微软亚洲研究院郑宇博士的AAAI 2017论文《Deep Spatio-Temporal Residual Networks for Citywide Crowd Flows Prediction》论文、数据和代码均已公开。
论文摘要:
Forecasting the flow of crowds is of great importance to traffic
management and public safety, and very challenging as it is affected by
many complex factors, such as inter-region traffic, events, and weather.
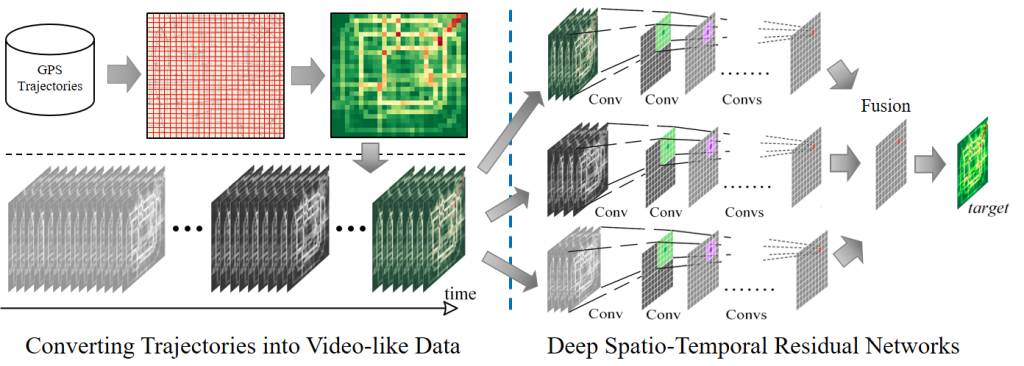
We propose a deep-learning-based approach, called ST-ResNet, to
collectively
forecast the inflow and outflow of crowds in each and every region of a
city. We design an end-to-end structure of ST-ResNet based on unique
properties of spatio-temporal data. More specifically, we employ the
residual neural network framework to model the temporal closeness,
period, and trend properties of crowd traffic. For each property, we
design a branch of residual convolutional units, each of which models
the spatial properties of crowd traffic. ST-ResNet learns to dynamically
aggregate the output of the three residual neural networks based on
data, assigning different weights to different branches and regions. The
aggregation is further combined with external factors, such as weather
and day of the week, to predict the final traffic of crowds in each and
every region. Experiments on two types of crowd flows in Beijing and New
York City (NYC) demonstrate that the proposed ST-ResNet outperforms six
well-known methods.
链接:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/deep-spatio-temporal-residual-networks-for-citywide-crowd-flows-prediction/
原文链接:
http://weibo.com/2073091511/Euqk2wGZR?type=comment#_rnd1486456048659





