作者根据每周发布总结的系列文章,汇总了2018年针对数据科学家/AI的最佳库、repos、包和工具。本文对其进行了梳理,列举了人工智能和数据科学的七大Python库。
本文作者Favio Vázquez从2018年开始发布《数据科学和人工智能每周文摘:Python & R》系列文章,为数据科学家介绍最好的库、repos、packages以及工具。
一年结束,作者列出了2018年的7大最好的Python库,这些库确实地改进了研究人员的工作方式。
作者:Favio Vázquez
原文链接:
https://heartbeat.fritz.ai/top-7-libraries-and-packages-of-the-year-for-data-science-and-ai-python-r-6b7cca2bf000
Top7 AdaNet:快速灵活的AutoML框架

(
https://github.com/tensorflow/adanet
)
AdaNet是一个轻量级的、可扩展的TensorFlow AutoML框架,用于使用AdaNet算法训练和部署自适应神经网络[Cortes et al. ICML 2017]。AdaNet结合了多个学习子网络,以减轻设计有效的神经网络所固有的复杂性。
这个软件包将帮助你选择最优的神经网络架构,实现一种自适应算法,用于学习作为子网络集合的神经架构。
你需要了解TensorFlow才能使用这个包,因为它实现了TensorFlow Estimator,但这将通过封装训练、评估、预测和导出服务来帮助你简化机器学习编程。
你可以构建一个神经网络的集合,这个库将帮助你优化一个目标,以平衡集合在训练集上的性能和将其泛化到未见过数据的能力之间的权衡。
安装
安装adanet之前需将TensorFlow升级到1.7或以上:
$ pip install "tensorflow>=1.7.0"
从源代码安装
要从源代码进行安装,首先需要安装bazel。
下一步,复制adanet和cd到它的根目录:
$ git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/adanet && cd adanet
从adanet根目录运行测试:
$ cd adanet
$ bazel test -c opt //...
确认一切正常后,将adanet安装为pip包。
现在,可以对adanet进行试验了。
import adanet
用法
Top6 TPOT:一个自动化的Python机器学习工具

(
https://github.com/EpistasisLab/tpot
)
TPOT全称是基于树的pipeline优化工具(Tree-based Pipeline Optimization Tool),这是一个非常棒Python自动机器学习工具,使用遗传编程优化机器学习pipeline。
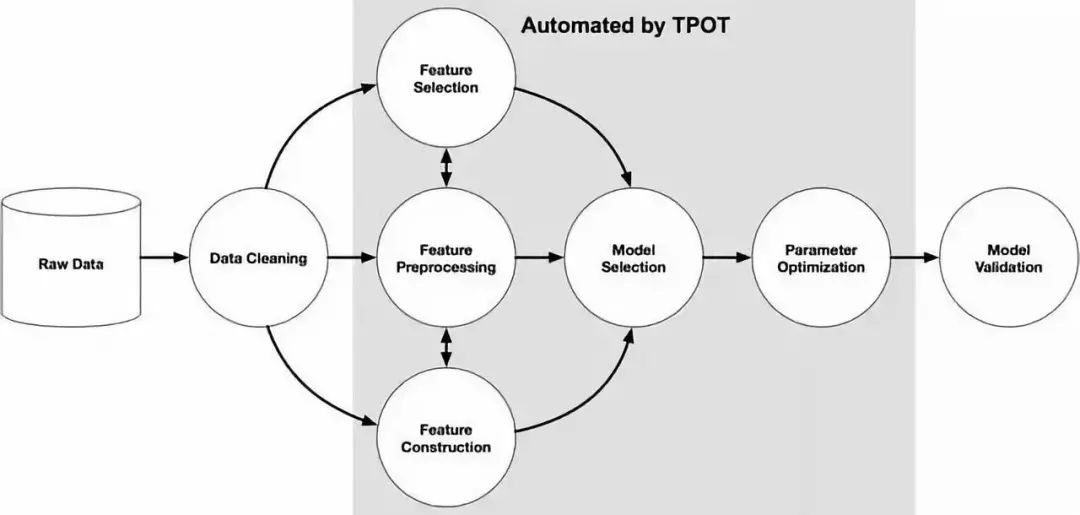
TPOT可以自动化许多东西,包括生命特性选择、模型选择、特性构建等等。如果你是Python机器学习者,很幸运,TPOT是构建在Scikit-learn之上的,所以它生成的所有代码看起来应该很熟悉。
它的作用是通过智能地探索数千种可能的pipeline来自动化机器学习中最繁琐的部分,找到最适合你的数据的pipeline,然后为你提供最佳的 Python 代码。
它的工作原理如下:
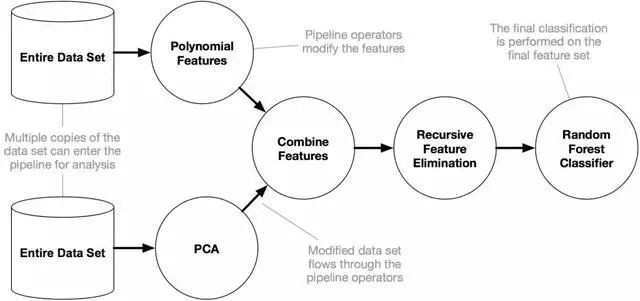
安装
运行以下代码:
例子:
首先让我们从基本的Iris数据集开始:
from tpot import TPOTClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
iris = load_iris()
X_trainX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target,
train_size=0.75, test_size=0.25)
tpot = TPOTClassifier(verbosity=2, max_time_mins=2)
tpot.fit(X_train, y_train)
tpot.export('tpot_iris_pipeline.py')
(左右滑动可查看完整代码)
我们在这里构建了一个非常基本的TPOT pipeline,它将尝试寻找最佳ML pipeline来预测iris.target。然后保存这个pipeline。之后,我们要做的就非常简单了——加载生成的.py文件,你将看到:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.kernel_approximation import RBFSampler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
tpot_data = np.recfromcsv('PATH/TO/DATA/FILE', delimiter='COLUMN_SEPARATOR', dtype=np.float64)
features = np.delete(tpot_data.view(np.float64).reshape(tpot_data.size, -1), tpot_data.dtype.names.index('class'), axis=1)
training_features, testing_features, training_classes, testing_classes =
train_test_split(features, tpot_data['class'], random_state=42)
exported_pipeline = make_pipeline(
RBFSampler(gamma=0.8500000000000001),
DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy", max_depth=3, min_samples_leaf=4, min_samples_split=9)
)
exported_pipeline.fit(training_features, training_classes)
results = exported_pipeline.predict(testing_features)
(左右滑动可查看完整代码)
就是这样。你已经以一种简单但强大的方式为Iris数据集构建一个分类器。
现在我们来看看MNIST的数据集:
from tpot import TPOTClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
digitsdigits == load_digitsload_di ()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(digits.data, digits.target,
train_size=0.75, test_size=0.25)
tpot = TPOTClassifier(verbosity=2, max_time_mins=5, population_size=40)
tpot.fit(X_train, y_train)
tpot.export('tpot_mnist_pipeline.py')
(左右滑动可查看完整代码)
接下来我们再次加载生成的 .py文件,你将看到:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import
train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
tpot_data = np.recfromcsv('PATH/TO/DATA/FILE', delimiter='COLUMN_SEPARATOR', dtype=np.float64)
features = np.delete(tpot_data.view(np.float64).reshape(tpot_data.size, -1), tpot_data.dtype.names.index('class'), axis=1)
training_features, testing_features, training_classes, testing_classes =
train_test_split(features, tpot_data['class'], random_state=42)
exported_pipeline = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=4, p=2, weights="distance")
exported_pipeline.fit(training_features, training_classes)
results = exported_pipeline.predict(testing_features)
Top5 SHAP:一个解释任何机器模型输出的统一方法
(
https://github.com/slundberg/shap
)
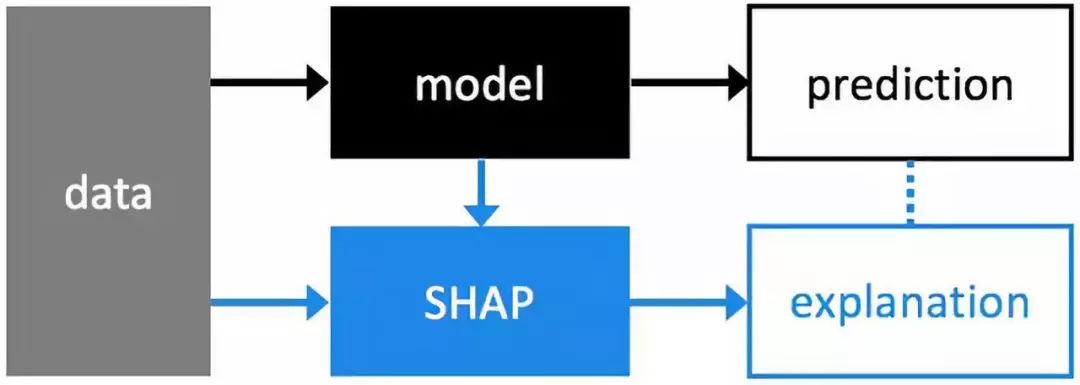
解释机器学习模型并不容易。然而,它对许多商业应用程序来说非常重要。幸运的是,有一些很棒的库可以帮助我们完成这项任务。在许多应用程序中,我们需要知道、理解或证明输入变量在模型中的运作方式,以及它们如何影响最终的模型预测。
SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations)是一种解释任何机器学习模型输出的统一方法。SHAP将博弈论与局部解释联系起来,并结合了之前的几种方法。
安装
SHAP可以从PyPI安装
或conda -forge
conda install -c conda-forge shap
用法
有很多不同的模型和方法可以使用这个包。在这里,我将以DeepExplainer中的一个例子为例。
Deep SHAP是深度学习模型中SHAP值的一种高速近似算法,它基于与DeepLIFT的连接,如SHAP的NIPS论文所述(https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03888)。
下面这个例子可以看到SHAP如何被用来解释MNIST数据集的Keras模型结果:
from __future__ import print_function
import keras
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flatten
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D
from keras import backend as K
batch_size = 128
num_classes = 10
epochs = 12
img_rows, img_cols = 28, 28
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], 1, img_rows, img_cols)
x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], 1, img_rows, img_cols)
input_shape = (1, img_rows, img_cols)
else:
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1)
x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1)
input_shape = (img_rows, img_cols, 1)
x_train = x_train.astype('float32')
x_test = x_test.astype('float32')
x_train /= 255
x_test /= 255
print('x_train shape:', x_train.shape)
print(x_train.shape[0], 'train samples')
print(x_test.shape[0], 'test samples')
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3, 3),
activation='relu'
,
input_shape=input_shape))
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss=keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy,
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adadelta(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
verbose=1,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test))
score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0)
print('Test loss:', score[0])
print('Test accuracy:', score[1])
(左右滑动可查看完整代码)

(
https://github.com/ironmussa/Optimus
)
Optimus V2旨在让数据清理更容易。这个API的设计对新手来说超级简单,对使用pandas的人来说也非常熟悉。Optimus扩展了Spark DataFrame功能,添加了.rows和.cols属性。
使用Optimus,你可以以分布式的方式清理数据、准备数据、分析数据、创建分析器和图表,并执行机器学习和深度学习,因为它的后端有Spark、TensorFlow和Keras。
Optimus是数据科学敏捷方法的完美工具,因为它几乎可以帮助你完成整个过程的所有步骤,并且可以轻松地连接到其他库和工具。
安装
pip install optimuspyspark
用法
在这个示例中,你可以从 URL 加载数据,对其进行转换,并应用一些预定义的清理功能:
from optimus import Optimus
op = Optimus()
# This is a custom function
def func(value, arg):
return "this was a number"
df =op.load.url("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ironmussa/Optimus/master/examples/foo.csv")
df
.rows.sort("product","desc")
.cols.lower(["firstName","lastName"])
.cols.date_transform("birth", "new_date", "yyyy/MM/dd", "dd-MM-YYYY")
.cols.years_between("birth", "years_between", "yyyy/MM/dd")
.cols.remove_accents("lastName")
.cols.remove_special_chars("lastName")
.cols.replace("product","taaaccoo","taco")
.cols.replace("product",["piza","pizzza"],"pizza")
.rows.drop(df["id"]<7)
.cols.drop("dummyCol")
.cols.rename(str.lower)
.cols.apply_by_dtypes("product",func,"string", data_type="integer")
.cols.trim("*")
.show()
你可以将这个表格
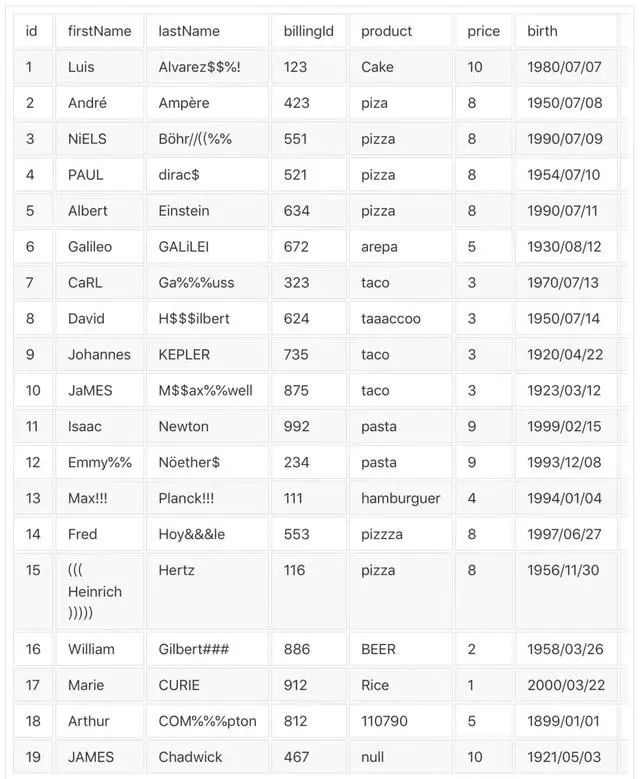
转换为这样:
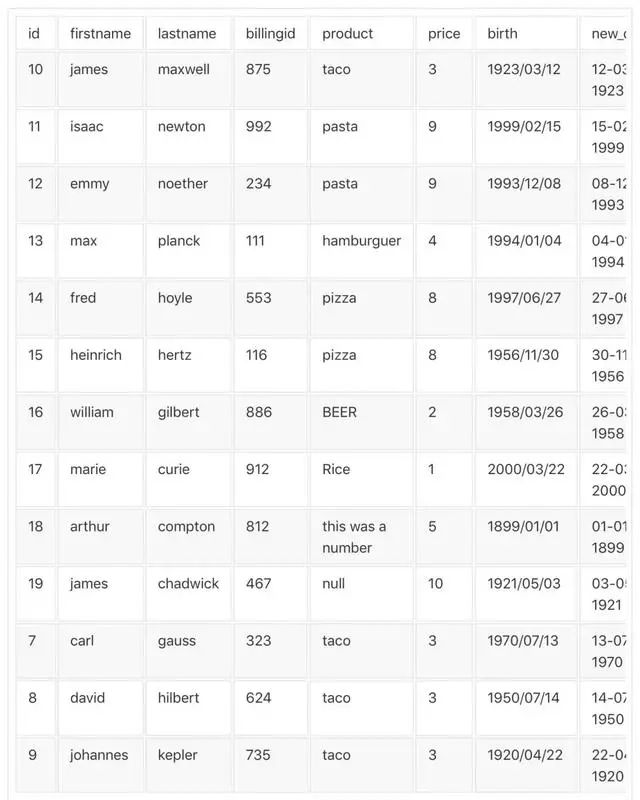
是不是很酷?

spaCy旨在帮助你完成实际的工作——构建真实的产品,或收集真实的见解。这个库尊重你的时间,尽量避免浪费。它易于安装,而且它的API简单而高效。spaCy被视为自然语言处理的Ruby on Rails。
spaCy是为深度学习准备文本的最佳方法。它与TensorFlow、PyTorch、Scikit-learn、Gensim以及Python强大的AI生态系统的其他部分无缝交互。使用spaCy,你可以很容易地为各种NLP问题构建语言复杂的统计模型。
安装
pip3 install spacy
$ python3 -m spacy download en
下面是主页面的一个示例:
import spacy
nlp = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm')
text = (u"When Sebastian Thrun started working on self-driving cars at "
u"Google in 2007, few people outside of the company took him "
u"seriously. “I can tell you very senior CEOs of major American "
u"car companies would shake my hand and turn away because I wasn’t "
u"worth talking to,” said Thrun, now the co-founder and CEO of "
u"online higher education startup Udacity, in an interview with "
u"Recode earlier this week.")
doc = nlp(text)
for entity in doc.ents:
print(entity.text, entity.label_)
doc1 = nlp(u"my fries were super gross")
doc2 = nlp(u"such disgusting fries")
similarity = doc1.similarity(doc2)
print(doc1.text, doc2.text, similarity)
在这个示例中,我们首先下载English tokenizer, tagger, parser, NER和word vectors。然后创建一些文本,打印找到的实体、短语和概念,最后确定两个短语的语义相似性。运行这段代码,你会得到:















