(点击
上方公众号
,可快速关注)
编译:伯乐在线 - 欣仔
如有好文章投稿,请点击 → 这里了解详情
区块链的基础概念很简单:一个分布式数据库,存储一个不断加长的 list,list 中包含着许多有序的记录。然而,在通常情况下,当我们谈到区块链的时候也会谈起使用区块链来解决的问题,这两者很容易混淆。像流行的比特币和以太坊这样基于区块链的项目就是这样。“区块链”这个术语通常和像交易、智能合约、加密货币这样的概念紧紧联系在一起。
这就令理解区块链变得不必要得复杂起来,特别是当你想理解源码的时候。下面我将通过 200 行 JS 实现的超级简单的区块链来帮助大家理解它,我给这段代码起名为 NaiveChain。
块结构
第一个逻辑步骤是决定块结构。为了保证事情尽可能的简单,我们只选择最必要的部分:index(下标)、timestamp(时间戳)、data(数据)、hash(哈希值)和 previous hash(前置哈希值)。
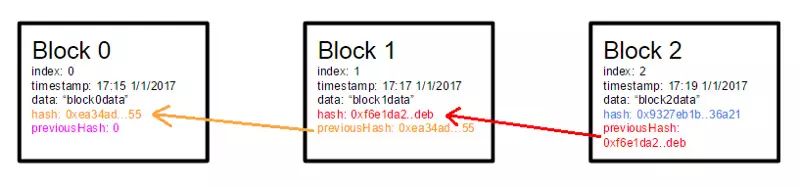
这个块中必须能找到前一个块的哈希值,以此来保证整条链的完整性。
class
Block
{
constructor
(
index
,
previousHash
,
timestamp
,
data
,
hash
)
{
this
.
index
=
index
;
this
.
previousHash
=
previousHash
.
toString
();
this
.
timestamp
=
timestamp
;
this
.
data
=
data
;
this
.
hash
=
hash
.
toString
();
}
}
块哈希
为了保存完整的数据,必须哈希区块。SHA-256会对块的内容进行加密,记录这个值应该和“挖矿”毫无关系,因为这里不需要解决工作量证明的问题。
var
calculateHash
=
(
index
,
previousHash
,
timestamp
,
data
)
=>
{
return
CryptoJS
.
SHA256
(
index
+
previousHash
+
timestamp
+
data
).
toString
();
};
块的生成
要生成一个块,必须知道前一个块的哈希值,然后创造其余所需的内容(= index, hash, data and timestamp)。块的data部分是由终端用户所提供的。
var
generateNextBlock
=
(
blockData
)
=>
{
var
previousBlock
=
getLatestBlock
();
var
nextIndex
=
previousBlock
.
index
+
1
;
var
nextTimestamp
=
new
Date
().
getTime
()
/
1000
;
var
nextHash
=
calculateHash
(
nextIndex
,
previousBlock
.
hash
,
nextTimestamp
,
blockData
);
return
new
Block
(
nextIndex
,
previousBlock
.
hash
,
nextTimestamp
,
blockData
,
nextHash
);
};
块的存储
内存中的Javascript数组被用于存储区块链。区块链的第一个块通常被称为“起源块”,是硬编码的。
var
getGenesisBlock
=
()
=>
{
return
new
Block
(
0
,
"0"
,
1465154705
,
"my genesis block!!"
,
"816534932c2b7154836da6afc367695e6337db8a921823784c14378abed4f7d7"
);
};
var
blockchain
=
[
getGenesisBlock
()];
确认块的完整性
在任何时候都必须能确认一个区块或者一整条链的区块是否完整。在我们从其他节点接收到新的区块,并需要决定接受或拒绝它们时,这一点尤为重要。
var
isValidNewBlock
=
(
newBlock
,
previousBlock
)
=>
{
if
(
previousBlock
.
index
+
1
!==
newBlock
.
index
)
{
console
.
log
(
'invalid index'
);
return
false
;
}
else
if
(
previousBlock
.
hash
!==
newBlock
.
previousHash
)
{
console
.
log
(
'invalid previoushash'
);
return
false
;
}
else
if
(
calculateHashForBlock
(
newBlock
)
!==
newBlock
.





