今天推介一个新的BCL北京城市实验室项目
“中国
城市
的空间失序”
(Spatial Disorder in China)
该项目涵盖
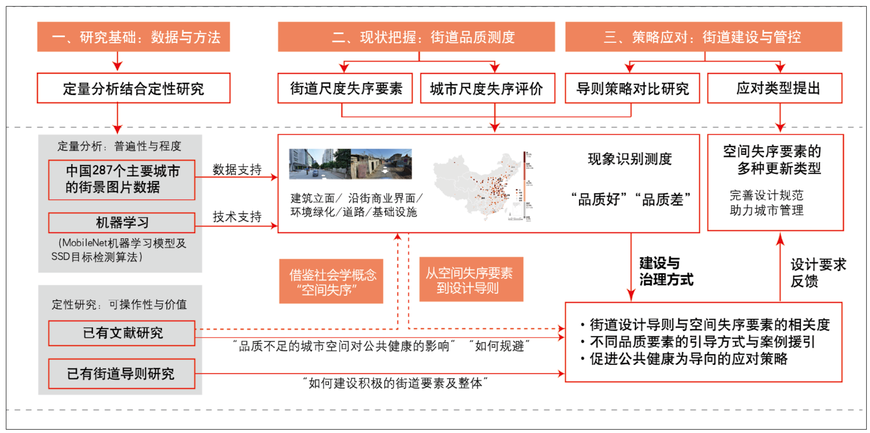
《城市公共空间失序的要素识别、测度、外部性与干预》、《促进公共健康为导向的街道空间品质提升策略——来自空间失序的视角》、《基于空间失序理论的城市街道空间品质大规模测度——以合肥市二环内为例》
等研究内容,以供大家学习与交流。
此外,这一方面的多个项目的研究工作正在继续,考虑到内容没有发表,后续时机成熟时继续补充推送。
更多关于城市空间失序的研究工作详见https://www.beijingcitylab.com/projects-1/49-spatial-disorder-in-china/(或点击文末“阅读原文”)
《城市公共空间失序的要素识别、测度、外部性与干预》
Element Identification, Measurement, Impacts Evaluation and Spatial Intervention of Disordered Urban Public Space
Under the call of the construction and quality improvement of urban space, the current uneven quality of the space caused by extensive urban development is worthy of attention, given the lack of maintenance of the old city core, the brown filed and vacant land, as well as the decay of the urban environment that is common in many cities. Drawing on a concept from sociology, this phenomenon of poor space quality and chaotic space order is defined as a physical disorder of urban space. With a new method of off-site built environment audits based on street view images, this study measures and evaluates the physical disorder of urban space within Beijing's Fifth Ring Road area. It finds that varying degrees of physical disorder is spread in this area, where the disorder has reached 50.1% among the 70,436 street points. The unkempt façades of buildings and roads lacking maintenance were the main factors of disorder that affect the quality of urban space in Beijing, leaving a negative impact on the vitality of the space. This study also carries out spatial intervention experiments that target specific disorder factors and can significantly improve the space. The large scale measurement of public spaces of poor quality or even disordered space provides an important basis for refined management and intervention of cities in the future.
PS:以下为【
北京城市实验室
Spatial Disorder in China
单元
】分享内容,具体内容可点击下方图片或点击文末阅读原文进入网站下载查看。

《促进公共健康为导向的街道空间品质提升策略——来自空间失序的视角》
Strategies for improving the quality of urban street space oriented to promoting public health: Perspective from spatial disorder
In recent years, space quality and design of streets have received increasing attention. In the field of public health, the insufficient quality of urban spatial characteristics or even disorder have been proved to directly or indirectly affect the physical and mental health of individuals, implying high-risk influence on individual behavior and delivering negative health outcomes. The improvement of micro-scale spatial features is beneficial to enhancing the activity-friendliness of public space and shaping positive psychological perceptions, thereby promoting public health. Focusing on the core goal of creating high-quality urban street space, this study takes the street space of the public space as the research object, and pays attention to the phenomenon of insufficient local space quality. Based on the current quality and significant characteristics of street space quality in China, it sorts out relevant design strategies in various street design guidelines for cities at home and abroad, and proposes design response strategies for different space quality factors, so as to explore the practical points to solve the problem of poor street space quality or physical disorder in Chinese cities, to pave a way for public health-oriented environmental maintenance, improvement and organic renewal, and to further serve the refined urban space management and design.
PS:以下为【
北京城市实验室
Spatial Disorder in China
单元
】分享内容,
具
体内容可点击下方图片
或点击文末阅读原文
进入网站下载查看。

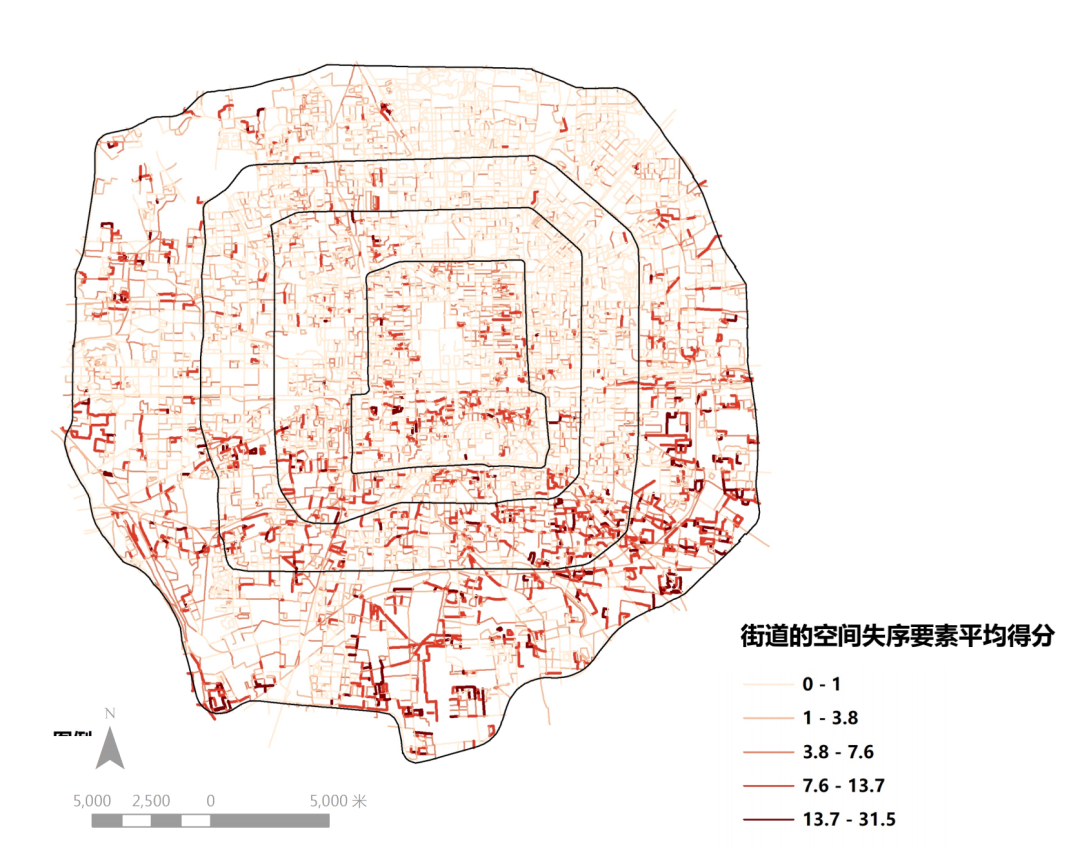
《基于空间失序理论的城市街道空间品质大规模测度——以合肥市二环内为例》
Large-scale Measurement of the Quality of Urban Street Space Based on Physical Disorder Theory:
A Case Study of Area within the Second Ring of Hefei City

With improvements and optimization in the field of urban construction and people's pursuit of a higher quality of life, spatial quality has become an important aspect of urban research. However, rapid developments in the Chinese economy in recent years have caused disordered local urban space. In this study, area within the second ring of Hefei City was used as the research object, and multi-source data (e.g., street view images) were applied as carriers. On this basis, the physical disorder phenomenon, the relationship between different street types and the degree of physical disorder in Hefei City were explored through technical methods such as virtual built-environment audit. For area within the second ring road of Hefei City, the results revealed as following: (1) for the overall spatial quality, the degree of physical disorder was 35.11%; (2) among the spatial features explored, the commercial elements along the street presented the highest disorder degree; and (3) the quality of the space along the streets of land servicing commercial-industry facilities (Class B) was the worst, while the quality along the streets of logistics and storage land (Class W) was the best. Based on physical disorder theory, this study quantitatively measured the quality of street space. In practice, these findings provide important insights toward improving the urban management of cities in the future. In theory, they address the limitations of current research into physical disorder in China's urban space.
PS:以下为【
北京城市实验室
Spatial Disorder in China
单元
】分享内容,
具
体内容可点击下方图片或
或点击文末阅读原文
进入网站下载查看。















