编辑 紫苏
动脉粥样硬化不稳定性斑块破裂以及随后的血栓事件形成是造成多数急性心血管事件的主要原因之一,巨噬细胞在动脉粥样硬化的发生发展中发挥着重要作用,是预测动脉硬化斑块稳定性的重要标志。
在过去的几十年中,利用纳米颗粒与斑块处巨噬细胞特异性结合的特点,分子成像剂成为该领域研究热点。现有的荧光探针存在的缺陷有:较宽的发射光谱以及不理想的激发波段使得光谱分辨率低,多种发光探针很难同时使用。核壳结构的量子点被报道具有高量子产量和较窄的荧光发光,然而其合成工艺复杂,不易制备,难以在活体细胞中广泛应用。因此,发展新的光谱可调谐的窄光谱的发光探针对于细胞生物学研究和应用意义重大。
中国科学院化学研究所分子动态稳态国家重点实验室的付红兵课题组和北京大学基础医学院心血管研究所郑乐民课题组共同合作,开展了一系列新型发光探针的研究工作。
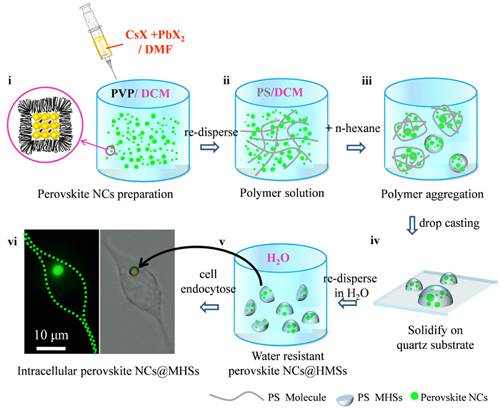
近期,该团队将制备的钙钛矿纳米晶体嵌入到防水聚合物中制备了纳米晶体/聚合物的半球状杂化结构,首次实现了高量子发光钙钛矿纳米材料在生物体系中的应用。
研究者首次选取了聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)作为表面配体,在室温制备高量子效率、高发光纯度的钙钛矿纳米晶体。实验证明以PVP作为纳米晶体的保护层,对纳米晶体的生长起到了很好的调控作用,同时作为介质层,将纳米晶体很好的富集到了聚合物(聚苯乙烯,PS)半球结构中。聚合物PS的保护大大提高了钙钛矿的水稳定性,使其可以作为多色探针应用到生物标记中。
该研究利用了高量子发光钙钛矿纳米材料良好的吸光能力、高量子产率、可调的较窄的发光光谱等优良特性。其发光光谱可以覆盖整个可见光区域,为分子影像预测动脉粥样硬化斑块的稳定性提供了理想的发光探针。该工作在室温合成钙钛矿晶体,钙钛矿防水应用的研究提供了新的思路。更为重要的是开创性的将钙钛矿材料应用到生物研究领域,对于钙钛矿材料的进一步交叉应用有很好的指导意义。
相关论文在线发表在
Advanced Functional Materials
(论文信息见文末)上,中国科学院化学研究所博士生张海华与北京大学医学部博士生王旭为共同第一作者,首都师范大学付红兵教授与北京大学医学部郑乐民教授为共同通讯作者。
相关论文信息
标题
Embedding Perovskite Nanocrystals into a Polymer Matrix for Tunable Luminescence Probes in Cell Imaging
发表日期
February 17, 2017
期刊
Advanced Functional Materials
作者
Haihua Zhang,Xu Wang,Qing Liao,Zhenzhen Xu,Haiyang Li,Lemin Zheng,Hongbing Fu
发表日期:
11 January 2017
DOI:
10.1002/adfm.201604382 View/save citation
摘要
Lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (NCs) with bright luminescence and broad spectral tunability are good candidates as smart probes for bioimaging, but suffer from hydrolysis even when exposed to atmosphere moisture. In this paper, a strategy is demonstrated by embedding CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, I) NCs into microhemispheres (MHSs) of polystyrene matrix to prepare “water-resistant” NCs@MHSs hybrids as multicolor multiplexed optical coding agents. First, a facile room-temperature solution self-assembly approach to highly luminescent colloidal CsPbX3 NCs is developed by injecting a stock solution of CsX⋅PbX2 in N,N-dimethylformamide into dichloromethane. Polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) is chosen as the capping ligand, which is physically adsorbed and wrapped on the surface of perovskite NCs to form a protective layer. The PVP protective layer not only leads to composition-tunable CsPbX3 NCs with high quantum yields and narrow emission linewidths of 12–34 nm but also acts as an interfacial layer, making perovskite NCs compatible with polystyrene polymers and facilitating the next step to embed CsPbX3 NCs into polymer MHSs. CsPbX3 NCs@MHSs are demonstrated as multicolor luminescence probes in live cells with high stability and nontoxicity. Using ten intensity levels and seven-color NCs@MHSs that show non-overlapping spectra, it will be possible to individually tag about ten million cells.














