原则就是:
the better is an individual; the higher is its chance of being a parent
选择算子在遗传算法迭代中将适应度函数引入进来,因为适应度函数式标定一个个体是否足够“好”的重要标准。但是选择过程又不能仅仅完全依赖于适应度函数,因为一个种群中的最优物种并不一定是在全局最优点附近。因此我们也应该给相对来说并那么“好”的个体一点机会让他们繁衍后代, 避免“早熟”。
选择算子在遗传算法迭代中将适应度函数引入进来,因为适应度函数式标定一个个体是否足够“好”的重要标准。但是选择过程又不能仅仅完全依赖于适应度函数,因为一个种群中的最优物种并不一定是在全局最优点附近。因此我们也应该给相对来说并那么“好”的个体一点机会让他们繁衍后代, 避免“早熟”。
Proportionate Roulette Wheel Selection
此轮盘赌选择策略,是最基本的选择策略之一,种群中的个体被选中的概率与个体相应的适应度函数的值成正比。我们需要将种群中所有个体的适应度值进行累加然后归一化,最终通过随机数对随机数落在的区域对应的个体进行选取,类似赌场里面的旋转的轮盘。
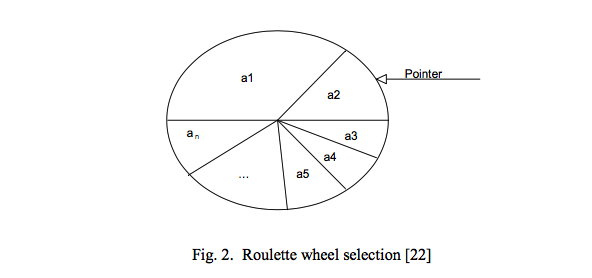
每个个体ai被选中的概率为:
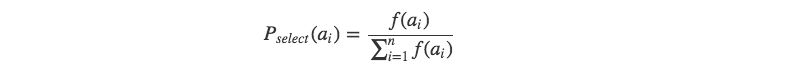
好了,下面可以将此算法写成一个可以gaft中执行的算子。
from
random
import
random
from
bisect
import
bisect_right
from
itertools
import
accumulate
from
...
plugin_interfaces
.
operators
.
selection
import
GASelection
class
RouletteWheelSelection
(
GASelection
)
:
def
__init__
(
self
)
:
'''
Selection operator with fitness proportionate selection(FPS) or
so-called roulette-wheel selection implementation.
'''
pass
def
select
(
self
,
population
,
fitness
)
:
'''
Select a pair of parent using FPS algorithm.
'''
# Normalize fitness values for all individuals.
fit
=
[
fitness
(
indv
)
for
indv
in
population
.
individuals
]
min_fit
=
min
(
fit
)
fit
=
[(
i
-
min_fit
)
for
i
in
fit
]
# Create roulette wheel.
sum_fit
=
sum
(
fit
)
wheel
=
list
(
accumulate
([
i
/
sum_fit
for
i
in
fit
]))
# Select a father and a mother.
father_idx
=
bisect_right
(
wheel
,
random
())
father
=
population
[
father_idx
]
mother_idx
=
(
father_idx
+
1
)
%
len
(
wheel
)
mother
=
population
[
mother_idx
]
return
father
,
mother
过程主要分为下面几个:
-
继承GASelection类
-
实现select方法
-
select的参数为GAPopulation实例和适应度函数
-
根据算法选择出两个需要繁衍的物种并返回即可
Tournament Selection
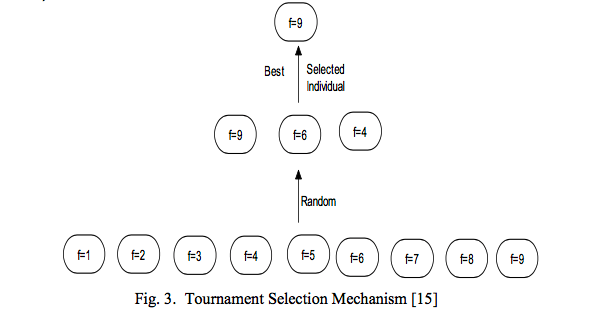
由于算法执行的效率以及易实现的的特点,锦标赛选择算法是遗传算法中最流行的选择策略。在本人的实际应用中的确此策略比基本的轮盘赌效果要好些。他的策略也很直观,就是我们再整个种群中抽取n个个体,让他们进行竞争(锦标赛),抽取其中的最优的个体。参加锦标赛的个体个数成为tournament size。通常当n=2便是最常使用的大小,也称作Binary Tournament Selection.
Tournament Selection的优势:
-
更小的复杂度O(n)
-
易并行化处理
-
不易陷入局部最优点
-
不需要对所有的适应度值进行排序处理
下图显示了n=3的Tournament Selection的过程:
可以开始写成自定义算子在gaft运行了:
from
random
import
sample
from
...
plugin_interfaces
.
operators
.
selection
import
GASelection
class
TournamentSelection
(
GASelection
)
:
def
__init__
(
self
,
tournament_size
=
2
)
:
'''
Selection operator using Tournament Strategy with tournament size equals
to two by default.
'''
self
.
tournament_size
=
tournament_size
def
select
(
self
,
population
,
fitness
)
:
'''
Select a pair of parent using Tournament strategy.
'''
# Competition function.
complete
=
lambda
competitors
:
max
(
competitors
,
key
=
fitness
)
# Check validity of tournament size.
if
self
.
tournament_size
>=
len
(
population
)
:
msg
=
'Tournament size({}) is larger than population size({})'
raise
ValueError
(
msg
.
format
(
self
.
tournament_size
,
len
(
population
)))
# Pick winners of two groups as parent.
competitors_1
=
sample
(
population
.
individuals
,
self
.
tournament_size
)
competitors_2
=
sample
(
population
.
individuals
,
self
.
tournament_size
)
father
,
mother
=
complete
(
competitors_1
),
complete
(
competitors_2
)
return
father
,
mother
Linear Ranking Selection
下面两个介绍的选择策略都是基于排序的选择策略,上面提到的第一种基本轮盘赌选择算法,有一个缺点,就是如果一个个体的适应度值为0的话,则被选中的概率将会是0, 这个个体将不能产生后代。于是我们需要一种基于排序的算法,来给每个个体安排相应的选中概率。
在Linear Ranking Selection中,种群中的个体首先根据适应度的值进行排序,然后给所有个体赋予一个序号,最好的个体为N, 被选中的概率为Pmax, 最差的个体序号为1, 被选中的概率为Pmin,于是其他的在他们中间的个体的概率便可以根据如下公式得到:
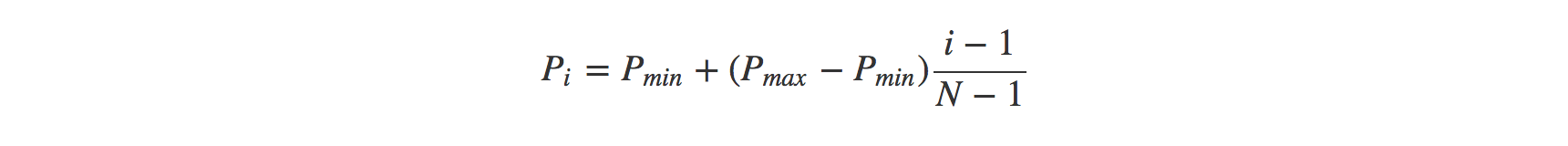
实现代码:
from
random
import
random
from
itertools
import
accumulate
from
bisect
import
bisect_right
from
...
plugin_interfaces
.
operators
.
selection
import
GASelection
class
LinearRankingSelection
(
GASelection
)
:
def
__init__
(
self
,
pmin
=
0.1
,
pmax
=
0.9
)
:
'''
Selection operator using Linear Ranking selection method.
Reference: Baker J E. Adaptive selection methods for genetic
algorithms[C]//Proceedings of an International Conference on Genetic
Algorithms and their applications. 1985: 101-111.
'''
# Selection probabilities for the worst and best individuals.
self
.
pmin
,
self
.
pmax
=
pmin
,
pmax
def
select
(
self
,
population
,
fitness
)
:
'''
Select a pair of parent individuals using linear ranking method.
'''
# Individual number.
NP
=
len
(
population
)
# Add rank to all individuals in population.
sorted_indvs
=
sorted
(
population
.
individuals
,
key
=
fitness
,
reverse
=
True
)
# Assign selection probabilities linearly.
# NOTE: Here the rank i belongs to {1, ..., N}
p
=
lambda
i
:
(
self
.
pmin
+
(
self
.
pmax
-
self
.
pmin
)
*
(
i
-
1
)
/
(
NP
-
1
))
probabilities
=
[
self
.
pmin
]
+
[
p
(
i
)
for
i
in
range
(
2
,
NP
)]
+
[
self
.
pmax
]
# Normalize probabilities.
psum
=
sum
(
probabilities
)
wheel
=
list
(
accumulate
([
p
/
psum
for
p
in
probabilities
]))
# Select parents.
father_idx
=
bisect_right
(
wheel
,
random
())
father
=
population
[
father_idx
]
mother_idx
=
(
father_idx
+
1
)
%
len
(
wheel
)
mother
=
population
[
mother_idx
]
return















