CVPR 2017 Oral Presentation论文《3DMatch: Learning Local Geometric Descriptors from RGB-D Reconstructions》摘要:
由于3D扫描数据的嘈杂、低分辨率和不完整的特性,现实世界深度图像中的匹配局部几何特征,是一项具有挑战性的任务。这些困难限制了当前最先进的方法的性能,这些方法通常基于几何属性上的直方图。在本文中,我们提出了3DMatch,一个数据驱动模型,学习一个局部体积补丁描述符,来建立部分3D数据之间的对应关系。为了收集我们模型的训练数据,我们提出了一种无监督的特征学习方法,利用现有RGB-D重建中发现的数百万个对应标签。实验表明,我们的描述符不仅能够匹配用于重建的新场景中的局部几何,还可以将其归纳为不同的任务和空间尺度(例如,亚马逊采摘挑战的实例级对象模型对齐和网格表面对应)。结果表明,3DMatch一直优于其他最先进的方法。
英文摘要:
Matching local geometric features on real-world depth images is a
challenging task due to the noisy, low-resolution, and incomplete nature
of 3D scan data. These difficulties limit the performance of current
state-of-art methods, which are typically based on histograms over
geometric properties. In this paper, we present 3DMatch, a data-driven
model that learns a local volumetric patch descriptor for establishing
correspondences between partial 3D data. To amass training data for our
model, we propose an unsupervised feature learning method that leverages
the millions of correspondence labels found in existing RGB-D
reconstructions. Experiments show that our descriptor is not only able
to match local geometry in new scenes for reconstruction, but also
generalize to different tasks and spatial scales (e.g. instance-level
object model alignment for the Amazon Picking Challenge, and mesh
surface correspondence). Results show that 3DMatch consistently
outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches by a significant margin.
Overview
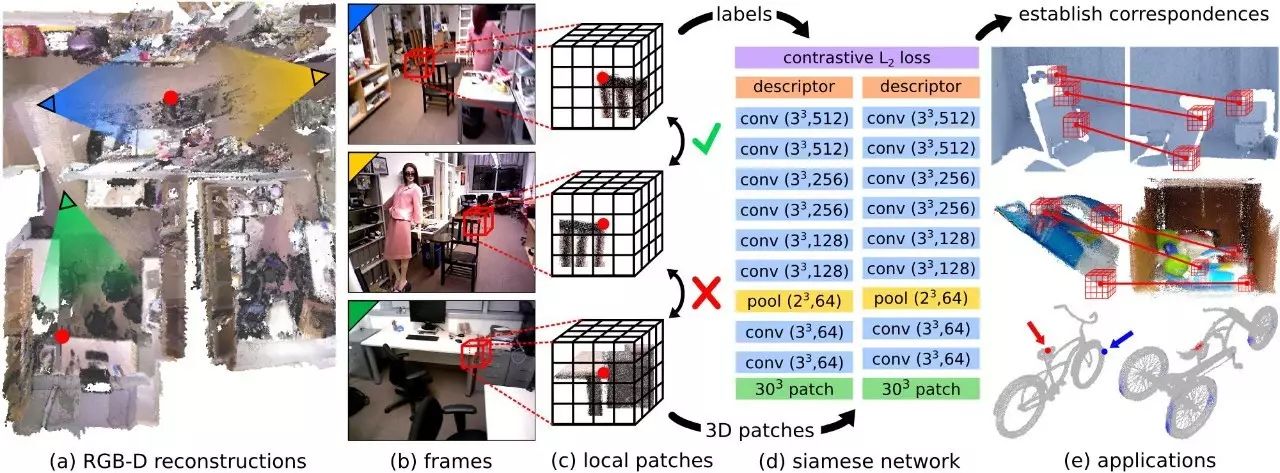
From existing RGB-D reconstructions (a), we extract local 3D patches and
correspondence labels from scans of different views (b). We collect
pairs of matching and non-matching local 3D patches converted into a
volumetric representation (c) to train a 3D ConvNet-based descriptor
(d). This geometric descriptor can be used to establish correspondences
for matching 3D geometry in various applications (e) such as
reconstruction, model alignment, and surface correspondence.
项目主页:
http://3dmatch.cs.princeton.edu/
原文链接:
http://weibo.com/5501429448/F3Pg7oPCx?ref=home&rid=9_0_202_2666934447555772670&type=comment





