作者:耳东陈
链接:www.cnblogs.com/dassmeta
HashMap也是我们使用非常多的Collection,它是基于哈希表的 Map 接口的实现,以key-value的形式存在。在HashMap中,key-value总是会当做一个整体来处理,系统会根据hash算法来来计算key-value的存储位置,我们总是可以通过key快速地存、取value。下面就来分析HashMap的存取。
一、定义
HashMap实现了Map接口,继承AbstractMap。其中Map接口定义了键映射到值的规则,而AbstractMap类提供 Map 接口的骨干实现,以最大限度地减少实现此接口所需的工作,其实AbstractMap类已经实现了Map,这里标注Map, LZ觉得应该是更加清晰吧!
public
class
HashMap
<
K
,
V
>
extends
AbstractMap
<
K
,
V
>
implements
Map
<
K
,
V
>,
Cloneable
,
Serializable
{
static
final
int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY =
1
<4;
static
final
int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY =
1
<30;
static
final
float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR =
0.75
f;
static
final
Entry
,
?>
[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
transient Entry
[] table = (Entry
[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
transient int size;
int threshold;
final
float loadFactor;
transient int modCount;
* This value may be overridden by defining the system property
* {
@code
jdk.map.althashing.threshold}. A property value of {
@code
1}
* forces alternative hashing to be used at all times whereas
* {
@code
-1} value ensures that alternative hashing is never used.
*/
static
final
int ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD_DEFAULT = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
二、构造函数
HashMap提供了三个构造函数:
-
HashMap():构造一个具有默认初始容量 (16) 和默认加载因子 (0.75) 的空 HashMap。
-
HashMap(int initialCapacity):构造一个带指定初始容量和默认加载因子 (0.75) 的空 HashMap。
-
HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor):构造一个带指定初始容量和加载因子的空 HashMap。
在这里提到了两个参数:初始容量,加载因子。这两个参数是影响HashMap性能的重要参数,其中容量表示哈希表中桶的数量,初始容量是创建哈希表时的容量,加载因子是哈希表在其容量自动增加之前可以达到多满的一种尺度,它衡量的是一个散列表的空间的使用程度,负载因子越大表示散列表的装填程度越高,反之愈小。
对于使用链表法的散列表来说,查找一个元素的平均时间是O(1+a),因此如果负载因子越大,对空间的利用更充分,然而后果是查找效率的降低;如果负载因子太小,那么散列表的数据将过于稀疏,对空间造成严重浪费。系统默认负载因子为0.75,一般情况下我们是无需修改的。
HashMap是一种支持快速存取的数据结构,要了解它的性能必须要了解它的数据结构。
三、数据结构
我们知道在Java中最常用的两种结构是数组和模拟指针(引用),几乎所有的数据结构都可以利用这两种来组合实现,HashMap也是如此。实际上HashMap是一个“链表散列”,如下是它数据结构:
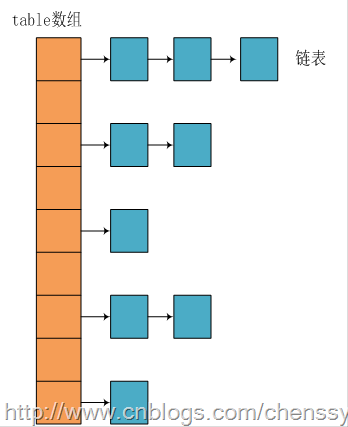
(本文图片引用见水印)
从上图我们可以看出HashMap底层实现还是数组,只是数组的每一项都是一条链。其中参数initialCapacity就代表了该数组的长度。下面为HashMap构造函数的源码:
public
HashMap
(
int
initialCapacity,
float
loadFactor)
{
if
(initialCapacity 0)
throw
new
IllegalArgumentException(
"Illegal initial capacity: "
+
initialCapacity);
if
(initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if
(loadFactor <=
0
|| Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw
new
IllegalArgumentException(
"Illegal load factor: "
+
loadFactor);
this
.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
从源码中可以看出,每次新建一个HashMap时,都会初始化一个table数组。table数组的元素为Entry节点。
static
class
Entry
<
K
,
V
>
implements
Map
.
Entry
<
K
,
V
>
{
final
K key;
V value;
Entry
next;
int
hash;
}
其中Entry为HashMap的内部类,它包含了键key、值value、下一个节点next,以及hash值,这是非常重要的,正是由于Entry才构成了table数组的项为链表。
上面简单分析了HashMap的数据结构,下面将探讨HashMap是如何实现快速存取的。
四、存储实现:put(key,vlaue)
首先我们先看源码
public
V
put
(
K key, V
value
)
{
if
(key ==
null
)
return
putForNullKey(
value
);
int
hash = hash(key.hashCode()); ------(
1
)
int
i = indexFor(hash, table.length); ------(
2
)
for
(Entry
e = table[i]; e !=
null
; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if
(e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.
equals
(k))) {
V oldValue = e.
value
;
e.
value
=
value
;
e.recordAccess(
this
);
return
oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key,
value
, i);
return
null
;
}
通过源码我们可以清晰看到HashMap保存数据的过程为:首先判断key是否为null,若为null,则直接调用putForNullKey方法。若不为空则先计算key的hash值,然后根据hash值搜索在table数组中的索引位置,如果table数组在该位置处有元素,则通过比较是否存在相同的key,若存在则覆盖原来key的value,否则将该元素保存在链头(最先保存的元素放在链尾)。若table在该处没有元素,则直接保存。这个过程看似比较简单,其实深有内幕。有如下几点:
1、 先看迭代处。此处迭代原因就是为了防止存在相同的key值,若发现两个hash值(key)相同时,HashMap的处理方式是用新value替换旧value,这里并没有处理key,这就解释了HashMap中没有两个相同的key。
2、 在看(1)、(2)处。这里是HashMap的精华所在。首先是hash方法,该方法为一个纯粹的数学计算,就是计算h的hash值。
final
int
hash(
Object
k) {
int
h = hashSeed;
if
(
0
!= h && k instanceof
String
) {
return
sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((
String
) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
h ^= (h >>>
20
) ^ (h >>>
12
);
return
h ^ (h >>>
7
) ^ (h >>>
4
);
}
HashMap的底层数组长度总是2的n次方,在构造函数中存在:capacity <<= 1;这样做总是能够保证HashMap的底层数组长度为2的n次方。当length为2的n次方时,h&(length - 1)就相当于对length取模,而且速度比直接取模快得多,这是HashMap在速度上的一个优化。至于为什么是2的n次方下面解释。
我们回到indexFor方法,该方法仅有一条语句:h&(length - 1),这句话除了上面的取模运算外还有一个非常重要的责任:均匀分布table数据和充分利用空间。
这里我们假设length为16(2^n)和15,h为5、6、7。
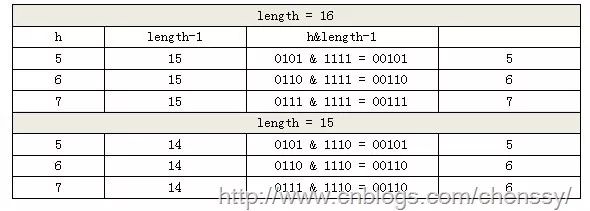
当n=15时,6和7的结果一样,这样表示他们在table存储的位置是相同的,也就是产生了碰撞,6、7就会在一个位置形成链表,这样就会导致查询速度降低。诚然这里只分析三个数字不是很多,那么我们就看0-15。