来源:hang 来自:Python开发者
segmentfault.com/a/1190000010473819
简介
刚接触python不久,做一个小项目来练练手。前几天看了《战狼2》,发现它在最新上映的电影里面是排行第一的,如下图所示。准备把豆瓣上对它的影评做一个分析。
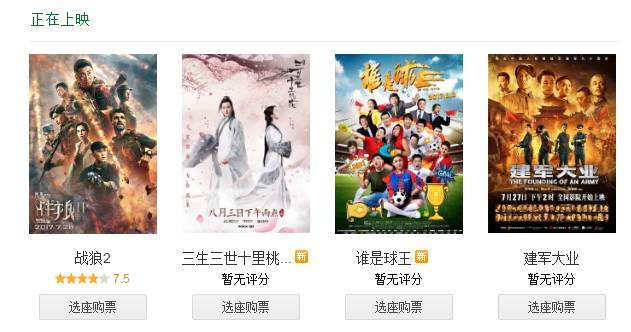
目标总览
主要做了三件事:
使用的python版本是3.5.
一、抓取网页数据
第一步要对网页进行访问,python中使用的是urllib库。代码如下:
from
urllib
import
request
resp
=
request
.
urlopen
(
'https://movie.douban.com/nowplaying/hangzhou/'
)
html_data
=
resp
.
read
().
decode
(
'utf-8'
)
其中https://movie.douban.com/nowplaying/hangzhou/是豆瓣最新上映的电影页面,可以在浏览器中输入该网址进行查看。
html_data是字符串类型的变量,里面存放了网页的html代码。
输入print(html_data)可以查看,如下图所示:

第二步,需要对得到的html代码进行解析,得到里面提取我们需要的数据。
在python中使用BeautifulSoup库进行html代码的解析。
(注:如果没有安装此库,则使用pip install BeautifulSoup进行安装即可!)
BeautifulSoup使用的格式如下:
BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser")
第一个参数为需要提取数据的html,第二个参数是指定解析器,然后使用find_all()读取html标签中的内容。
但是html中有这么多的标签,该读取哪些标签呢?其实,最简单的办法是我们可以打开我们爬取网页的html代码,然后查看我们需要的数据在哪个html标签里面,再进行读取就可以了。如下图所示:

从上图中可以看出在div id=”nowplaying“标签开始是我们想要的数据,里面有电影的名称、评分、主演等信息。所以相应的代码编写如下:
from
bs4
import
BeautifulSoup
as
bs
soup
=
bs
(
html_data
,
'html.parser'
)
nowplaying_movie
=
soup
.
find_all
(
'div'
,
id
=
'nowplaying'
)
nowplaying_movie_list
=
nowplaying_movie
[
0
].
find_all
(
'li'
,
class_
=
'list-item'
)
其中nowplaying_movie_list 是一个列表,可以用print(nowplaying_movie_list[0])查看里面的内容,如下图所示:

在上图中可以看到data-subject属性里面放了电影的id号码,而在img标签的alt属性里面放了电影的名字,因此我们就通过这两个属性来得到电影的id和名称。(注:打开电影短评的网页时需要用到电影的id,所以需要对它进行解析),编写代码如下:
nowplaying_list
=
[]
for
item
in
nowplaying_movie_list
:
nowplaying_dict
=
{}
nowplaying_dict
[
'id'
]
=
item
[
'data-subject'
]
for
tag_img_item
in
item
.
find_all
(
'img'
)
:
nowplaying_dict
[
'name'
]
=
tag_img_item
[
'alt'
]
nowplaying_list
.
append
(
nowplaying_dict
)
其中列表nowplaying_list中就存放了最新电影的id和名称,可以使用print(nowplaying_list)进行查看,如下图所示:
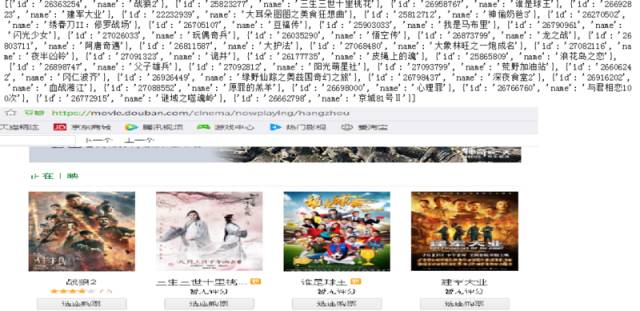
可以看到和豆瓣网址上面是匹配的。这样就得到了最新电影的信息了。接下来就要进行对最新电影短评进行分析了。例如《战狼2》的短评网址为:https://movie.douban.com/subject/26363254/comments?start=0&limit=20
其中26363254就是电影的id,start=0表示评论的第0条评论。
接下来接对该网址进行解析了。打开上图中的短评页面的html代码,我们发现关于评论的数据是在div标签的comment属性下面,如下图所示:

因此对此标签进行解析,代码如下:
requrl
=
'https://movie.douban.com/subject/'
+
nowplaying_list
[
0
][
'id'
]
+
'/comments'
+
'?'
+
'start=0'
+
'&limit=20'
resp
=
request
.
urlopen
(
requrl
)
html_data
=
resp
.
read
().
decode
(
'utf-8'
)
soup
=
bs
(
html_data
,
'html.parser'
)
comment_div_lits
=
soup
.
find_all
(
'div'
,
class_
=
'comment'
)
此时在comment_div_lits 列表中存放的就是div标签和comment属性下面的html代码了。在上图中还可以发现在p标签下面存放了网友对电影的评论,如下图所示:

因此对comment_div_lits 代码中的html代码继续进行解析,代码如下:
eachCommentList
=
[];
for
item
in
comment_div_lits
:
if
item
.
find_all
(
'p'
)[
0
].
string
is
not
None
:
eachCommentList
.
append
(
item
.
find_all
(
'p'
)[
0
].
string
)
使用print(eachCommentList)查看eachCommentList列表中的内容,可以看到里面存里我们想要的影评。如下图所示:

好的,至此我们已经爬取了豆瓣最近播放电影的评论数据,接下来就要对数据进行清洗和词云显示了。
二、数据清洗
为了方便进行数据进行清洗,我们将列表中的数据放在一个字符串数组中,代码如下:
comments
=
''
for
k
in
range
(
len
(
eachCommentList
))
:
comments
=
comments
+
(
str
(
eachCommentList
[
k
])).
strip
()
使用print(comments)进行查看,如下图所示:

可以看到所有的评论已经变成一个字符串了,但是我们发现评论中还有不少的标点符号等。这些符号对我们进行词频统计时根本没有用,因此要将它们清除。所用的方法是正则表达式。python中正则表达式是通过re模块来实现的。代码如下:
import
re
pattern
=
re
.
compile
(
r
'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+'
)
filterdata
=
re
.
findall
(
pattern
,
comments
)
cleaned_comments
=
''
.
join
(
filterdata
)
继续使用print(cleaned_comments)语句进行查看,如下图所示:

我们可以看到此时评论数据中已经没有那些标点符号了,数据变得“干净”了很多。
因此要进行词频统计,所以先要进行中文分词操作。在这里我使用的是结巴分词。如果没有安装结巴分词,可以在控制台使用pip install jieba进行安装。(注:可以使用pip list查看是否安装了这些库)。代码如下所示:
import
jieba
#分词包
import
pandas
as
pd
segment
=
jieba
.
lcut
(
cleaned_comments
)
words_df
=
pd
.
DataFrame
({
'segment'
:
segment
})
因为结巴分词要用到pandas,所以我们这里加载了pandas包。可以使用words_df.head()查看分词之后的结果,如下图所示:

从上图可以看到我们的数据中有“看”、“太”、“的”等虚词(停用词),而这些词在任何场景中都是高频时,并且没有实际的含义,所以我们要他们进行清除。
我把停用词放在一个stopwords.txt文件中,将我们的数据与停用词进行比对即可(注:只要在百度中输入stopwords.txt,就可以下载到该文件)。去停用词代码如下代码如下:
stopwords
=
pd
.
read_csv
(
"stopwords.txt"
,
index_col
=
False
,
quoting
=
3
,
sep
=
"\t"
,
names
=
[
'stopword'
],
encoding
=
'utf-8'
)
#quoting=3全不引用
words_df
=
words_df
[
~
words_df
.
segment
.
isin
(
stopwords
.
stopword
)]
继续使用words_df.head()语句来查看结果,如下图所示,停用词已经被出去了。

接下来就要进行词频统计了,代码如下:
import
numpy
#numpy计算包
words_stat
=
words_df
.
groupby
(
by
=
[
'segment'
])[
'segment'
].
agg
({
"计数"
:
numpy
.
size
})
words_stat
=
words_stat
.
reset_index
().
sort_values
(
by
=
[
"计数"
],
ascending
=
False
)
用words_stat.head()进行查看,结果如下:
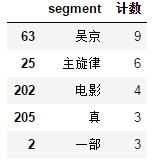
由于我们前面只是爬取了第一页的评论,所以数据有点少,在最后给出的完整代码中,我爬取了10页的评论,所数据还是有参考价值。
三、用词云进行显示
代码如下:
import
matplotlib
.
pyplot
as
plt
%
matplotlib
inline
import
matplotlib
matplotlib
.
rcParams
[
'figure.figsize'
]
=
(
10.0
,
5.0
)
from
wordcloud
import
WordCloud
#词云包
wordcloud
=
WordCloud
(
font_path
=
"simhei.ttf"
,
background_color
=
"white"
,
max_font_size
=
80
)
#指定字体类型、字体大小和字体颜色
word_frequence
=
{
x
[
0
]
:
x
[
1
]
for
x
in
words_stat
.
head
(
1000
).
values
}
word_frequence_list
=
[]
for
key
in
word_frequence
:
temp
=
(
key
,
word_frequence
[
key
])
word_frequence_list
.
append
(
temp
)
wordcloud
=
wordcloud
.
fit_words
(
word_frequence_list
)
plt
.
imshow
(
wordcloud
)
其中simhei.ttf使用来指定字体的,可以在百度上输入simhei.ttf进行下载后,放入程序的根目录即可。显示的图像如下:

到此为止,整个项目的介绍就结束了。由于自己也还是个初学者,接触python不久,代码写的并不好。而且第一次写技术博客,表达的有些冗余,请大家多多包涵,有不对的地方,请大家批评指正。以后我也会将自己做的小项目以这种形式写在博客上和大家一起交流!最后贴上完整的代码。
完整代码
#coding:utf-8
__author__
=
'hang'
import
warnings
warnings
.
filterwarnings
(
"ignore"
)
import
jieba
#分词包
import
numpy
#numpy计算包
import
codecs
#codecs提供的open方法来指定打开的文件的语言编码,它会在读取的时候自动转换为内部unicode
import
re
import
pandas
as
pd
import
matplotlib
.
pyplot
as
plt
from
urllib
import
request
from
bs4
import
BeautifulSoup
as
bs
%
matplotlib
inline
import
matplotlib
matplotlib
.
rcParams
[
'figure.figsize'
]
=
(
10.0
,
5.0
)
from
wordcloud
import
WordCloud
#词云包
#分析网页函数
def
getNowPlayingMovie_list
()
:
resp
=
request
.
urlopen
(
'https://movie.douban.com/nowplaying/hangzhou/'
)
html_data
=
resp
.
read
().
decode
(
'utf-8'
)
soup
=
bs
(
html_data
,
'html.parser'
)
nowplaying_movie
=
soup
.
find_all
(
'div'
,
id
=
'nowplaying'
)
nowplaying_movie_list
=
nowplaying_movie
[
0
].
find_all
(
'li'
,
class_
=
'list-item'
)
nowplaying_list
=
[]
for
item
in
nowplaying_movie_list
:
nowplaying_dict
=
{}
nowplaying_dict
[
'id'
]
=
item
[
'data-subject'
]
for
tag_img_item
in
item
.
find_all
(
'img'
)
:
nowplaying_dict
[
'name'
]
=
tag_img_item
[
'alt'
]
nowplaying_list
.
append
(
nowplaying_dict
)
return
nowplaying_list
#爬取评论函数
def
getCommentsById
(
movieId
,
pageNum
)
:
eachCommentList
=
[];
if
pageNum
>
0
:
start
=
(
pageNum
-
1
)
*
20
else
:
return
False
requrl
=
'https://movie.douban.com/subject/'
+
movieId
+
'/comments'
+
'?'
+
'start='
+
str
(
start
)
+
'&limit=20'
print
(
requrl
)
resp
=
request
.
urlopen
(
requrl
)
html_data
=
resp
.
read
().
decode
(
'utf-8'
)
soup
=
bs
(
html_data
,
'html.parser'
)
comment_div_lits
=
soup
.
find_all
(
'div'
,
class_
=
'comment'
)
for
item
in
comment_div_lits
:
if
item
.
find_all
(
'p'
)[
0
].
string
is
not
None
:
eachCommentList
.
append
(
item
.
find_all
(
'p'
)[
0
].
string
)

















