来自:掘金,作者:9龙
链接:https://juejin.im/post/6844903849753329678
一、引言
java8最大的特性就是引入Lambda表达式,即函数式编程,可以将行为进行传递。总结就是:使用不可变值与函数,函数对不可变值进行处理,映射成另一个值。
二、java重要的函数式接口
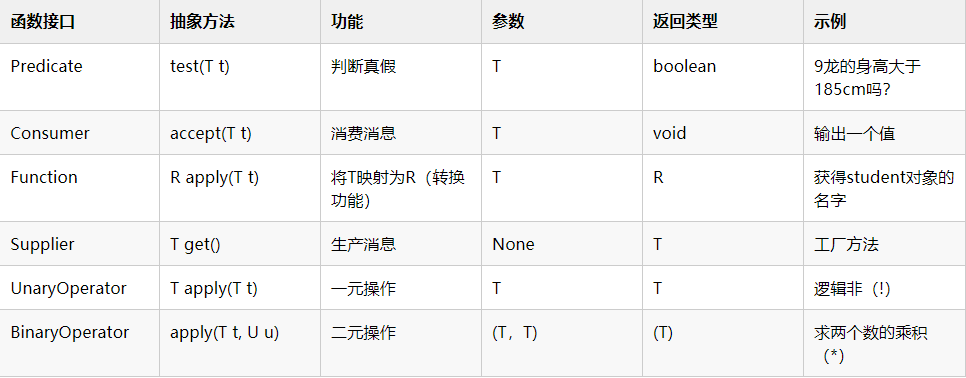
1、什么是函数式接口
函数接口是只有一个抽象方法的接口,用作 Lambda 表达式的类型。使用@FunctionalInterface注解修饰的类,编译器会检测该类是否只有一个抽象方法或接口,否则,会报错。可以有多个默认方法,静态方法。
1.1 java8自带的常用函数式接口。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate predicate = x -> x > 185;
Student student = new Student("9龙", 23, 175);
System.out.println(
"9龙的身高高于185吗?:" + predicate.test(student.getStature()));
Consumer<String> consumer = System.out::println;
consumer.accept("命运由我不由天");
FunctionString> function = Student::getName;
String name = function.apply(student);
System.out.println(name);
Supplier supplier =
() -> Integer.valueOf(BigDecimal.TEN.toString());
System.out.println(supplier.get());
UnaryOperator<Boolean> unaryOperator = uglily -> !uglily;
Boolean apply2 = unaryOperator.apply(true);
System.out.println(apply2);
BinaryOperator operator = (x, y) -> x * y;
Integer integer = operator.apply(2, 3);
System.out.println(integer);
test(() -> "我是一个演示的函数式接口");
}
/**
* 演示自定义函数式接口使用
*
* @param worker
*/
public static void test(Worker worker) {
String work = worker.work();
System.out.println(work);
}
public interface Worker {
String work();
}
}
//9龙的身高高于185吗?:false
//命运由我不由天
//9龙
//10
//false
//6
//我是一个演示的函数式接口
以上演示了lambda接口的使用及自定义一个函数式接口并使用。
下面,我们看看java8将函数式接口封装到流中如何高效的帮助我们处理集合。
注意:Student::getName例子中这种编写lambda表达式的方式称为方法引用。格式为ClassNmae::methodName。是不是很神奇,java8就是这么迷人。
示例:本篇所有示例都基于以下三个类。OutstandingClass:班级;Student:学生;SpecialityEnum:特长。

1.2 惰性求值与及早求值
惰性求值:只描述Stream,操作的结果也是Stream,这样的操作称为惰性求值。惰性求值可以像建造者模式一样链式使用,最后再使用及早求值得到最终结果。
及早求值:得到最终的结果而不是Stream,这样的操作称为及早求值。
2、常用的流
2.1 collect(Collectors.toList())
将流转换为list。还有toSet(),toMap()等。及早求值。
public
class TestCase {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List studentList = Stream.of(new Student("路飞", 22, 175),
new Student("红发", 40, 180),
new Student("白胡子", 50, 185)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(studentList);
}
}
//输出结果
//[Student{name='路飞', age=22, stature=175, specialities=null},
//Student{name='红发', age=40, stature=180, specialities=null},
//Student{name='白胡子', age=50, stature=185, specialities=null}]
2.2 filter
顾名思义,起过滤筛选的作用。内部就是Predicate接口。惰性求值。
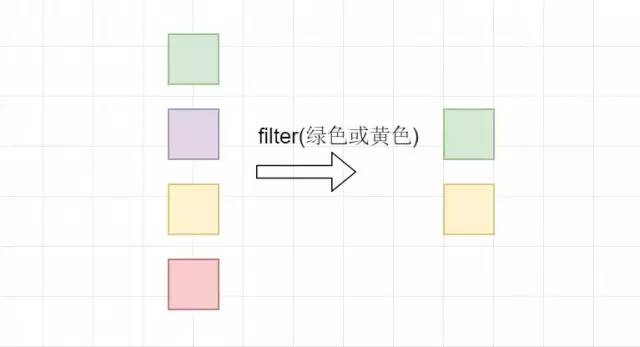
比如我们筛选出出身高小于180的同学。
public class TestCase {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List students = new ArrayList<>(3);
students.add(new Student("路飞", 22, 175));
students.add(new Student("红发", 40, 180));
students.add(new Student("白胡子", 50, 185));
List list = students.stream()
.filter(stu -> stu.getStature() 180)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
}
}
//输出结果
//[Student{name='路飞', age=22, stature=175, specialities=null}]
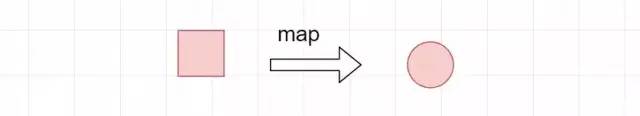
2.3 map
转换功能,内部就是Function接口。惰性求值
public class TestCase {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List students = new ArrayList<>(3);
students.add(new Student("路飞", 22, 175));
students.add(new Student("红发", 40, 180));
students.add(new Student("白胡子", 50, 185));
List names = students.stream().map(student -> student.getName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(names);
}
}
//输出结果
//[路飞, 红发, 白胡子]
例子中将student对象转换为String对象,获取student的名字。
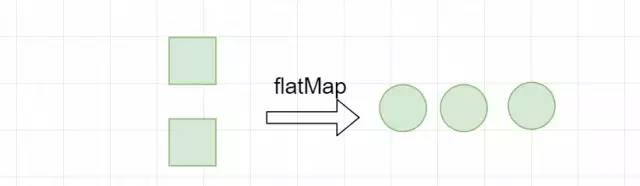
2.4 flatMap
将多个Stream合并为一个Stream。惰性求值
public class TestCase {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List students = new ArrayList<>(3);
students.add(new Student("路飞", 22, 175));
students.add(new Student("红发", 40, 180));
students.add(new Student("白胡子", 50, 185));
List studentList = Stream.of(students,
asList(new Student("艾斯", 25, 183),
new Student("雷利", 48, 176)))
.flatMap(students1 -> students1.stream()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(studentList);
}
}
//输出结果
//[Student{name='路飞', age=22, stature=175, specialities=null},
//Student{name='红发', age=40, stature=180, specialities=null},
//Student{name='白胡子', age=50, stature=185, specialities=null},
//Student{name='艾斯', age=25, stature=183, specialities=null},
//Student{name='雷利', age=48, stature=176, specialities=null}]
调用Stream.of的静态方法将两个list转换为Stream,再通过flatMap将两个流合并为一个。
2.5 max和min
我们经常会在集合中求最大或最小值,使用流就很方便。及早求值。
public class TestCase {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List students = new ArrayList<>(3);
students.add(new Student("路飞"





