根据《神经科学杂志》(JNeurosci)发表的一项研究,某些流感病毒感染可能与某些短期脑部神经症状相关联,
在研究实验中两组受甲型流感病毒(分别感染甲型H7N7/H3N2毒株)感染的雌性小鼠在感染一个月后表现出了海马体功能和结构变化,表现了与记忆力相关的损伤衰退,研究局限于流感对实验小鼠脑部神经的短期影响,流感是否对人类脑部健康存在长期影响仍未表明。
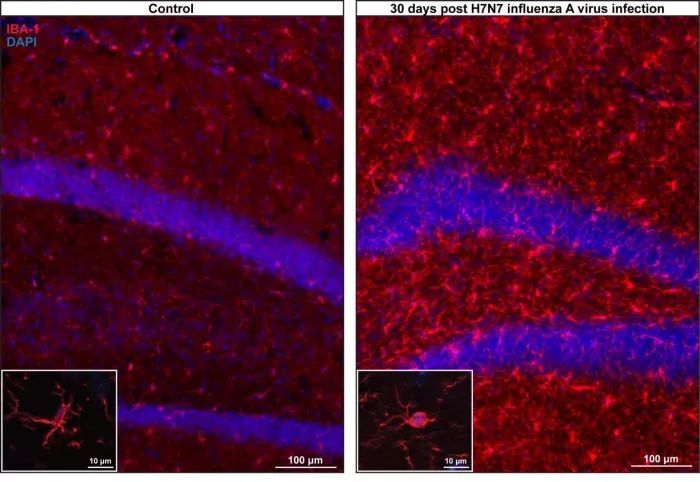
研究者分组雌性实验小鼠分别感染甲型流感中的H3N2/H1N1和H7N7三种亚型毒株,其中感染甲型H7N7和H3N2毒株的小鼠实验组自感染一个月后被观察出现了记忆力衰竭,通过分析发现这些小鼠的海马体神经在被毒株感染后引起的炎症后出现了结构性变化。研究解释,这些炎症能够在感染发生一个月后“引起神经元的连接呈现较长期的病毒特异性改变,这与记忆存储力紧密关联”。
此外,流感病毒还会触发特定大脑区域的免疫细胞,并处于相对长期的活跃抵抗,这本身就引起了基因表达变化,被认为与某些特定心理疾病相关联,如抑郁和精神分裂症。此研究发现局限于小鼠,目前尚无明确占据表明这些流感病毒是否对于人类脑神经细胞产生类似的损害,引起记忆力衰退等变化。
Abstract
Acute influenza infection has been reported to be associated with neurological symptoms. However, the long-term consequences for the CNS of an infection with neurotropic but also with non-neurotropic influenza A virus (IAV) variants remain elusive. We can show that spine loss in the hippocampus after infection with neurotropic H7N7 (rSC35M) as well as non-neurotropic H3N2 (maHK68) in female C57BL/6 mice persists well beyond the acute phase of the disease. While spine number was significantly reduced 30 days post infection (pi) with H7N7 or H3N2, full recovery could only be observed much later at 120 days pi. Notably, infection with H1N1 virus which was shown previously to acutely affect spine number and hippocampus-dependent learning had no significant long-term effects. Spine loss was associated with an increase in the number of activated microglia, reduced long-term potentiation in the hippocampus, and an impairment in spatial memory formation indicating that IAV associated inflammation induced functional and structural alterations in hippocampal networks. Transcriptome analyses revealed regulation of many inflammatory as well as neuron- and glia-specific genes in H3N2 and H7N7 infected mice at day 18 and in H7N7 infected mice at day 30 pi that related to the structural and functional alterations. Our data provide evidence that neuroinflammation induced by neurotropic H7N7 and infection of the lung with a non-neurotropic H3N2 IAV result in long-term impairments in the CNS. IAV infection in humans may therefore not only lead to short-term responses in infected organs but also trigger neuroinflammation and associated chronic alterations in the CNS.
原文链接:
http://www.jneurosci.org/content/earl
(本文转自中国病毒学论坛)
面对生命,惟有责任


